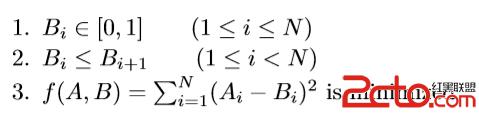HDU 4923 Room and Moor(瞎搞題)
瞎搞題啊。找出1 1 0 0這種序列,然後存起來,這種情況下最好的選擇是1的個數除以這段的總和。然後從前向後掃一遍,變掃邊進行合並。每次合並,合並的是他的前驅。這樣到最後從t-1找出的那條鏈就是最後滿足條件的數的大小。
Room and Moor
Time Limit: 12000/6000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 307 Accepted Submission(s): 90
Problem Description
PM Room defines a sequence A = {A
1, A
2,..., A
N}, each of which is either 0 or 1. In order to beat him, programmer Moor has to construct another sequence B = {B
1, B
2,... , B
N} of the same length,
which satisfies that:
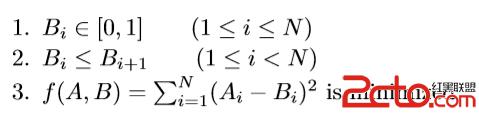
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The number of test cases T(T<=100) occurs in the first line of input.
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer N (1<=N<=100000), which denotes the length of A and B.
The second line consists of N integers, where the ith denotes A
i.
Output
Output the minimal f (A, B) when B is optimal and round it to 6 decimals.
Sample Input
4
9
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1
9
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
4
0 0 1 1
4
0 1 1 1
Sample Output
1.428571
1.000000
0.000000
0.000000
Source
2014 Multi-University Training Contest 6
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include