Usually voc Dataset or coco Data sets label The category can meet most of the target detection requirements , But when it comes to business in a specific scenario , You need to customize your own dataset , The model at this time , You can't directly use the model trained above
At this time, the model needs to be transferred for learning , There are usually two methods of transfer learning :
The difference between the two is whether to freeze the weight of the outer layer of the whole layer .
The above method is the first one here
The model of target detection has been obtained above onnx, Next, you need to test the model , Deploy and forecast to verify whether the model can be used
Use ONNXRuntime The model can be loaded normally during testing
import os
import onnxruntime
def load_onnx(model_dir):
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir)
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path)
input_names = [input.name for input in session.get_inputs()]
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
return session, input_names, output_names
session, input_names, output_names = load_onnx('model.onnx')
print(input_names, output_names)

Model deployment , Is to put our model , Make one Detector object , It is convenient to call the following object detection
Before deployment, you need to
PaddleDetection/output_inference/yolov3_mobilenet_v3_large_270e_voc/infer_cfg.yml, Put it in save onnx The model is in the same folder
hold onnx Change the model name to inference.onnx

structure onnx Detection reasoner , The folder is as follows 
establish onnx_detection detector detection.py
import os
import yaml
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
from functools import reduce
from .preprocess import preprocess, Resize, Normalize, Permute, PadStride
# Global dictionary
SUPPORT_MODELS = {
'YOLO', 'SSD', 'RetinaNet', 'EfficientDet', 'RCNN', 'TTF', 'FCOS'
}
class Detector(object):
""" Args: config (object): config of model, defined by `Config(model_dir)` model_dir (str): root path of __model__, __params__ and infer_cfg.yml use_gpu (bool): whether use gpu run_mode (str): mode of running(fluid/trt_fp32/trt_fp16) threshold (float): threshold to reserve the result for output. """
def __init__(self, config, model_dir):
self.config = config
self.session, self.input_names, self.output_names = load_onnx(
model_dir)
def preprocess(self, im):
preprocess_ops = []
for op_info in self.config.preprocess_infos:
new_op_info = op_info.copy()
op_type = new_op_info.pop('type')
if op_type == 'Resize':
new_op_info['arch'] = self.config.arch
preprocess_ops.append(eval(op_type)(**new_op_info))
im, im_info = preprocess(im, preprocess_ops)
inputs = create_inputs(im, im_info, self.config.arch)
return inputs, im_info
def postprocess(self, np_boxes, im_info, threshold=0.5):
if self.config.arch in ['SSD']:
w, h = im_info['origin_shape']
np_boxes[:, 2] *= h
np_boxes[:, 3] *= w
np_boxes[:, 4] *= h
np_boxes[:, 5] *= w
expect_boxes = (np_boxes[:, 1] > threshold) & (np_boxes[:, 0] > -1)
np_boxes = np_boxes[expect_boxes, :]
return np_boxes
def predict(self, image, threshold=0.5):
''' Args: image (str/np.ndarray): path of image/ np.ndarray read by cv2 threshold (float): threshold of predicted box' score Returns: results (dict): include 'boxes': np.ndarray: shape:[N,6], N: number of box, matix element:[class, score, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max] MaskRCNN's results include 'masks': np.ndarray: shape:[N, class_num, mask_resolution, mask_resolution] '''
inputs, im_info = self.preprocess(image)
np_boxes = self.session.run(self.output_names, inputs)[0]
results = []
if reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, np_boxes.shape) >= 6:
for result in self.postprocess(np_boxes,
im_info,
threshold=threshold):
results.append([int(result[0]), result[1]] +
[int(_) for _ in result[2:]])
return results
def create_inputs(im, im_info, model_arch='YOLO'):
"""generate input for different model type Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of image model_arch (str): model type Returns: inputs (dict): input of model """
inputs = {
}
inputs['image'] = im
origin_shape = list(im_info['origin_shape'])
pad_shape = list(
im_info['pad_shape']) if im_info['pad_shape'] is not None else list(
im_info['resize_shape'])
scale_x, scale_y = im_info['scale']
if 'YOLO' in model_arch:
im_size = np.array([origin_shape]).astype('int32')
inputs['im_size'] = im_size
elif 'RetinaNet' in model_arch or 'EfficientDet' in model_arch:
scale = scale_x
im_info = np.array([pad_shape + [scale]]).astype('float32')
inputs['im_info'] = im_info
elif ('RCNN' in model_arch) or ('FCOS' in model_arch):
scale = scale_x
im_info = np.array([pad_shape + [scale]]).astype('float32')
im_shape = np.array([origin_shape + [1.]]).astype('float32')
inputs['im_info'] = im_info
inputs['im_shape'] = im_shape
elif 'TTF' in model_arch:
scale_factor = np.array([scale_x, scale_y] * 2).astype('float32')
inputs['scale_factor'] = scale_factor
return inputs
class Det_Config():
"""set config of preprocess, postprocess and visualize Args: model_dir (str): root path of model.yml """
def __init__(self, model_dir):
# parsing Yaml config for Preprocess
deploy_file = os.path.join(model_dir, 'infer_cfg.yml')
with open(deploy_file) as f:
yml_conf = yaml.safe_load(f)
self.check_model(yml_conf)
self.arch = yml_conf['arch']
self.preprocess_infos = yml_conf['Preprocess']
self.min_subgraph_size = yml_conf['min_subgraph_size']
self.labels = yml_conf['label_list']
self.print_config()
def check_model(self, yml_conf):
""" Raises: ValueError: loaded model not in supported model type """
for support_model in SUPPORT_MODELS:
if support_model in yml_conf['arch']:
return True
raise ValueError("Unsupported arch: {}, expect {}".format(
yml_conf['arch'], SUPPORT_MODELS))
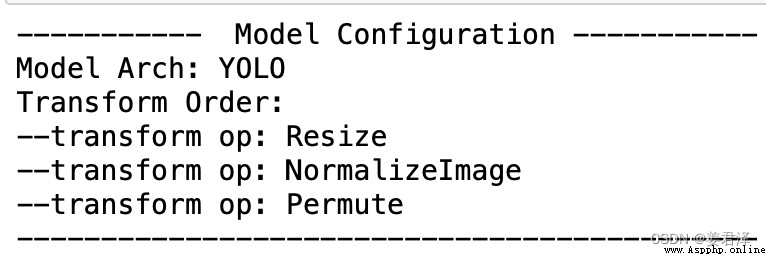
def print_config(self):
print('----------- Model Configuration -----------')
print('%s: %s' % ('Model Arch', self.arch))
print('%s: ' % ('Transform Order'))
for op_info in self.preprocess_infos:
print('--%s: %s' % ('transform op', op_info['type']))
print('--------------------------------------------')
def load_onnx(model_dir):
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'inference.onnx')
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path)
input_names = [input.name for input in session.get_inputs()]
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
return session, input_names, output_names
establish onnx_detection Reasoner preprocess.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
# Global dictionary
RESIZE_SCALE_SET = {
'RCNN',
'RetinaNet',
'FCOS',
'SOLOv2',
}
def decode_image(im_file, im_info):
"""read rgb image Args: im_file (str/np.ndarray): path of image/ np.ndarray read by cv2 im_info (dict): info of image Returns: im (np.ndarray): processed image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of processed image """
if isinstance(im_file, str):
with open(im_file, 'rb') as f:
im_read = f.read()
data = np.frombuffer(im_read, dtype='uint8')
im = cv2.imdecode(data, 1) # BGR mode, but need RGB mode
im = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
im_info['origin_shape'] = im.shape[:2]
im_info['resize_shape'] = im.shape[:2]
else:
# im = cv2.cvtColor(im_file, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
im = im_file
im_info['origin_shape'] = im.shape[:2]
im_info['resize_shape'] = im.shape[:2]
return im, im_info
class Resize(object):
"""resize image by target_size and max_size Args: arch (str): model type target_size (int): the target size of image max_size (int): the max size of image use_cv2 (bool): whether us cv2 image_shape (list): input shape of model interp (int): method of resize """
def __init__(self,
arch,
target_size,
max_size,
use_cv2=True,
image_shape=None,
interp=cv2.INTER_LINEAR):
self.target_size = target_size
self.max_size = max_size
self.image_shape = image_shape
self.arch = arch
self.use_cv2 = use_cv2
self.interp = interp
def __call__(self, im, im_info):
""" Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of image Returns: im (np.ndarray): processed image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of processed image """
im_channel = im.shape[2]
im_scale_x, im_scale_y = self.generate_scale(im)
im_info['resize_shape'] = [
im_scale_x * float(im.shape[0]), im_scale_y * float(im.shape[1])
]
if self.use_cv2:
im = cv2.resize(im,
None,
None,
fx=im_scale_x,
fy=im_scale_y,
interpolation=self.interp)
else:
resize_w = int(im_scale_x * float(im.shape[1]))
resize_h = int(im_scale_y * float(im.shape[0]))
if self.max_size != 0:
raise TypeError(
'If you set max_size to cap the maximum size of image,'
'please set use_cv2 to True to resize the image.')
im = im.astype('uint8')
im = Image.fromarray(im)
im = im.resize((int(resize_w), int(resize_h)), self.interp)
im = np.array(im)
# padding im when image_shape fixed by infer_cfg.yml
if self.max_size != 0 and self.image_shape is not None:
padding_im = np.zeros((self.max_size, self.max_size, im_channel),
dtype=np.float32)
im_h, im_w = im.shape[:2]
padding_im[:im_h, :im_w, :] = im
im = padding_im
im_info['scale'] = [im_scale_x, im_scale_y]
return im, im_info
def generate_scale(self, im):
""" Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) Returns: im_scale_x: the resize ratio of X im_scale_y: the resize ratio of Y """
origin_shape = im.shape[:2]
im_c = im.shape[2]
if self.max_size != 0 and self.arch in RESIZE_SCALE_SET:
im_size_min = np.min(origin_shape[0:2])
im_size_max = np.max(origin_shape[0:2])
im_scale = float(self.target_size) / float(im_size_min)
if np.round(im_scale * im_size_max) > self.max_size:
im_scale = float(self.max_size) / float(im_size_max)
im_scale_x = im_scale
im_scale_y = im_scale
else:
im_scale_x = float(self.target_size) / float(origin_shape[1])
im_scale_y = float(self.target_size) / float(origin_shape[0])
return im_scale_x, im_scale_y
class Normalize(object):
"""normalize image Args: mean (list): im - mean std (list): im / std is_scale (bool): whether need im / 255 is_channel_first (bool): if True: image shape is CHW, else: HWC """
def __init__(self, mean, std, is_scale=True, is_channel_first=False):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
self.is_scale = is_scale
self.is_channel_first = is_channel_first
def __call__(self, im, im_info):
""" Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of image Returns: im (np.ndarray): processed image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of processed image """
im = im.astype(np.float32, copy=False)
if self.is_channel_first:
mean = np.array(self.mean)[:, np.newaxis, np.newaxis]
std = np.array(self.std)[:, np.newaxis, np.newaxis]
else:
mean = np.array(self.mean)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
std = np.array(self.std)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
if self.is_scale:
im = im / 255.0
im -= mean
im /= std
return im, im_info
class Permute(object):
"""permute image Args: to_bgr (bool): whether convert RGB to BGR channel_first (bool): whether convert HWC to CHW """
def __init__(self, to_bgr=False, channel_first=True):
self.to_bgr = to_bgr
self.channel_first = channel_first
def __call__(self, im, im_info):
""" Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of image Returns: im (np.ndarray): processed image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of processed image """
if self.channel_first:
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy()
if self.to_bgr:
im = im[[2, 1, 0], :, :]
return im, im_info
class PadStride(object):
""" padding image for model with FPN Args: stride (bool): model with FPN need image shape % stride == 0 """
def __init__(self, stride=0):
self.coarsest_stride = stride
def __call__(self, im, im_info):
""" Args: im (np.ndarray): image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of image Returns: im (np.ndarray): processed image (np.ndarray) im_info (dict): info of processed image """
coarsest_stride = self.coarsest_stride
if coarsest_stride == 0:
return im
im_c, im_h, im_w = im.shape
pad_h = int(np.ceil(float(im_h) / coarsest_stride) * coarsest_stride)
pad_w = int(np.ceil(float(im_w) / coarsest_stride) * coarsest_stride)
padding_im = np.zeros((im_c, pad_h, pad_w), dtype=np.float32)
padding_im[:, :im_h, :im_w] = im
im_info['pad_shape'] = padding_im.shape[1:]
return padding_im, im_info
def preprocess(im, preprocess_ops):
# process image by preprocess_ops
im_info = {
'scale': [1., 1.],
'origin_shape': None,
'resize_shape': None,
'pad_shape': None,
}
im, im_info = decode_image(im, im_info)
for operator in preprocess_ops:
im, im_info = operator(im, im_info)
im = np.array((im, )).astype('float32')
return im, im_info
init.py
from .detection import Det_Config
from .detection import Detector
Import detector and reasoner deployment generation onnx Test object
from onnx_detection import Det_Config, Detector
model_dir = 'paddle2onnx/onnx-model'
det_config = Det_Config(model_dir)
detector = Detector(det_config, model_dir)
import cv2
img_path = 'PaddleDetection/dataset/voc/JPEGImages/001.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img =cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results = detector.predict(img,threshold=0.5)
def draw_results(results, img):
for result in results:
class_id, scores, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = result
cv2.rectangle(img, (x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max), (255, 255, 255))
draw_results(results, img)
cv2.imwrite('save.jpg', img)
from IPython.display import display, Image
display(Image('save.jpg', format='jpg'))
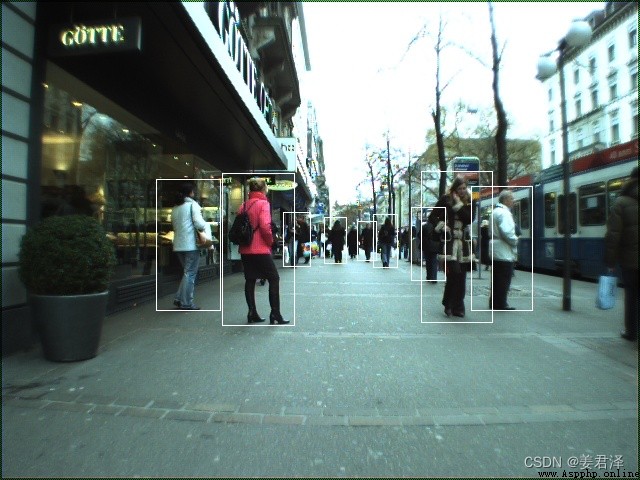

So far we have obtained the target detector , And know the result of the test output
[class_id, scores, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max]
Create a detector class
import cv2
import numpy as np
class ObjectionDetection:
def __init__(self,detector,threshold):
self.detector=detector
self.threshold=threshold
self.classes=[]
def load_class_names(self,class_path='label.txx')
with open(class_path,'r') as f:
class_name=f.strip()
self.classes.append(class_name)
self.colors=np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(80, 3))
return self.classes
def detect(self,img):
return self.detector.predict(img,self.threshold)
detector It is the one deployed above detector
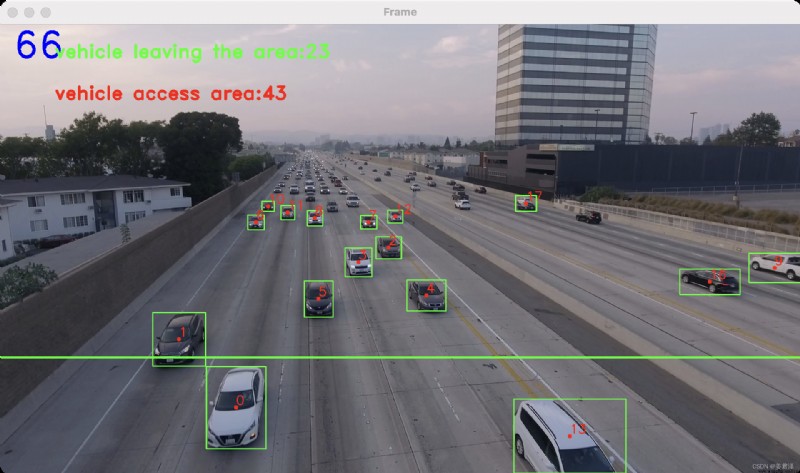
The core purpose of target tracking , Judge the object detected in each frame , Objects detected in front and back frames , Whether it is the same object .
