Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85836329
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85836329
Use the given board.py, Use Monte Carlo tree search algorithm to complete black and white chess AI.
AI Functions to be completed :
In the current chessboard state , Choose a legal and algorithmically optimal placement , As return value
The search and decision-making time shall not exceed one minute , If there is no legal location, return None
At the end of the game ( That is, both parties have no legal settlement position ) when , Try to maximize the difference in the number of chess pieces between your side and your opponent
design idea
While (time_is_enough):
For (node = root; all son_node.visited in node.sons; node =
choson_son)
Choson_son = the son with max UCB of node
# Selection, From the root down , Select a node whose son has not been fully accessed
Expand_Candidate = x if ((x in node.sons) and (not x.visited))
Node_to_expand = random.choice(Expand_Candidate)
# Expansion, Randomly select a child node that has not been visited
Leaf = node
For (node = Node_to_sxpand; node has son; node =
random.choice(node.sons))
Leaf = node
# Simulation, Randomly select the child node until the leaf node
For (node = Leaf; node != root; node = node.father)
Update(node)
# Back Propagation, Update the visited information and the results / Reward score information
During search , every time “ sampling ” There are four steps : choice , Expand , Simulation and back propagation :
But according to UCB Of score Function composition , In fact, we can find out k If it's just the coefficient of multiplication , It's essentially C, But add one k It can be easily adjusted and more intuitive .
Finally, the number of searches can have an impact on the search results , Given the time limit of one minute , Although used in testing 25s The effect of sampling time is good , But when submitting, it should still be against the time limit ( laugh )
Code content
================================================================
//UCB1:
def UCB1(self, color, board_in):
""" :param color: The color corresponding to the current node :param board_in: Current chessboard status :return : According to the sampling results , Yes AI Fang's most favorable position """
board = deepcopy(board_in)
score_act = None
act = None
action_list = list(board.get_legal_actions(color))
rec_sum = 0 # Record the total score of this node ( Used to calculate select Child nodes of )
for action in action_list:
play_board = deepcopy(board)
play_board._move(action, color)
tmp_key = tuple(np.ravel(play_board._board))
# Calculate the action Of the corresponding chessboard key value
if self.rec.get((color, tmp_key)):
# Once visited, the total score will continue to be calculated
rec_sum += self.rec.get((color, tmp_key))
for action in action_list:
play_board = deepcopy(board)
play_board._move(action, color)
tmp_key = tuple(np.ravel(play_board._board))
score_tmp = (self.scr.get((color, tmp_key)) / self.rec.get((color,
tmp_key)) +
self.C * math.sqrt(
math.log(rec_sum) / self.rec.get((color, tmp_key))
))
# Calculate the key value And integral
if score_act == None:
score_act, act = (score_tmp, action)
else:
if score_act < score_tmp:
score_act, act = (score_tmp, action)
# Update the child node with the highest score
return act
====================================================================
// choice :
def Select(self, board):
""" :param board: Enter the chessboard to be searched :return: color yes select The color of the chess pieces that have been settled at the last node , act It's the last one The position of the fall , tmpkey Is the state of the chessboard """
color = self.color
while(True):
# always select Until a node is not fully extended
action_list = list(board.get_legal_actions(color))
if len(action_list) == 0:
return None, None, None
all_explored = True # Whether all the child nodes of this node have visited
non_vis_son = [] # Record the child nodes that have not been visited
rec_sum = 0 # Record the total score of this node ( Used to calculate select Child nodes of )
for action in action_list:
play_board = deepcopy(board)
play_board._move(action, color)
tmp_key = tuple(np.ravel(play_board._board))
# Calculate the action Of the corresponding chessboard key value
if not self.rec.get((color, tmp_key)):
# If you haven't visited, you will record This child node And update the information not accessed by the node
all_explored = False
non_vis_son.append((action, tmp_key))
else:
# Once visited, the total score will continue to be calculated
rec_sum += self.rec.get((color, tmp_key))
if all_explored:
# If you have visited all , Select the son with the highest score in this node
act = self.UCB1(color, board)
else:
# There are unreached nodes , An unreached node is returned randomly , As extend The object of
act, tmp_key = (random.choice(non_vis_son))
