在做系統的時候,經常遇到前台錄入一大堆的查詢條件,然後點擊查詢提交後台,在Controller裡面生成對應的查詢SQL或者表達式,數據庫執行再將結果返回客戶端。
例如如下頁面,輸入三個條件,日志類型、開始和結束日期,查詢後台系統操作日志,並顯示。
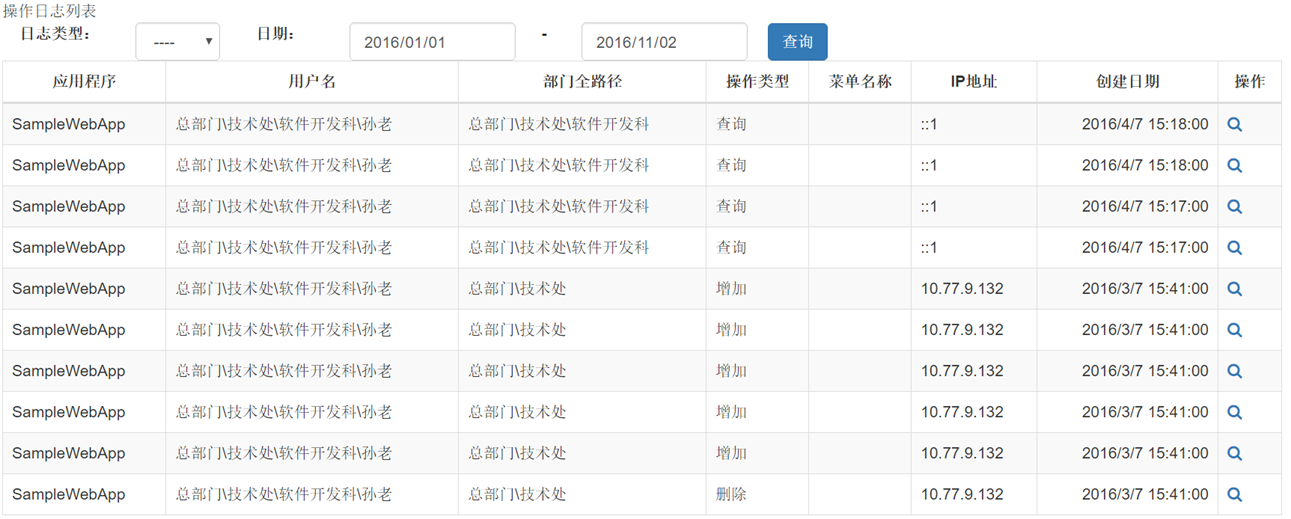
這種類似頁面在系統中還是比較多的,通常情況下,我們會在cshtml中放上日志類型、開始、結束日期這三個控件,controller的action有對應的三個參數,然後在action、邏輯層或者倉儲層實現將這三個參數轉換為linq,例如轉成c=>c.BeginDate>=beginDate && c.EndDate < endDate.AddDay(1) && c.OperType == operType。
這裡有個小技巧,就是結束日期小於錄入的結束日期+1天。一般大家頁面中錄入結束日期的時候都是只到日期,不帶時分秒,例如結束日期為2016年1月31日,endDate 就是2016-01-31。其實這時候,大家的想法是到2016年1月31日23:59:59秒止。如果數據庫中存儲的是帶時分秒的時間,例如2016-01-31 10:00:00.000,而程序中寫的是c.EndDate < endDate的話,那麼這個2016年1月31日零點之後的全不滿足條件。所以,這裡應該是小於錄入的結束日期+1。
如果我們有更多的條件怎麼辦?如果有的條件允許為空怎麼辦?如果有幾十個這樣的頁面的?難道要一個個的去寫麼?
