這次實現了堆,這個堆不是指系統堆棧的堆,是一種數據結構,見下圖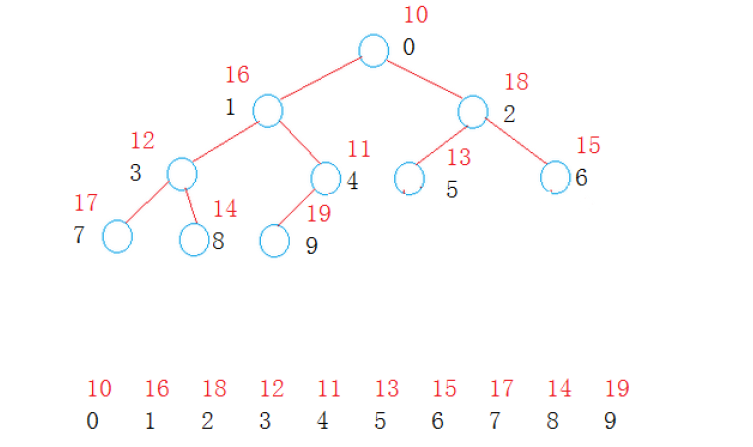
堆的本質就是一個數組(上圖中,紅色的是值,黑色的是下標)簡單的來說就是把一個數組看成是二叉樹,就像上圖
大堆和小堆分別是指根節點比孩子節點的值大或者是小,看了上圖之後就可以發現,父親節點和孩子節點之間下表的關系,parnet=(child-1)/2
利用這個關系就可以實現堆了,堆的基本方法有構造,析構,插入,刪除,像大堆小堆這樣特殊的堆肯定是要有調整函數來保持他們的特性的,所以我還寫了向上調整和向下調整的函數
為了讓大堆和小堆之間切換自如(就是方便維護),我寫了兩個仿函數,建立堆的對象時傳個模版參數就好了
1 #pragma once
2 #include<iostream>
3 #include<vector>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 template<class T>
7 struct Less
8 {
9 bool operator()(const T& l,const T& r)
10 {
11 return l < r;
12 }
13 };
14
15 template<class T>
16 struct Greater
17 {
18 bool operator()(const T& l ,const T& r)
19 {
20 return l > r;
21 }
22 };
23
24
25
26
27
28 template<class T, class Compare = Less<T>>
29 class Heap
30 {
31 public:
32 Heap()
33 {
34
35 }
36 Heap(vector<T> a)
37 :array(a)
38 {
39 for (int i = (array.size() - 2) / 2; i >=0 ; --i)
40 {
41 AdjustDown(i);
42 }
43 }
44 Heap(T *a, size_t size)
45 {
46 for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
47 {
48 array.push_back(a[i]);
49 }
50 for (int i = (array.size() - 2) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
51 {
52 AdjustDown(i);
53 }
54 }
55 ~Heap()
56 {
57
58 }
59 void Push(T x)
60 {
61 array.push_back(x);
62 AdjustUp(array.size()-1);
63 }
64 void Pop()
65 {
66 swap(array.front(), array.back());
67 array.pop_back();
68 AdjustDown(0);
69 }
70 void AdjustDown(int root)
71 {
72 int child = root * 2 + 1;
73 while (child < array.size())
74 {
75 if (child + 1 < array.size() && Compare()(array[child + 1], array[child]))
76 {
77 child++;
78 }
79 if (Compare(array[root], array[child]))
80 {
81 swap(array[root], array[child]);
82 root = child;
83 child = root * 2 + 1;
84 }
85 else
86 {
87 break;
88 }
89 }
90 }
91 void AdjustUp(int child)
92 {
93 int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
94 while (child > 0)
95 {
96 if (Compare()(array[child], array[parent]))
97 {
98 swap(array[child], array[parent]);
99 child = parent;
100 parent = (child - 1) / 2;
101 }
102 else
103 {
104 break;
105 }
106 }
107 }
108 void Print()
109 {
110 for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); ++i)
111 {
112 cout << array[i] << " ";
113 }
114 cout << endl;
115 }
116 int Size()
117 {
118 return array.size();
119 }
120 protected:
121 vector<T> array;
122 };
123
124
125 void TestHeap()
126 {
127 Heap<int> hp;
128 int a[10] = { 5,3,6,2,1,7,8,9,4,0 };
129 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
130 {
131 hp.Push(a[i]);
132 }
133 hp.Print();
134 }
當一個一個push插入的時候我們只需要把這個元素插入到數組的最後,然後順著二叉樹向上調整就可以了(只需要調整這一條線)
刪除頭元素(根節點)的時候,為了不破壞結構,我們選擇先跟處於最後位置的元素交換,之後在末尾刪除掉“根節點”,然後因為最大值(最小值)被換到了根節點,不符合小堆(大堆)的結構要求,只需要順著這條路一直向下調整就可以了
我還寫了一個構造函數接收的參數是一個vector,這是把整個vector調整成大堆(小堆),先找到最後一個元素的父親節點,一直往前向下調整就可以了,因為這個父親節點之前也肯定都是有孩子父親節點