雙鏈表:在單鏈表的每個結點中,再設置一個指向其前驅結點的指針域
線性表的雙向鏈表存儲結構:
typedef struct Node
{
DataType _data;
struct Node *_next;
struct Node *_front;
}Node;
通過雙鏈表的存儲結構我們發現雙鏈表可以反向查找結點優於單鏈表 ,實質上雙鏈表就是以空間換取時間,雖然雙鏈表具有可以反向查找數據的優點但是它也存在缺點:在插入和刪除一個結點時需要維護兩個指針變量,特別是在雙鏈表的插入中指針的指向順序是不可修改的。
雙鏈表的插入過程:
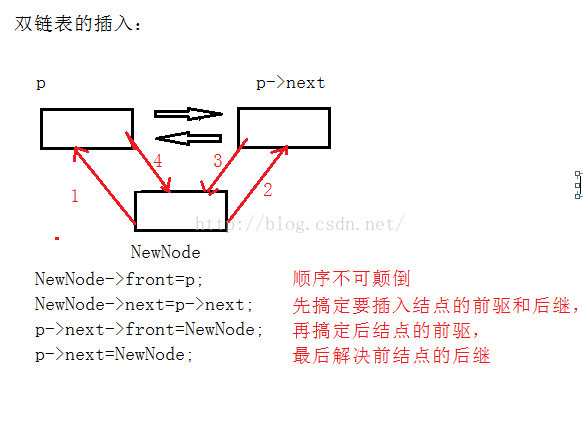
雙鏈表的刪除過程:
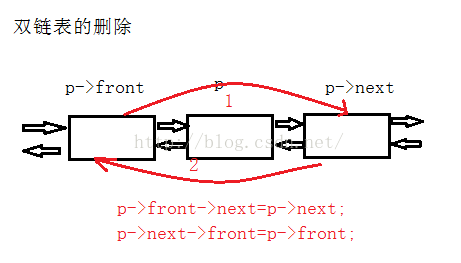
C++實現雙鏈表的基本功能:
typedef int DataType;
class LinkList;
class Node
{
friend LinkList;
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os,Node &n);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &os,LinkList &list);
public:
Node(DataType x)
:_data(x)
,_next(NULL)
,_front(NULL)
{}
private:
DataType _data;
Node *_next;
Node *_front;
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os,Node &n)
{
os<_data);
if(_tail)
{
_tail->_next=tmp;
tmp->_front=_tail;
_tail=tmp;
}
else //空鏈表
{
_head=tmp;
_tail=tmp;
}
cur=cur->_next;
}
}
~LinkList()
{
Node *cur=_head;
while(cur)
{
Node *del=cur;
cur=cur->_next;
delete del;
del=NULL;
}
}
public:
void PushBack(DataType x)
{
Node *NewNode=new Node(x);
if(_tail)
{
_tail->_next=NewNode;
NewNode->_front=_tail;
_tail=NewNode;
}
else
{
_head=NewNode;
_tail=NewNode;
}
}
void PopBack()
{
if(!_head && !_tail) //空鏈表
{
cout<<"鏈表已空不可尾刪"<_front;
_tail->_next=NULL;
delete tmp;
tmp=NULL;
}
}
void PushFront(DataType x)
{
Node *NewNode=new Node(x);
if(_head)
{
Node *tmp=_head;
NewNode->_next=tmp;
tmp->_front=NewNode;
}
else
{
_tail=NewNode;
}
_head=NewNode; //更新頭
}
void PopFront()
{
if(!_head && !_tail) //空鏈表
{
cout<<"鏈表已空不可頭刪"<_next;
_head->_front=NULL;
delete del;
del=NULL;
}
}
Node *FindNum(DataType x)
{
Node *cur=_head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->_data == x)
return cur;
cur=cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
void Insert(Node *pos,DataType x) //在指定位置後插
{
Node *NewNode=new Node(x);
if(pos->_next)
{
NewNode->_front=pos;
NewNode->_next=pos->_next;
pos->_next->_front=NewNode;
pos->_next=NewNode;
}
else //在最後一個結點後插,類似PushBack
{
pos->_next=NewNode;
NewNode->_front=pos;
_tail=NewNode; //更新尾
}
}
void Insert(int,Node *pos,DataType x) //在指定位置前插
{
Node *NewNode=new Node(x);
if(pos->_front)
{
NewNode->_next=pos;
pos->_front->_next=NewNode;
NewNode->_front=pos->_front;
pos->_front=NewNode;
}
else //在第一個結點的前插,類似PushFront
{
NewNode->_next=pos;
pos->_front=NewNode;
_head=NewNode; //更新頭
}
}
void Remove(DataType &x)
{
Node *pos=this->FindNum(x);
if(pos != NULL)
{
if((!(pos->_front)) && pos->_next) //刪除第一個結點
{
Node *tmp=pos->_next;
tmp->_front=NULL;
_head=tmp;
}
else if(pos->_front && (!(pos->_next))) //刪除最後一個結點
{
Node *tmp=pos->_front;
tmp->_next=NULL;
_tail=tmp;
}
else //刪除中間節點
{
Node *front=pos->_front;
Node *next=pos->_next;
next->_front=front;
front->_next=next;
}
delete pos;
pos=NULL;
}
}
void RemoveAll(DataType &x)
{
Node *cur=_head;
Node *ret=this->FindNum(x);
if(ret != _head) //可刪除第一個結點不是要刪除的元素
{
while(cur)
{
Remove(x);
cur=cur->_next;
}
}
}
void Sort()
{
int flag=1;
Node *cur=_head;
Node *tail=NULL;
while(cur != tail)
{
while(cur->_next != tail)
{
if(cur->_data > cur->_next->_data)
{
DataType tmp=cur->_data;
cur->_data=cur->_next->_data;
cur->_next->_data=tmp;
flag=0;
}
cur=cur->_next;
}
if(flag == 1)
break;
tail=cur;
cur=_head;
}
}
void Erase(Node *pos)
{
if((!(pos->_front)) && pos->_next) //刪除第一個結點
{
Node *tmp=pos->_next;
tmp->_front=NULL;
_head=tmp;
}
else if(pos->_front && (!(pos->_next))) //刪除最後一個結點
{
Node *tmp=pos->_front;
tmp->_next=NULL;
_tail=tmp;
}
else //刪除中間節點
{
Node *front=pos->_front;
Node *next=pos->_next;
next->_front=front;
front->_next=next;
}
delete pos;
pos=NULL;
}
private:
Node *_head;
Node *_tail;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream &os,LinkList &list)
{
Node *cur=list._head;
while(cur)
{
os<<(*cur)<<" ";
cur=cur->_next;
}
return os;
}
在C++實現中如果遇到結點結構最好定義為struct,否則就會像上述情況一樣需要聲明多次友元,反而破壞了類的封裝性
測試代碼:
void menu()
{
cout<<"************1.尾插************2.尾刪**************"<
OVER