基於以上的考慮,我們為了簡化操作,編寫了自動生成組合查詢條件的通用框架。做法主要有如下幾步:
下面詳細介紹下具體的過程。
1、前端頁面采用一定的格式設置Html控件的Id和Name,這裡我們約定的寫法是{Op}__{PropertyName},就是操作符、兩個下劃線、屬性名。
1 <form asp-action="List" method="post" class="form-inline"> 2 <div class="form-group"> 3 <label class="col-md-4 col-xs-4 col-sm-4 control-label">日志類型:</label> 4 <div class="col-md-8 col-xs-8 col-sm-8"> 5 <select id="Eq__LogOperType" name="Eq__LogOperType" class="form-control" asp-items="@operateTypes"></select> 6 </div> 7 </div> 8 <div class="form-group"> 9 <label class="col-md-4 col-xs-4 col-sm-4 control-label">日期:</label> 10 <div class="col-md-8 col-xs-8 col-sm-8"> 11 <input type="date" id="Gte__CreateDate" name="Gte__CreateDate" class="form-control" value="@queryCreateDateStart.ToDateString()" /> 12 </div> 13 </div> 14 <div class="form-group"> 15 <label class="col-md-4 col-xs-4 col-sm-4 control-label"> - </label> 16 <div class="col-md-8 col-xs-8 col-sm-8"> 17 <input type="date" id="Lt__CreateDate" name="Lt__CreateDate" class="form-control" value="@queryCreateDateEnd.ToDateString()" /> 18 </div> 19 </div> 20 <button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">查詢</button> 21 </form>
例如,日志類型查詢條件要求日志類型等於所選擇的類型。日志類的日志類型屬性是LogOperType,等於的操作符是Eq,這樣Id就是Eq__LogOperType。同樣的操作日期在開始和結束日期范圍內,開始和結束日期的Id分別為Gte__CreateDate和Lt__CreateDate。
2、編寫ModelBinder,接收前端傳來的參數,生成查詢條件類。
這裡,我們定義一個查詢條件類,QueryConditionCollection,注釋寫的還是比較明確的:
1 /// <summary>
2 /// 操作條件集合
3 /// </summary>
4 public class QueryConditionCollection : KeyedCollection<string, QueryConditionItem>
5 {
6 /// <summary>
7 /// 初始化
8 /// </summary>
9 public QueryConditionCollection()
10 : base()
11 {
12 }
13
14 /// <summary>
15 /// 從指定元素提取鍵
16 /// </summary>
17 /// <param name="item">從中提取鍵的元素</param>
18 /// <returns>指定元素的鍵</returns>
19 protected override string GetKeyForItem(QueryConditionItem item)
20 {
21 return item.Key;
22 }
23 }
24
25 /// <summary>
26 /// 操作條件
27 /// </summary>
28 public class QueryConditionItem
29 {
30 /// <summary>
31 /// 主鍵
32 /// </summary>
33 public string Key { get; set; }
34 /// <summary>
35 /// 名稱
36 /// </summary>
37 public string Name { get; set; }
38
39 /// <summary>
40 /// 條件操作類型
41 /// </summary>
42 public QueryConditionType Op { get; set; }
43
44 ///// <summary>
45 ///// DataValue是否包含單引號,如'DataValue'
46 ///// </summary>
47 //public bool IsIncludeQuot { get; set; }
48
49 /// <summary>
50 /// 數據的值
51 /// </summary>
52 public object DataValue { get; set; }
53 }
按照我們的設計,上面日志查詢例子應該產生一個QueryConditionCollection,包含三個QueryConditionItem,分別是日志類型、開始和結束日期條件項。可是,如何通過前端頁面傳來的請求數據生成QueryConditionCollection呢?這裡就用到了ModelBinder。ModelBinder是MVC的數據綁定的核心,主要作用就是從當前請求提取相應的數據綁定到目標Action方法的參數上。
1 public class QueryConditionModelBinder : IModelBinder
2 {
3 private readonly IModelMetadataProvider _metadataProvider;
4 private const string SplitString = "__";
5
6 public QueryConditionModelBinder(IModelMetadataProvider metadataProvider)
7 {
8 _metadataProvider = metadataProvider;
9 }
10
11 public async Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
12 {
13 QueryConditionCollection model = (QueryConditionCollection)(bindingContext.Model ?? new QueryConditionCollection());
14
15 IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, StringValues>> collection = GetRequestParameter(bindingContext);
16
17 List<string> prefixList = Enum.GetNames(typeof(QueryConditionType)).Select(s => s + SplitString).ToList();
18
19 foreach (KeyValuePair<string, StringValues> kvp in collection)
20 {
21 string key = kvp.Key;
22 if (key != null && key.Contains(SplitString) && prefixList.Any(s => key.StartsWith(s, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase)))
23 {
24 string value = kvp.Value.ToString();
25 if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value))
26 {
27 AddQueryItem(model, key, value);
28 }
29 }
30 }
31
32 bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(model);
33
34 //todo: 是否需要加上這一句?
