下面通過編寫Demo的方式,驗證各種反射的性能。
1、傳統方式反射
Type t = typeof(Person);
MethodInfo methodInfo = t.GetMethod("Say");
Person person = new Person();
string word = "hello";
Person p = null;
object[] param = new object[] { word, p, 3 };
int TestTimes = 1000000; //測試次數,可自行調節看效果
#region 傳統方式反射
try
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < TestTimes; i++)
{
methodInfo.Invoke(person, param);
}
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(TestTimes.ToString() + " times invoked by Reflection: " + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
}
catch (System.Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("傳統方式反射 直接錯誤:" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("傳統方式反射 內部錯誤:" + ex.InnerException.Message);
}
#endregion
2、實例化反射
#region 實例化反射
try
{
//Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
//watch.Start();
//for (int i = 0; i < TestTimes; i++)
//{
// Assembly Asm = Assembly.Load("testInvoke");//反射出空間
// Type type = Asm.GetType("testInvoke.Person");//反射出空間下的類
// object AssClas = Activator.CreateInstance(type);//動態實例化反射回來的指定空間下的指定類
// IPerson objPerson = (Person)AssClas; ////轉換為接口類型
// objPerson.Say(ref word, out p, 3);
//}
//watch.Stop();
//Console.WriteLine(TestTimes.ToString() + " times invoked by InstanceReflection@1: " + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
Assembly Asm = Assembly.Load("testInvoke");//反射出空間
Type type = Asm.GetType("testInvoke.Person");//反射出空間下的類
object AssClas = Activator.CreateInstance(type);//動態實例化反射回來的指定空間下的指定類
IPerson objPerson = (Person)AssClas; //轉換為接口類型
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < TestTimes; i++)
{
objPerson.Say(ref word, out p, 3);
}
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(TestTimes.ToString() + " times invoked by InstanceReflection@2: " + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
}
catch (System.Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("實例化反射 錯誤:" + ex.Message);
}
#endregion
3、快速反射
#region 快速反射
try
{
Stopwatch watch1 = new Stopwatch();
FastInvoke.FastInvokeHandler fastInvoker = FastInvoke.GetMethodInvoker(methodInfo);
watch1.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < TestTimes; i++)
{
fastInvoker(person, param);
}
watch1.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(TestTimes.ToString() + " times invoked by FastInvoke: " + watch1.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
}
catch (System.Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("快速反射 錯誤:" + ex.Message);
}
#endregion
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Reflection.Emit;
using System.Reflection;
namespace testInvoke
{
class FastInvoke
{
public delegate object FastInvokeHandler(object target, object[] paramters);
static object InvokeMethod(FastInvokeHandler invoke, object target, params object[] paramters)
{
return invoke(null, paramters);
}
public static FastInvokeHandler GetMethodInvoker(MethodInfo methodInfo)
{
DynamicMethod dynamicMethod = new DynamicMethod(string.Empty, typeof(object), new Type[] { typeof(object), typeof(object[]) }, methodInfo.DeclaringType.Module);
ILGenerator il = dynamicMethod.GetILGenerator();
ParameterInfo[] ps = methodInfo.GetParameters();
Type[] paramTypes = new Type[ps.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.Length; i++)
{
if (ps[i].ParameterType.IsByRef)
paramTypes[i] = ps[i].ParameterType.GetElementType();
else
paramTypes[i] = ps[i].ParameterType;
}
LocalBuilder[] locals = new LocalBuilder[paramTypes.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.Length; i++)
{
locals[i] = il.DeclareLocal(paramTypes[i], true);
}
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.Length; i++)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldarg_1);
EmitFastInt(il, i);
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldelem_Ref);
EmitCastToReference(il, paramTypes[i]);
il.Emit(OpCodes.Stloc, locals[i]);
}
if (!methodInfo.IsStatic)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldarg_0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.Length; i++)
{
if (ps[i].ParameterType.IsByRef)
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldloca_S, locals[i]);
else
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldloc, locals[i]);
}
if (methodInfo.IsStatic)
il.EmitCall(OpCodes.Call, methodInfo, null);
else
il.EmitCall(OpCodes.Callvirt, methodInfo, null);
if (methodInfo.ReturnType == typeof(void))
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldnull);
else
EmitBoxIfNeeded(il, methodInfo.ReturnType);
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.Length; i++)
{
if (ps[i].ParameterType.IsByRef)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldarg_1);
EmitFastInt(il, i);
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldloc, locals[i]);
if (locals[i].LocalType.IsValueType)
il.Emit(OpCodes.Box, locals[i].LocalType);
il.Emit(OpCodes.Stelem_Ref);
}
}
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ret);
FastInvokeHandler invoder = (FastInvokeHandler)dynamicMethod.CreateDelegate(typeof(FastInvokeHandler));
return invoder;
}
private static void EmitCastToReference(ILGenerator il, System.Type type)
{
if (type.IsValueType)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Unbox_Any, type);
}
else
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Castclass, type);
}
}
private static void EmitBoxIfNeeded(ILGenerator il, System.Type type)
{
if (type.IsValueType)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Box, type);
}
}
private static void EmitFastInt(ILGenerator il, int value)
{
switch (value)
{
case -1:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_M1);
return;
case 0:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_0);
return;
case 1:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_1);
return;
case 2:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_2);
return;
case 3:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_3);
return;
case 4:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_4);
return;
case 5:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_5);
return;
case 6:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_6);
return;
case 7:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_7);
return;
case 8:
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_8);
return;
}
if (value > -129 && value < 128)
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_S, (SByte)value);
}
else
{
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldc_I4, value);
}
}
}
}
4、不用反射,直接調用
#region 直接調用
try
{
Stopwatch watch2 = new Stopwatch();
watch2.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < TestTimes; i++)
{
person.Say(ref word, out p, 3);
}
watch2.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(TestTimes.ToString() + " times invoked by DirectCall: " + watch2.ElapsedMilliseconds + "ms");
}
catch (System.Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("直接調用 錯誤:" + ex.Message);
}
#endregion
以上4種調用方式,100萬次調用結果如下:
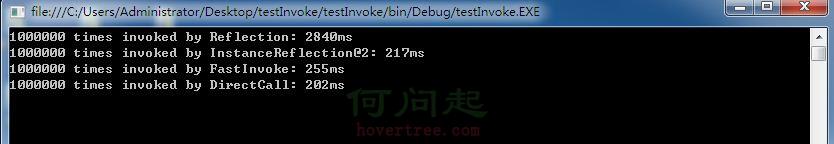
所以得出以下結論:
1. 不用反射,直接調用,效率最高。
2. 實例化反射,效率次之。
3. 快速反射,效率次之。
4. 傳統反射,效率最差。
以上調用方式,後3種調用方式雖然效率有先後,但性能在一個數量級上,與傳統反射相比,優越性較明顯。
另外補充一點,實例化反射如果算上創建實例的性能損耗,試驗結果如下圖:
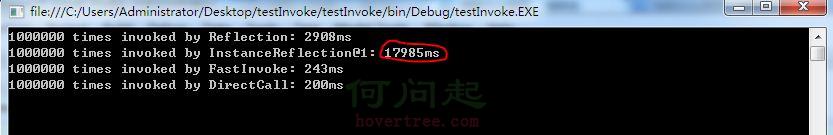
所以,如果需要頻繁創建實例,建議不要采用實例化反射。
源碼下載:files.cnblogs.com/tianzhiliang/testInvoke.rar
作者:何問起
出處:http://hovertrre.com