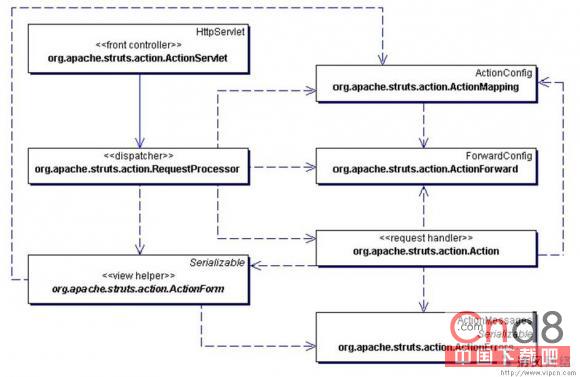
下圖是Struts的工作流程,前邊我們提到,所有的請求都提交給ActionServlet來處理。
 點擊查看大圖
點擊查看大圖 ActionServlet是一個FrontController,它是一個標准的Servlet,它將request轉發給RequestProcessor來處理,
ActionMapping是ActionConfig的子類,實質上是對struts-config.XML的一個映射,從中可以取得所有的配置信息
RequestProcessor根據提交過來的url,如*.do,從ActionMapping 中得到相應的ActionForn和Action。然後將request的參數對應到ActionForm中,進行form驗證。假如驗證通過則調用Action的execute()方法來執行Action,最終返回ActionFoward。
ActionFoward是對mapping中一個foward的包裝,對應於一個url
ActionForm使用了ViewHelper模式,是對Html中form的一個封裝。其中包含有validate方法,用於驗證form數據的有效性。ActionForm是一個符合JavaBean規范的類,所有的屬性都應滿足get和set對應。對於一些復雜的系統,還可以采用DynaActionForm來構造動態的Form,即通過預制參數來生成Form。這樣可以更靈活的擴展程序。
ActionErrors是對錯誤信息的包裝,一旦在執行action或者form.validate中出現異常,即可產生一個ActionError並最終加入到ActionErrors。在Form驗證的過程中,假如有Error發生,則會將頁面重新導向至輸入頁,並提示錯誤。
Action是用於執行業務邏輯的RequsestHandler。每個Action都只建立一個instance。Action不是線程安全的,所以不應該在Action中訪問特定資源。一般來說,應改使用 Business Delegate 模式來對Business tier進行訪問以解除耦合。
Struts提供了多種Action供選擇使用。普通的Action只能通過調用execute執行一項任務,而DispatchAction可以根據配置參數執行,而不是僅進入execute()函數,這樣可以執行多種任務。如insert,update等。LookupDispatchAction可以根據提交表單按鈕的名稱來執行函數。
我們可以先回到剛才的例子,理解一下Struts的流程。
下面我們看Struts自帶的example實例:
說明:實例二是Struts自帶的example程序, 實現了登錄,注冊,修改功能。
代碼中大量應用了struts taglib,並且采用validator插件進行form的驗證。
但是代碼樹立了一個不好的榜樣,即把大量的業務邏輯寫在了action中。
部分代碼如下:
登錄:Logon.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
// 聲明Taglib
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld" prefix="bean" %>
<%@ taglib uri="/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld" prefix="html" %>
<html:html locale="true">
<head>
// bean是用來從ApplicationResource中讀取i18n信息
<title><bean:message key="Logon.title"/></title>
<html:base/>
</head>
<body bgcolor="white">
// 錯誤信息部分
<html:errors/>
// 登錄form,action為logion.do
<html:form action="/Logon" focus="username"
onsubmit="return validateLogonForm(this);">
<table border="0" width="100%">
<tr>
<th align="right">
<bean:message key="prompt.username"/>:
</th>
<td align="left">
<html:text property="username" size="16" maxlength="18"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th align="right">
<bean:message key="prompt.passWord" bundle="alternate"/>:
</th>
<td align="left">
<html:password property="password" size="16" maxlength="18" redisplay="false"/>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">
<html:submit value="Submit"/>
</td>
<td align="left">
<html:reset/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</html:form>
// Validator插件,用於form驗證
<html:javascript formName="LogonForm" dynamicJavascript="true" staticJavascript="false"/>
<script language="Javascript1.1" src="staticJavascript.jsp"></script>
</body>
</html:html>
struts-config.xml配置
<form-beans>
<!-- Logon form bean -->
<form-bean name="LogonForm" type="org.apache.struts.validator.DynaValidatorForm">
<form-property name="username" type="java.lang.String"/>
<form-property name="password" type="java.lang.String"/>
</form-bean>
<!-- Subscription form bean -->
<form-bean name="subscriptionForm"type="org.apache.struts.webapp.example.SubscriptionForm"/>
</form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<!-- Edit mail subscription -->
<action path="/editSubscription"
type="org.apache.struts.webapp.example.EditSubscriptionAction"
attribute="subscriptionForm"
scope="request"
validate="false">
<forward name="failure" path="/mainMenu.jsp"/>
<forward name="sUCcess" path="/subscription.jsp"/>
</action>
...
subscriptionForm 是一個標准的ActionForm,其中reset方法用於清除form的值,validate方法用於驗證
public final class SubscriptionForm extends ActionForm {
// The maintenance action we are performing (Create or Edit).
private String action = "Create";
// Should we auto-connect at startup time?
private boolean autoConnect = false;
// The host name.
private String host = null;
private String password = null;
private String type = null;
private String username = null;
public String getAction() { return (this.action); }
public void setAction(String action) { this.action = action; }
public boolean getAutoConnect() { return (this.autoConnect); }
public void setAutoConnect(boolean autoConnect) { this.autoConnect = autoConnect; }
public String getHost() { return (this.host); }
public void setHost(String host) { this.host = host; }
public String getPassword() { return (this.password); }
public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; }
public String getType() { return (this.type); }
public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; }
public String getUsername() { return (this.username); }
public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; }
/**
* Reset all properties to their default values.
*
* @param mapping The mapping used to select this instance
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
*/
public void reset(ActionMapping mapping, HttpServletRequest request) {
this.action = "Create";
this.autoConnect = false;
this.host = null;
this.password = null;
this.type = null;
this.username = null;
}
/**
* Validate the properties that have been set from this HTTP request,
* and return an <code>ActionErrors</code> object that encapsulates any
* validation errors that have been found. If no errors are found, return
* <code>null</code> or an <code>ActionErrors</code> object with no
* recorded error messages.
*
* @param mapping The mapping used to select this instance
* @param request The servlet request we are processing
*/
public ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping,
HttpServletRequest request) {
ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors();
if ((host == null) (host.length() < 1))
errors.add("host",
new ActionError("error.host.required"));
if ((username == null) (username.length() < 1))
errors.add("username",
new ActionError("error.username.required"));
if ((password == null) (password.length() < 1))
errors.add("password",
new ActionError("error.password.required"));
if ((type == null) (type.length() < 1))
errors.add("type",
new ActionError("error.type.required"));
else if (!"imap".equals(type) && !"pop3".equals(type))
errors.add("type",new ActionError("error.type.invalid", type));
return (errors);
}
}
LogonAction
public final class LogonAction extends Action {
/**
* Process the specified HTTP request, and create the corresponding HTTP
* response (or forward to another web component that will create it).
* Return an <code>ActionForward</code> instance describing where and how
* control should be forwarded, or <code>null</code> if the response has
* already been completed.
*
* @param mapping The ActionMapping used to select this instance
* @param form The optional ActionForm bean for this request (if any)
* @param request The HTTP request we are processing
* @param response The HTTP response we are creating
*
* @exception Exception if business logic throws an exception
*/
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping,
ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
// Extract attributes we will need
Locale locale = getLocale(request);
MessageResources messages = getResources(request);
User user = null;
// Validate the request parameters specified by the user
ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors();
String username = (String)
PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(form, "username");
String password = (String)
PropertyUtils.getSimpleProperty(form, "password");
UserDatabase database = (UserDatabase)
servlet.getServletContext().getAttribute(Constants.DATABASE_KEY);
if (database == null)
errors.add(ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR,
new ActionError("error.database.missing"));
else {
user = getUser(database, username);
if ((user != null) && !user.getPassword().equals(password))
user = null;
if (user == null)
errors.add(ActionErrors.GLOBAL_ERROR,
new ActionError("error.password.mismatch"));
}
// Report any errors we have discovered back to the original form
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
saveErrors(request, errors);
return (mapping.getInputForward());
}
// Save our logged-in user in the session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(Constants.USER_KEY, user);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("LogonAction: User '" + user.getUsername() +
"' logged on in session " + session.getId());
}
// Remove the obsolete form bean
if (mapping.getAttribute() != null) {
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope()))
request.removeAttribute(mapping.getAttribute());
else
session.removeAttribute(mapping.getAttribute());
}
// Forward control to the specified success URI
return (mapping.findForward("success"));
}
/**
* Look up the user, throwing an exception to simulate business logic
* rule exceptions.
*
* @param database Database in which to look up the user
* @param username Username specified on the Logon form
*
* @exception ModuleException if a business logic rule is violated
*/
public User getUser(UserDatabase database, String username)
throws ModuleException {
// Force an ArithmeticException which can be handled eXPlicitly
if ("arithmetic".equals(username)) {
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
// Force an application-specific exception which can be handled
if ("expired".equals(username)) {
throw new ExpiredPasswordException(username);
}
// Look up and return the specified user
return ((User) database.findUser(username));
}
}