This criterion is based on two frames , It is judged by the detected rectangular box spacing distance ,
Through a dictionary data {}, To save the object's id, And the center point of the object .
Take vehicle detection as an example , When the vehicle enters this detection range , According to the time sequence when the vehicle enters the detection range , A unique object has been assigned to each vehicle id, And the current center point position data , As below
tracking_objects[object_id]=pt
As each frame is updated , Get a new central location pt2, Judge the size by the center position of the front and back frames , Here is an analogy , If the difference between the two centers is less than 20, It is considered that the objects detected in the previous frame are the same as those detected in the next frame . The center position of the previous frame pt2 Iterative assignment
tracking_objects[object_id]=pt2
Create trackers object_tracking.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
from object_detection import ObjectDetection
import math
# Add a line to the video , Judge the driving condition of the vehicle through the collision between the rectangular box and the straight line
line = [(0, 800), (1920, 800)]
# The total number of vehicles
counter = 0
# Vehicle data for the forward lane
counter_up = 0
# Vehicle data for the reverse lane
counter_down = 0
# Line to line collision detection : Cross product method to judge whether two lines intersect
# Calculate the cross product symbol
def ccw(A, B, C):
return (C[1] - A[1]) * (B[0] - A[0]) > (B[1] - A[1]) * (C[0] - A[0])
# testing AB and CD Whether the two lines intersect
def intersect(A, B, C, D):
return ccw(A, C, D) != ccw(B, C, D) and ccw(A, B, C) != ccw(A, B, D)
# Initialize Object Detection
od = ObjectDetection()
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("los_angeles.mp4")
# Initialize count
count = 0
center_points_prev_frame = []
tracking_objects = {
}
track_id = 0
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
count += 1
if not ret:
break
# Point current frame
center_points_cur_frame = []
# Detect objects on frame
(class_ids, scores, boxes) = od.detect.predict(frame,threshold0.5)
for box in boxes:
(x, y, w, h) = box
cx = int((x + x + w) / 2)
cy = int((y + y + h) / 2)
center_points_cur_frame.append((cx, cy))
#print("FRAME N°", count, " ", x, y, w, h)
# cv2.circle(frame, (cx, cy), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Only at the beginning we compare previous and current frame
if count <= 2:
for pt in center_points_cur_frame:
for pt2 in center_points_prev_frame:
distance = math.hypot(pt2[0] - pt[0], pt2[1] - pt[1])
if distance < 20:
tracking_objects[track_id] = pt
track_id += 1
else:
tracking_objects_copy = tracking_objects.copy()
center_points_cur_frame_copy = center_points_cur_frame.copy()
for object_id, pt2 in tracking_objects_copy.items():
object_exists = False
for pt in center_points_cur_frame_copy:
distance = math.hypot(pt2[0] - pt[0], pt2[1] - pt[1])
# Update IDs position
if distance < 20:
tracking_objects[object_id] = pt
object_exists = True
if pt in center_points_cur_frame:
center_points_cur_frame.remove(pt)
continue
# Remove IDs lost
if not object_exists:
tracking_objects.pop(object_id)
# Add new IDs found
for pt in center_points_cur_frame:
tracking_objects[track_id] = pt
track_id += 1
for object_id, pt in tracking_objects.items():
cv2.circle(frame, pt, 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.putText(frame, str(object_id), (pt[0], pt[1] - 7), 0, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
for pt in center_points_cur_frame:
for pt2 in center_points_prev_frame:
i = int(0)
if intersect(pt, pt2, line[0], line[1]):
counter += 1
# Determine the direction of travel
if pt2[1] > pt[0]:
counter_down += 1
else:
counter_up += 1
i += 1
print("Tracking objects")
print(tracking_objects)
print("CUR FRAME LEFT PTS")
print(center_points_cur_frame)
text_counter_up = 'vehicle leaving the area:%s' % (counter_down)
text_counter_down = 'vehicle access area:%s' % (counter_up)
cv2.line(frame, line[0], line[1], (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(frame, str(counter), (30, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 3.0, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(frame, text_counter_up, (130, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1.5, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(frame, text_counter_down, (130, 180), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 255), 3)
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
# Make a copy of the points
center_points_prev_frame = center_points_cur_frame.copy()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()