35 await Task.FromResult(0);
36 }
37
38 private void AddQueryItem(QueryConditionCollection model, string key, string value)
39 {
40 int pos = key.IndexOf(SplitString);
41 string opStr = key.Substring(0, pos);
42 string dataField = key.Substring(pos + 2);
43
44 QueryConditionType operatorEnum = QueryConditionType.Eq;
45 if (Enum.TryParse<QueryConditionType>(opStr, true, out operatorEnum))
46 model.Add(new QueryConditionItem
47 {
48 Key = key,
49 Name = dataField,
50 Op = operatorEnum,
51 DataValue = value
52 });
53 }
54 }
主要流程是,從當前上下文中獲取請求參數(Querystring、Form等),對於每個符合格式要求的請求參數生成QueryConditionItem並加入到QueryConditionCollection中。
為了將ModelBinder應用到系統中,我們還得增加相關的IModelBinderProvider。這個接口的主要作用是提供相應的ModelBinder對象。為了能夠應用QueryConditionModelBinder,我們必須還要再寫一個QueryConditionModelBinderProvider,繼承IModelBinderProvider接口。
1 public class QueryConditionModelBinderPrivdier : IModelBinderProvider
2 {
3 public IModelBinder GetBinder(ModelBinderProviderContext context)
4 {
5 if (context == null)
6 {
7 throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context));
8 }
9
10 if (context.Metadata.ModelType != typeof(QueryConditionCollection))
11 {
12 return null;
13 }
14
15 return new QueryConditionModelBinder(context.MetadataProvider);
16 }
17 }
下面就是是在Startup中注冊ModelBinder。
services.AddMvc(options =>
{
options.ModelBinderProviders.Insert(0, new QueryConditionModelBinderPrivdier());
});
3、將查詢類轉換為EF的查詢Linq表達式。
我們的做法是在QueryConditionCollection類中編寫方法GetExpression。這個只能貼代碼了,裡面有相關的注釋,大家可以仔細分析下程序。
1 public Expression<Func<T, bool>> GetExpression<T>()
2 {
3 if (this.Count() == 0)
4 {
5 return c => true;
6 }
7
8 //構建 c=>Body中的c
9 ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "c");
10
11 //獲取最小的判斷表達式
12 var list = Items.Select(item => GetExpression<T>(param, item));
13 //再以邏輯運算符相連
14 var body = list.Aggregate(Expression.AndAlso);
15
16 //將二者拼為c=>Body
17 return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(body, param);
18 }
19
20 private Expression GetExpression<T>(ParameterExpression param, QueryConditionItem item)
21 {
22 //屬性表達式
23 LambdaExpression exp = GetPropertyLambdaExpression<T>(item, param);
24
25 //常量表達式
26 var constant = ChangeTypeToExpression(item, exp.Body.Type);
27
28 //以判斷符或方法連接
29 return ExpressionDict[item.Op](exp.Body, constant);
30 }
31
32 private LambdaExpression GetPropertyLambdaExpression<T>(QueryConditionItem item, ParameterExpression param)
33 {
34 //獲取每級屬性如c.Users.Proiles.UserId
35 var props = item.Name.Split('.');
36
37 Expression propertyAccess = param;
38
39 Type typeOfProp = typeof(T);
40
41 int i = 0;
42 do
43 {
44 PropertyInfo property = typeOfProp.GetProperty(props[i]);
45 if (property == null) return null;
46 typeOfProp = property.PropertyType;
47 propertyAccess = Expression.MakeMemberAccess(propertyAccess, property);
48 i++;
49 } while (i < props.Length);
50
51 return Expression.Lambda(propertyAccess, param);
52 }
53
54 #region ChangeType
55 /// <summary>
56 /// 轉換SearchItem中的Value的類型,為表達式樹
57 /// </summary>
58 /// <param name="item"></param>
59 /// <param name="conversionType">目標類型</param>
60 private Expression ChangeTypeToExpression(QueryConditionItem item, Type conversionType)
61 {
62 if (item.DataValue == null)
63 return Expression.Constant(item.DataValue, conversionType);
64
65 #region 數組
66 if (item.Op == QueryConditionType.In)