board._move(act, color)
return (color, act, tmp_key)
# When you get here, you should select Next node
board._move(act, color)
tmp_key = tuple(np.ravel(board._board))
# Move later , Update new chessboard's key value
self.vis.add((color, tmp_key))
# Record the node information on the path
color = "X" if color == "O" else "O"
# Toggle color
====================================================================
// Expand :
def Expand(self, board, color, act, tmpkey):
""" :param board: The current chessboard to be expanded :param color: The color of the chess pieces that have been settled :param act: The current position of the finished product :param tmpkey: Current chessboard status :return: Returns the difference obtained by multiplying the coefficient """
game_state, scr_diff = self.Simulate(board, color)
self.rec[(color, tmpkey)] = 1
# Record the number of visits under this node +1
if (game_state == 0 and self.color == "O") or (game_state == 1 and
self.color == "X"):
scr_diff = - scr_diff
# hold scr_diff Change to (AI- other party ) The difference between , You can have a negative
scr_diff *= 0.4
# Add a coefficient
if color == self.color:
# If the color of the current decision node is AI The color of the , Then add the difference , Otherwise, subtract the difference
self.scr[(color, tmpkey)] = scr_diff
else:
self.scr[(color, tmpkey)] = - scr_diff
return scr_diff
====================================================================
// simulation :
def Simulate(self, board, player):
""" Use random to simulate the process of playing chess :param board: Current chessboard status :param player: Currently, the player who has just completed the settlement :return: (winner, Fractional difference ), among winner yes 0 Black chess , 1 White chess , 2 It ends in a draw """
while(True):
player = "X" if player == "O" else "O"
# Switch the chess player
legal_actions = list(board.get_legal_actions(player))
if len(legal_actions) == 0:
if self.game_over(board):
return board.get_winner()
# 0 Black chess , 1 White chess , 2 It ends in a draw
# Then there is a parameter of fractional difference
break
else:
continue
if len(legal_actions) == 0:
action = None
else:
action = random.choice(legal_actions)
# Use random drop to simulate
if action is None:
continue
else:
board._move(action, player)
if self.game_over(board):
return board.get_winner()
====================================================================
//Back Propagation:
def BackPropagate(self, scr_diff):
""" :param scr_diff: Multiplied by the coefficient AI The score difference with the opponent """
for (color, key) in self.vis:
self.rec[(color, key)] += 1
if color == self.color:
# If the color of the current decision node is AI The color of the , Then add the difference , Otherwise, subtract the difference
self.scr[(color, key)] += scr_diff
else:
self.scr[(color, key)] -= scr_diff
====================================================================
//UCTS Major part :
def MCTS_choice(self, board_input):
""" :param board_input: Enter the current chessboard :return: Return the coordinates of the drop The status node of the tree is represented by rec and scr Two dict To store , Saved ( The current settlement is , Chessboard status ): ( Number of visits , Total score ) The state of """
starttime = datetime.datetime.now()
count = 0
while True:
count += 1
currenttime = datetime.datetime.now()
if (currenttime - starttime).seconds > 3 or count > 1000:
break
board = deepcopy(board_input)
color = "X" if self.color == "O" else "O"
# color It's the other person's color
self.vis = set()
# Record the path searched in the tree , Easy to update
color, act, tmpkey = self.Select(board)
# color yes select The color of the chess pieces that have been settled at the last node
# act It's the position of the last one
# tmpkey Is the state of the chessboard
if color == None:
# If there is no place to live , Go to the next round of trying
continue
scr_diff = self.Expand(board, color, act, tmpkey)
# Expand Get the score of the current extension node , And for bp
self.BackPropagate(scr_diff)
print(count)
return self.UCB1(self.color, board_input)



Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85836329
Resource download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/sheziqiong/85836329
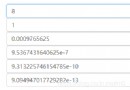 The essential difference between float32 and float64 (the influence of type on deep learning and the use of Python)
The essential difference between float32 and float64 (the influence of type on deep learning and the use of Python)
First, we need to know what is
 Python Matplotlib data visualization case - generate histogram, pie chart (sector chart) and word cloud.
Python Matplotlib data visualization case - generate histogram, pie chart (sector chart) and word cloud.
at present python,spark,scala