Hanoi Tower Troubles Again!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
People stopped moving discs from peg to peg after they know the number of steps needed to complete the entire task. But on the other hand, they didn't not stopped thinking about similar puzzles with the Hanoi Tower. Mr.S invented a little game on it. The game consists of N pegs and a LOT of balls. The balls are numbered 1,2,3... The balls look ordinary, but they are actually magic. If the sum of the numbers on two balls is NOT a square number, they will push each other with a great force when they're too closed, so they can NEVER be put together touching each other.
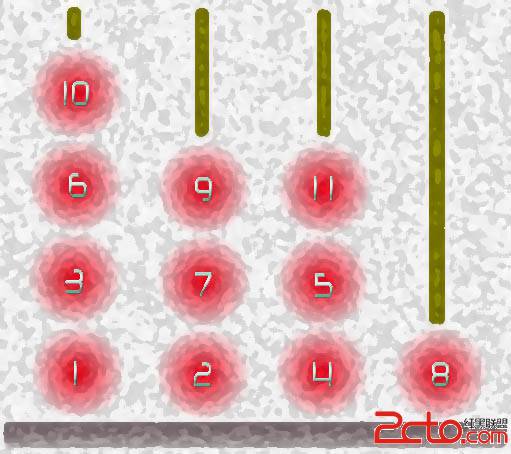 The player should place one ball on the top of a peg at a time. He should first try ball 1, then ball 2, then ball 3... If he fails to do so, the game ends. Help the player to place as many balls as possible. You may take a look at the picture above, since it shows us a best result for 4 pegs.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T, indicating the number of test cases. (1<=T<=50) Each test case contains a single integer N(1<=N<=50), indicating the number of pegs available.
Output
For each test case in the input print a line containing an integer indicating the maximal number of balls that can be placed. Print -1 if an infinite number of balls can be placed.
Sample Input
2
4
25
Sample Output
11
337
給出n個柱子,從第一個柱子開始放珠子,珠子編號從1開始,要求每個柱子上相鄰兩個珠子的和是可開方的。
[cpp]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int a[55];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int poit=1;
int s=1;
while(1)
{
if(poit>n)
break;
if(a[poit]==0)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
else
{
int b=a[poit]+s;
int c=sqrt(b);
if(c*c==b)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
}
poit++;
}
printf("%d\n",s-1);
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int a[55];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int poit=1;
int s=1;
while(1)
{
if(poit>n)
break;
if(a[poit]==0)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
else
{
int b=a[poit]+s;
int c=sqrt(b);
if(c*c==b)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
}
poit++;
}
printf("%d\n",s-1);
}
return 0;
}
The player should place one ball on the top of a peg at a time. He should first try ball 1, then ball 2, then ball 3... If he fails to do so, the game ends. Help the player to place as many balls as possible. You may take a look at the picture above, since it shows us a best result for 4 pegs.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T, indicating the number of test cases. (1<=T<=50) Each test case contains a single integer N(1<=N<=50), indicating the number of pegs available.
Output
For each test case in the input print a line containing an integer indicating the maximal number of balls that can be placed. Print -1 if an infinite number of balls can be placed.
Sample Input
2
4
25
Sample Output
11
337
給出n個柱子,從第一個柱子開始放珠子,珠子編號從1開始,要求每個柱子上相鄰兩個珠子的和是可開方的。
[cpp]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int a[55];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int poit=1;
int s=1;
while(1)
{
if(poit>n)
break;
if(a[poit]==0)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
else
{
int b=a[poit]+s;
int c=sqrt(b);
if(c*c==b)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
}
poit++;
}
printf("%d\n",s-1);
}
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int a[55];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int poit=1;
int s=1;
while(1)
{
if(poit>n)
break;
if(a[poit]==0)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
else
{
int b=a[poit]+s;
int c=sqrt(b);
if(c*c==b)
{
a[poit]=s;
s++;
poit=1;
continue;
}
}
poit++;
}
printf("%d\n",s-1);
}
return 0;
}