67 {
68 var arr = (item.DataValue as Array);
69 var expList = new List<Expression>();
70 //確保可用
71 if (arr != null)
72 for (var i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
73 {
74 //構造數組的單元Constant
75 var newValue = arr.GetValue(i);
76 expList.Add(Expression.Constant(newValue, conversionType));
77 }
78
79 //構造inType類型的數組表達式樹,並為數組賦初值
80 return Expression.NewArrayInit(conversionType, expList);
81 }
82 #endregion
83
84 var value = conversionType.GetTypeInfo().IsEnum ? Enum.Parse(conversionType, (string)item.DataValue)
85 : Convert.ChangeType(item.DataValue, conversionType);
86
87 return Expression.Constant(value, conversionType);
88 }
89 #endregion
90
91 #region SearchMethod 操作方法
92 private readonly Dictionary<QueryConditionType, Func<Expression, Expression, Expression>> ExpressionDict =
93 new Dictionary<QueryConditionType, Func<Expression, Expression, Expression>>
94 {
95 {
96 QueryConditionType.Eq,
97 (left, right) => { return Expression.Equal(left, right); }
98 },
99 {
100 QueryConditionType.Gt,
101 (left, right) => { return Expression.GreaterThan(left, right); }
102 },
103 {
104 QueryConditionType.Gte,
105 (left, right) => { return Expression.GreaterThanOrEqual(left, right); }
106 },
107 {
108 QueryConditionType.Lt,
109 (left, right) => { return Expression.LessThan(left, right); }
110 },
111 {
112 QueryConditionType.Lte,
113 (left, right) => { return Expression.LessThanOrEqual(left, right); }
114 },
115 {
116 QueryConditionType.Contains,
117 (left, right) =>
118 {
119 if (left.Type != typeof (string)) return null;
120 return Expression.Call(left, typeof (string).GetMethod("Contains"), right);
121 }
122 },
123 {
124 QueryConditionType.In,
125 (left, right) =>
126 {
127 if (!right.Type.IsArray) return null;
128 //調用Enumerable.Contains擴展方法
129 MethodCallExpression resultExp =
130 Expression.Call(
131 typeof (Enumerable),
132 "Contains",
133 new[] {left.Type},
134 right,
135 left);
136
137 return resultExp;
138 }
139 },
140 {
141 QueryConditionType.Neq,
142 (left, right) => { return Expression.NotEqual(left, right); }
143 },
144 {
145 QueryConditionType.StartWith,
146 (left, right) =>
147 {
148 if (left.Type != typeof (string)) return null;
149 return Expression.Call(left, typeof (string).GetMethod("StartsWith", new[] {typeof (string)}), right);
150
151 }
152 },
153 {
154 QueryConditionType.EndWith,
155 (left, right) =>
156 {
157 if (left.Type != typeof (string)) return null;
158 return Expression.Call(left, typeof (string).GetMethod("EndsWith", new[] {typeof (string)}), right);
159 }
160 }
161 };
162 #endregion
4、提交數據庫執行並反饋結果
在生成了表達式後,剩下的就比較簡單了。倉儲層直接寫如下的語句即可:
var query = this.dbContext.OperLogs.AsNoTracking().Where(predicate).OrderByDescending(o => o.CreateDate).ThenBy(o => o.OperLogId);
predicate就是從QueryConditionCollection.GetExpression方法中生成的,類似
Expression<Func<OperLogInfo, bool>> predicate = conditionCollection.GetExpression<OperLogInfo>();
QueryConditionCollection從哪裡來呢?因為有了ModelBinder,Controller的Action上直接加上參數,類似
public async Task<IActionResult> List(QueryConditionCollection queryCondition) { ... }
至此,自動生成的組合查詢就基本完成了。之後我們程序的寫法,只需要在前端頁面定義查詢條件的控件,Controller的Action中加上QueryConditionCollection參數,然後調用數據庫前將QueryConditionCollection轉換為表達式就OK了。不再像以往一樣在cshtml、Controller中寫一大堆的程序代碼了,在條件多、甚至有可選條件時,優勢更為明顯。
面向雲的.net core開發框架