上一篇文章《STL系列》之vector原理及實現,介紹了vector的原理及實現,這篇文章介紹map的原理及實現。STL實現源碼下載。
STL中map的實現是基於RBTree的,我在實現的時候沒有采用RBTree,覺得這東西有點復雜,我的map采用的是排序數組(CSortVector)。map中的Key存在排序數據中,通過二分查找判斷某個Key是否在map中,時間復雜度為O(logN)。在用一個CVector存Key和Value,為了方便拿到Key和Value,這裡有點冗余,Key被存了兩次。
現在先介紹我的CSortVector,先貼出完整的代碼,如下:
![]()
#ifndef _CSORTVECTOR_H_
#define _CSORTVECTOR_H_
namespace cth
{
template<typename T>
class csortvector:public NoCopy
{
public:
typedef const T* const_iterator;
typedef T* iterator;
csortvector()
{
initData(0);
}
csortvector(int capa,const T& val=T())
{
initData(capa);
newCapacity(capacity_);
for (int i=0;i<size_;i++)
buf[i]=val;
}
~csortvector()
{
if (buf)
{
delete[] buf;
buf=NULL;
}
size_=capacity_=0;
}
int add(const T& t )
{
int index=-1;
if (size_==0)
{
newCapacity(calculateCapacity());
buf[size_++]=t;
index=0;
}else{
int start=0;
int end=size_-1;
while(start<=end)
{
index=(start+end)/2;
if(buf[index]==t)
{
goto SORTVECTOR_INSERT;
}
else if(buf[index]>t)
{
end=index-1;
}
else
{
start=index+1;
}
}
if(buf[index]<t)
{
index++;
}
SORTVECTOR_INSERT:
insert(index,t);
}
return index;
}
void insert(int index,const T& t)
{
assert(index>=0 && index<=size_);
if (size_==capacity_)
{
newCapacity(calculateCapacity());
}
memmove(buf+index+1,buf+index,(size_-index)*sizeof(T));
buf[index]=t;
size_++;
}
int indexOf(const T& t)
{
int begin=0;
int end=size_-1;
int index=-1;
while (begin<=end)
{
index=begin+(end-begin)/2;
if (buf[index]==t)
{
return index;
}else if (buf[index]<t)
{
begin=index+1;
}else{
end=index-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int remove(const T& t)
{
int index=indexOf(t);
if (index>=0)
{
memmove(buf+index ,buf+index+1,(size_-index)*sizeof(T));
buf[--size_]=T();
}
return index;
}
void erase(const_iterator iter)
{
remove(*iter);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(&buf[0]);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(&buf[size_]);
}
const T& operator[](int index) const
{
assert(size_>0 && index>=0 && index<size_);
return buf[index];
}
void clear()
{
if (buf)
{
for (int i=0;i<size_;i++)
{
buf[i]=T();
}
}
size_=capacity_=0;
}
bool empty() const
{
return size_==0;
}
int size() const
{
return size_;
}
int capacity() const
{
return capacity_;
}
private:
void newCapacity(int capa)
{
assert (capa>size_) ;
capacity_=capa;
T* newBuf=new T[capacity_];
if (buf)
{
memcpy(newBuf,buf,size_*sizeof(T) );
delete [] buf;
}
buf=newBuf;
}
inline void initData(int capa)
{
buf=NULL;
size_=capacity_=capa>0?capa:0;
}
inline int calculateCapacity()
{
return capacity_*3/2+1;
}
int size_;
int capacity_ ;
T* buf;
};
}
#endif
View Code
CSortVector和CVector有點類似,只不過CSortVector中的數據在插入的時候需要排序,其他的接口比較相識。CSortVector的關鍵實現就是二分查找。新增和刪除的時候都是通過二分查找,定位到指定的位置,在進行相關操作。這裡有必要特意列出二分查找的實現,如下:
int indexOf(const T& t)
{
int begin=0;
int end=size_-1;
int index=-1;
while (begin<=end)
{
index=begin+(end-begin)/2;
if (buf[index]==t)
{
return index;
}else if (buf[index]<t)
{
begin=index+1;
}else{
end=index-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
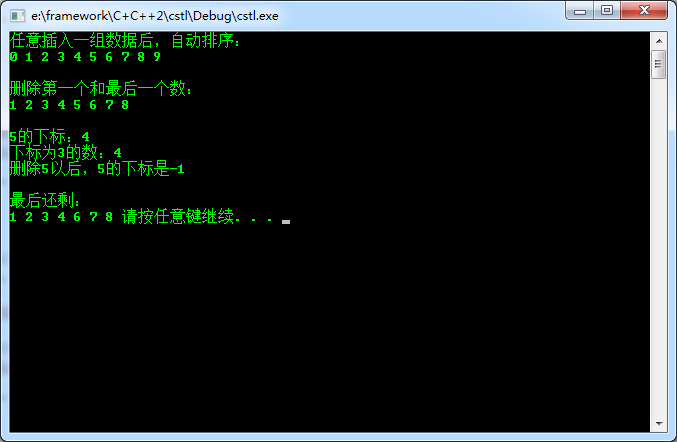
CSortVector測試代碼如下:
void csortvectorTest()
{
csortvector<int> l;
l.add(2);
l.add(4);
l.add(9);
l.add(3);
l.add(7);
l.add(1);
l.add(5);
l.add(8);
