本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/p/cpp-static2.html,轉載請注明源地址
定義:
以關鍵字static聲明的數據成員
class Box
{
public:
int volume() const;
private:
int iwitch;
int length;
int heigth;
static int count;
};
初始化:
靜態數據成員必須初始化且只能在類外初始化,初始化時不能加static,格式:類型 類名::靜態數據成員名 [= 初值];
class Box
{
public:
int volume() const;
private:
int iwitch;
int length;
int heigth;
static int count;
};
int Box::count; //必須在類外初始化
注意:不能通過構造函數初始化、不能通過初始化列表初始化
訪問:
靜態數據成員屬於類而不屬於具體的對象,為不同對象共有。因此,公有靜態數據成員在類外的訪問方式有兩種
類名::公有靜態數據成員
對象名.公有靜態數據成員
靜態數據成員可被其所在類的任何成員函數直接引用void Box::display()const
{
cout << Box:: s_iCount << " ";
cout << s_iCount << " ";
}
存儲:
靜態數據成員編譯時開辟內存單元,占據全局區類的對象創建前就能使用。
靜態數據成員的內存單元獨立開辟,不屬於具體的某個對象,為不同的對象共有。為什麼要引入靜態數據成員?
各對象之間的數據有了溝通的渠道,實現了數據的共享,C++中涉及到對象之間的數據共享時應使用靜態數據成員,而不要使用全局變量,因為全局變量不能體現封裝特性。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Type
{
public:
Type(int ax=0);
static int s_value;
void print();
private:
int m_value;
};
int Type::s_value;
Type::Type(int ax)
{
m_value=ax;
}
void Type::print()
{
cout<<"m_value="
<<++m_value
<<endl;
cout<<"s_value="
<<++s_value
<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Type::s_value=90;
Type c1,c2;
c1.print();
c2.print();
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
應用舉例:統計創建對象的個數
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class student
{
public:
student(string aName="codingwu")
{
strName=aName;
count++;
cout << "Cons"<<" "<<strName <<endl;
}
~student()
{
count--;
cout<< "Des"<<" "<<strName<<endl;
}
void printCount()const
{
cout<<"COUNT = "<<count<<endl;
}
private:
static int count;
string strName;
};
int student::count;
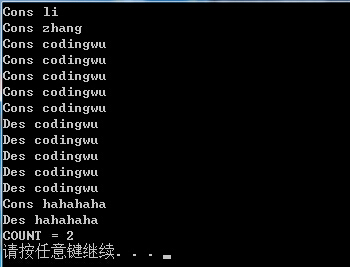
int main()
{
student stu("li");
student stu1("zhang");
student *p=new student[5];
delete []p;
student("hahahaha");
stu.printCount();
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
運行結果:
1、概念:
用static聲明的成員函數
2、訪問方式:
屬於類類型的而不屬於具體對象
3、特點
①靜態成員函數專門用於訪問靜態成員(包括數據成員和成員函數)
②是屬於類的而不屬於具體對象,因此既可以通過類名訪問,也可以通過對象名引用
③其實靜態成員函數就是在類內的全局函數
④靜態成員函數沒有this指針#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Type
{
public:
static void print();
Type(int aValue = 0);
private:
int m_iValue;
static int s_iValue;
};
int Type::s_iValue;
Type::Type(int aValue)
{
m_iValue = aValue;
s_iValue++;
}
void Type::print()
{
//cout << ++m_iValue;//Error
cout << s_iValue << endl;
}
int main()
{
Type::print();
Type c1,c2;
c1.print();
c2.print();
return 0;
}
注意:
非靜態成員函數可以訪問本類中的任何成員
靜態成員函數專門用於訪問靜態成員,不能直接訪問非靜態成員。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student(int aNum=0,int aAge=0,double aScore=0);
void total();
static double s_average();
double m_iScore;
private:
static int s_iCount;//對象個數
static double s_iSum;//總成績
int m_iNum;
int m_iAge;
};
double Student::s_iSum;
int Student::s_iCount;
Student::Student(int aNum,int aAge,double aScore):m_iNum(aNum),m_iAge(aAge),
m_iScore(aScore)
{
}
void Student::total()
{
s_iSum += m_iScore;
s_iCount++;
}
double Student::s_average()
{
return s_iSum/s_iCount;
}
int main()
{
Student stud[3] =
{
Student(1001,18,60),
Student(1002,19,90),
Student(1005,20,0),
};
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++)
stud[i].total();
cout << Student::s_average()<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}