《UNIX環境高級編程》中的程序清單4-7就介紹了如何實現遞歸地統計某個目錄下面的文件!我剛開始看過它的代碼後,覺得照著敲太沒意思了,所以就合上書自己寫了一遍!為此還寫了一篇博文,這是博文地址: 在linux下用C語言實現遞歸查看某個目錄中的所有文件【CSDN】!
今天做《Unix環境高級編程》的課後題,看到題目4.11這裡提供了一種新的實現這個程序的思路,那就是每回讀到一個目錄,就通過chdir函數進入到這個目錄,然後再通過opendir函數和readdir函數來讀取這個目錄中的文件,然後一個一個分析,如果是目錄,則進行遞歸調用。如果不是目錄,則對這個文件進行計數後立刻返回!這樣一個一個分析完目錄中的所有文件之後再來進行一個chdir(".."),返回到上一級的目錄。具體的實現代碼如下:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<string.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<errno.h>
5 #include<linux/limits.h>
6 #include<unistd.h>
7 #include<sys/types.h>
8 #include<sys/stat.h>
9 #include<dirent.h>
10
11 //所有函數的聲明
12 typedef int MyFunc(const char *,const struct stat*,int);
13 static MyFunc myfunc; //定義處理文件的函數
14 static int myftw(const char *,MyFunc *);
15 static int dopath(MyFunc *);
16
17 //定義的全局變量
18 static char *fullpath; //存放文件的名稱的變量
19 static long sock_c,lnk_c,reg_c,blk_c,dir_c,chr_c,fifo_c,total_c; //統計各種文件類型的數量
20
21 //myfunc函數中需要定義的宏
22 #define FTW_F 1 //文件類型是文件
23 #define FTW_D 2 //文件類型是目錄
24 #define FTW_NS 3 //一個文件不能stat
25 #define FTW_ND 4 //一個目錄不能被讀
26 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
27 {
28 if(argc != 2)
29 {
30 printf("Usage:%s pathname\n",argv[0]+2);
31 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
32 }
33 myftw(argv[1],myfunc);
34 total_c = sock_c+lnk_c+reg_c+blk_c+dir_c+chr_c+fifo_c;
35 if(0 == total_c)
36 {
37 total_c = 1;
38 }
39 printf("socket files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",sock_c,sock_c*100.0/total_c);
40 printf("link files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",lnk_c,lnk_c*100.0/total_c);
41 printf("regular files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",reg_c,reg_c*100.0/total_c);
42 printf("block files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",blk_c,blk_c*100.0/total_c);
43 printf("directory files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",dir_c,dir_c*100.0/total_c);
44 printf("character files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",chr_c,chr_c*100.0/total_c);
45 printf("FIFO files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",fifo_c,fifo_c*100.0/total_c);
46 printf("total files = %7ld, %5.2f%%\n",total_c,total_c*100.0/total_c);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
50 static int myftw(const char* pathname,MyFunc *pmyfunc)
51 {
52 int ret;
53
54 fullpath = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*PATH_MAX);
55 strcpy(fullpath,pathname);
56 ret = dopath(myfunc);
57 free(fullpath);
58
59 return ret;
60 }
61 static int dopath(MyFunc *pmyfunc)
62 {
63 int ret;
64 struct stat statbuf;
65 char *ptr;
66 DIR *dp;
67 struct dirent* dirp;
68
69 if(-1 == lstat(fullpath,&statbuf))
70 {
71 ret = pmyfunc(fullpath,&statbuf,FTW_NS);
72 return ret;
73 }
74 if(S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode) != 1)
75 {
76 ret = pmyfunc(fullpath,&statbuf,FTW_F);
77 return ret;
78 }
79
80 //使目錄文件++
81 if(0 != (ret=pmyfunc(fullpath,&statbuf,FTW_D)))
82 return ret;
83
84 //如果是目錄文件則進入這個目錄
85 if(-1 == chdir(fullpath))
86 {
87 printf("%s[chdir]%s\n",fullpath,strerror(errno));
88 ret == -1;
89 return ret;
90 }
91
92 //打開當前目錄
93 if(NULL == (dp=opendir(".")))
94 {
95 ret = pmyfunc(fullpath,&statbuf,FTW_ND);
96 return ret;
97 }
98 while(NULL != (dirp=readdir(dp)))
99 {
100 //忽略.和..文件(dot)
101 if(0==strcmp(dirp->d_name,".") || 0==strcmp(dirp->d_name,".."))
102 continue;
103 memset(fullpath,0,PATH_MAX);
104 strcpy(fullpath,dirp->d_name);
105
106 if(0 != (ret=dopath(myfunc))) //進行遞歸
107 break;
108 }
109 chdir(".."); //將當前目錄設置為上一級目錄
110 //對關閉文件進行判斷
111 if(-1 == closedir(dp))
112 {
113 printf("不能關閉%s\nError:%s",fullpath,strerror(errno));
114 }
115
116 return ret;
117 }
118 static int myfunc(const char * pathname,const struct stat * statptr,int type)
119 {
120 switch(type)
121 {
122 case FTW_F:
123 switch(statptr->st_mode & S_IFMT)
124 {
125 case S_IFSOCK: sock_c++; break;
126 case S_IFLNK: lnk_c++; break;
127 case S_IFREG: reg_c++; break;
128 case S_IFBLK: blk_c++; break;
129 case S_IFCHR: chr_c++; break;
130 case S_IFIFO: fifo_c++; break;
131 case S_IFDIR:
132 printf("Error:這裡不應該出現目錄文件%s!\n\nError:%s\n",pathname,strerror(errno));
133 break;
134 }
135 break;
136 case FTW_D:
137 dir_c++; break;
138 case FTW_ND:
139 printf("不能打開目錄%s\nError:%s\n",pathname,strerror(errno));
140 break;
141 case FTW_NS:
142 printf("不能打開文件%s\nError:%s\n",pathname,strerror(errno));
143 break;
144 }
145 return 0;
146 }
我這個代碼並不是我自己合上書寫的,而是在W.Richard Stevens書中給出的代碼的基礎上改的!在此要特別感謝這些真正的大神給我們提供了這麼優秀的書籍!這是這個程序的運行結果,
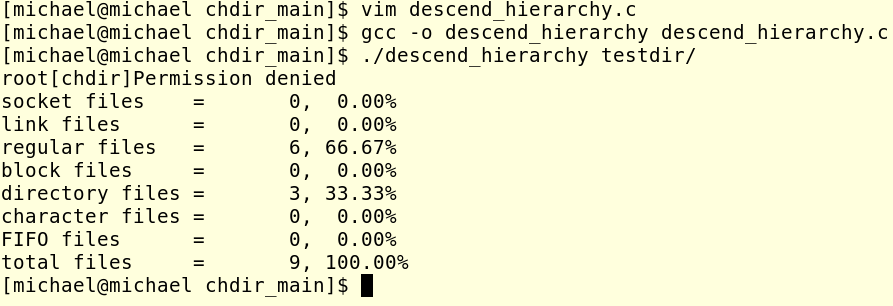
那個第一行是我特意設置的,那個root是一個文件夾的名字,是屬於root用戶的,所以我這裡並不能讀取,會報出一個錯誤!下面是這個改進後的程序和原來書中的程序的一個對比,發現效率還真的是提高不少啊!
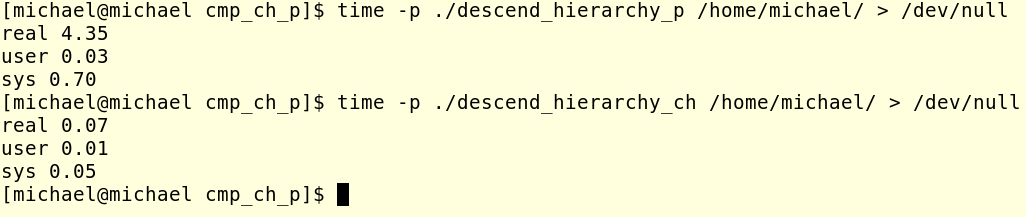
那個descend_hierarchy_p的那個程序是書上給的程序,每回讀取都是讀取的絕對路徑的名稱!而那個descend_hierarchy_ch命令就是每回碰到一個目錄就進入到那個文件夾中,然後再來讀取,這樣每回讀取的時候讀取的就是相對路徑的名稱了!