l.add(0);
l.add(6);
cout<<"任意插入一組數據後,自動排序:"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
l.erase(l.begin());
l.erase(l.end()-1);
cout<<"刪除第一個和最後一個數:"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"5的下標:"<<l.indexOf(5)<<endl;
cout<<"下標為3的數:"<<l[3]<<endl;
l.remove(5);
cout<<"刪除5以後,5的下標是"<<l.indexOf(5)<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"最後還剩:"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<l.size();i++)
{
cout<<l[i]<<" ";
}
}
運行結果如下:
注意:由於CSortVector中的元素要排序,所以其中的元素要實現運算符”<”。
介紹完CSortVector,接下來說說CMap。其實CSortVector已經解決CMap的大部分功能了,後者只需要在前者的基礎之上簡單的封裝即可完事。CMap源碼如下:

![]()
#ifndef _CMAP_H_
#define _CMAP_H_
#include "csortvector.h"
namespace cth
{
template<typename Key,typename Value>
struct pair
{
typedef Key first_type;
typedef Value second_type;
pair(){}
pair(const Key& key,const Value& val):first(key),second(val){}
pair(const pair& other):first(other.first),second(other.second){}
Key first;
Value second;
};
class NoCopy
{
public:
inline NoCopy(){}
NoCopy(const NoCopy&);
NoCopy& operator=(const NoCopy&);
};
template<typename Key,typename Value>
class cmap:public NoCopy
{
public:
typedef pair<Key,Value>* iterator;
typedef const pair<Key,Value>* const_iterator;
cmap(){}
int insert(const pair<Key,Value>& item)
{
iterator iter=find(item.first);
if (iter!=end())
{
return iter-begin();
}
int index=Keys.add(item.first);
if (index>=0)
{
index=Values.insert(Values.begin() + index,item);
}
return index;
}
int insert(const Key& key,const Value& val)
{
pair<Key,Value> item;
item.first=key;
item.second=val;
return insert(item);
}
Value& operator[](const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.indexOf(key);
if (index<0)
{
index=insert(key,Value());
}
return Values[index].second;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(&*Values.begin());
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(&*Values.end());
}
iterator find(const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.indexOf(key);
if (index<0)
{
return end();
}else
{
return iterator(&Values[index]);
}
}
void erase(const Key& key)
{
int index=Keys.remove(key) ;
if (index>=0)
{
cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index;
Values.erase(iter);
}
}
void erase(const_iterator iter)
{
int index=Keys.remove(iter->first) ;
if (index>=0)
{
cvector<pair<Key,Value>>::iterator iter=Values.begin()+index;
Values.erase(iter);
}
}
int size()
{
return Keys.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return Keys.size()==0;
}
void clear()
{
Keys.clear();
Values.clear();
}
private:
csortvector<Key> Keys;
cvector<pair<Key,Value>> Values;
};
}
#endif
View Code
插入操作,CMap的插入操作分兩種,一種是通過insert方法;另一種是通過操作符[]。
Insert方法是先找到Key在Keys中的位置,如果已經存在就返回,CMap不允許重復,如果不存在就通過二分查找找到對應的位置,插入Key,並在Values中對應的地方插入Value。
通過操作符[]插入:如m[1]=1;剛開始我也不知道這個是怎麼實現的,後來突然明白,操作符[]返回的是一個引用,其實就是給我m[1]的返回值賦值,調用的也是返回值的operator=,CMap只用實現operator[]就行。
其他的方法都是一些簡單的封裝,這裡就不在累贅,最後概述一下CMap的實現:
CMap是基於一個排序數組CSortVector實現的,將Key存入排序數據中,Value和Key通過Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中,通過二分查找確定某個Key是否存在,不存在就將這個Key插入排序數據中,返回Key在數組中的索引,並將Pair<Key,Value>存在CVector中對應的位置。刪除還是通過二分查找尋找,找到就將兩個數組中對應的元素刪除。
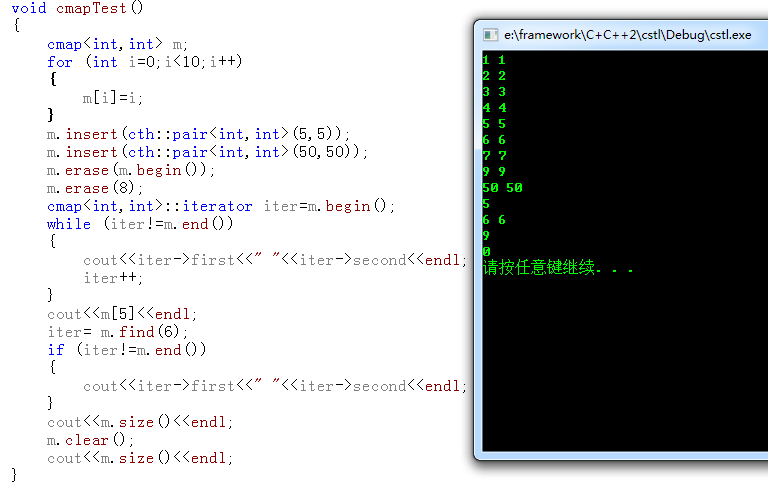
CMap測試代碼運行如下: