Harris: https://blog.csdn.net/Keep_Trying_Go/article/details/125384144
Shi-Tomasi:https://blog.csdn.net/Keep_Trying_Go/article/details/125384218
reflection : Given the Harris Corner detection , Why SIFT Key point detection ?
(1)Harris The corner has the property of rotation invariance ; But after zooming , The original corner may not necessarily be a corner ;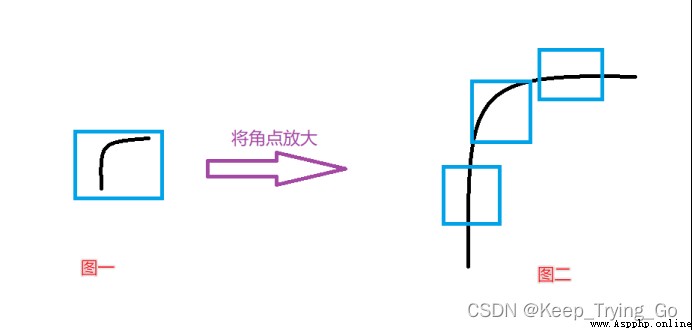
You can see that when the corners of the first picture are enlarged , It becomes the second picture , But when we go to the test again, we can't detect any corners , It's the edge . So I put forward SIFT.
among gray—— original image , Three channel or single channel images can be made ;KP—— Key points ;img—— Draw points onto the original image ;color—— Color information of the drawn feature points , The default drawing is random color ;
Flags——
(1)cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DEFAULT: Create output image matrix , Draw matching pairs and feature points using existing output images , Draw only the middle point for each key
(2)cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_OVER_OUTIMG: Do not create output image matrix , Instead, draw matching pairs on the output image
(3)cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS: Draw a key point graph with size and direction for each feature point
(4)cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS: The feature points of a single point are not drawn
import os
import cv2
import cv2
img=cv2.imread('images/HaLiSi.jpg')
img=cv2.resize(src=img,dsize=(450,450))
gray=cv2.cvtColor(src=img,code=cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#SIFT objects creating
sift=cv2.SIFT_create()
# To test , The second parameter is None, Indicates to test the whole picture
kp=sift.detect(gray,None)
# Draw corners
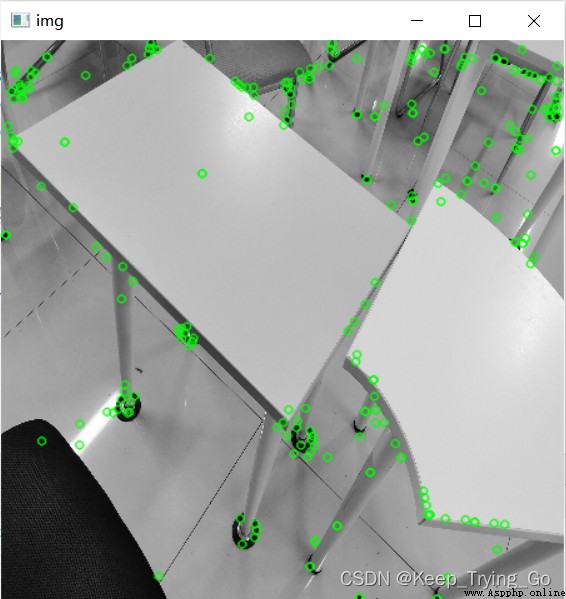
cv2.drawKeypoints(image=gray,keypoints=kp,outImage=img,color=(0,255,0))
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('pycharm')
(1) Key points : Location , Size and direction ;
Calculation SIFT Narrator :
(2) A set of vector values of the pixels around the key that contribute to it are recorded , It is not subject to affine transformation , The influence of light transformation, etc .
Key match :
# Mode one : Feature matching
kp,des=sift.compute(img,kp)
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
img=cv2.imread('images/HaLiSi.jpg')
img=cv2.resize(src=img,dsize=(450,450))
gray=cv2.cvtColor(src=img,code=cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#SIFT objects creating
sift=cv2.SIFT_create()
# To test , The second parameter is None, Indicates to test the whole picture
kp=sift.detect(gray,None)
# Feature matching
kp,des=sift.compute(gray,kp)
print(des)
# kp,des=sift.detectAndCompute(gray)
# Draw corners
cv2.drawKeypoints(image=gray,keypoints=kp,outImage=img,color=(0,255,0))
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('Pycharm')
At the same time, key point detection and feature matching
Kp,des=sift.detectAndCompute(img,None)
Img: Input image ( grayscale );
Mask: Appoint img Which area in the .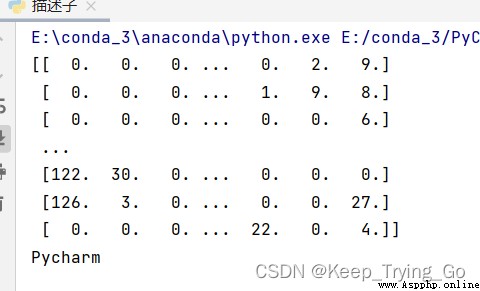
 Time points are classified into different intervals (time periods), and the occurrence times of each time period are counted, Python
Time points are classified into different intervals (time periods), and the occurrence times of each time period are counted, Python
Time points are classified int
 Software use case in micropython kernel development notebook: print based program debugging
Software use case in micropython kernel development notebook: print based program debugging
Jane Medium : This paper gives