Java NIO即Java Non-blocking IO(Java非阻塞I/O),是Jdk1.4之後增加的一套操作I/O工具包,又被叫做Java New IO。
Nio要解決的問題網上的解釋一大堆,諸如銀行取號、餐廳點餐等等。這些列子就不再具體地重復了,實際上就是為了使用現有的資源提供更高的生產效率。
這讓我想起了以前學習政治的時候課本裡的故事,資本家為了賺取更多的剩余價值往往會想方設法提高生產效率。如何提高呢?舉個簡單例子,一個汽車生產廠商有若干條生產線(一條生產線負責汽車制造的所有環節),每個生產線都有相同的工人數目,每個工人都負責一個生產環節,也就是說生產發動機和生產輪胎的工人數目是一樣的,但是很明顯生產發動機需要的時間肯定比輪胎要長很多,那麼在每一條生產線上生產發動機的那個工人往往滿負荷工作,而生產輪胎的工人卻很閒,這樣生產效率很低。因此廠家打破了這種一條生產線生產汽車所有環節的模式,改為一個汽車零部件一條生產線,那麼在發動機生產線雇傭的工人數目一定多於輪胎生產線,這樣每條生產線的工人都不會閒著,通過資源的合理分配最大化利用了工人的價值,提高了生產效率,賺取了剩余價值。
而如何通過資源合理分配來提高生產效率就是nio在計算機io領域要解決的問題。
同步和異步是針對應用程序和內核的交互而言的:
同步指的是用戶進程觸發IO操作並等待或者輪詢的去查看IO操作是否就緒;異步是指用戶進程觸發IO操作以後便開始做自己的事情,而當IO操作已經完成的時候會得到IO完成的通知。
阻塞和非阻塞是針對於進程在訪問數據的時候,根據IO操作的就緒狀態來采取的不同方式,說白了是一種讀取或者寫入操作函數的實現方式:
阻塞方式下讀取或者寫入函數將一直等待;非阻塞方式下,讀取或者寫入函數會立即返回一個狀態值。
Reactor模式應用於同步IO場景,事件分離者等待某個事件的發生或者可操作狀態的變化(比如文件描述符可讀寫,或者是socket可讀寫),事件分離者就把這個事件傳給事先注冊的事件處理函數或者回調函數,由後者來做實際的讀寫操作。
在Reactor模式中有如下幾個角色:
1. Reactor
事件分離者,其核心是Selector,負責響應IO事件,一旦發生,廣播發送給相應的Handler去處理。具體為一個Selector和一個ServerSocketChannel。ServerSocketChannel注冊到Selector中,獲取的SelectionKey綁定一個Acceptor(也可以理解為一個Handler)。
參考代碼如下:
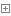
1 import java.io.IOException;
2 import java.net.InetAddress;
3 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
4 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
5 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
6 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
7 import java.util.Iterator;
8 import java.util.Set;
9
10 /**
11 * 反應器模式 用於解決多用戶訪問並發問題
12 */
13 public class Reactor implements Runnable {
14 public final Selector selector;
15 public final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
16
17 public Reactor(int port) throws IOException {
18 selector = Selector.open();
19 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
20 InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), port);
21 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
22 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
23
24 // 向selector注冊該channel
25 SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
26
27 // 利用selectionKey的attache功能綁定Acceptor 如果有事情,觸發Acceptor
28 selectionKey.attach(new Acceptor(this));
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public void run() {
33 try {
34 while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
35 selector.select();
36 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
37 Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
38 // Selector如果發現channel有OP_ACCEPT或READ事件發生,下列遍歷就會進行。
39 while (it.hasNext()) {
40 // 來一個事件 第一次觸發一個accepter線程,SocketReadHandler
41 SelectionKey selectionKey = it.next();
42 dispatch(selectionKey);
43 selectionKeys.clear();
44 }
45 }
46 } catch (IOException e) {
47 e.printStackTrace();
48 }
49 }
50
51 /**
52 * 運行Acceptor或SocketReadHandler
53 *
54 * @param key
55 */
56 void dispatch(SelectionKey key) {
57 Runnable r = (Runnable) (key.attachment());
58 if (r != null) {
59 r.run();
60 }
61 }
62
63 }
View Code
2. Acceptor
也可以理解為一個Handler,這個Handler只負責創建具體處理IO請求的Handler,如果Reactor廣播時SelectionKey創建一個Handler負責綁定相應的SocketChannel到Selector中。下次再次有IO事件時會調用對用的Handler去處理。
參考代碼如下:

1 import java.io.IOException;
2 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
3
4 public class Acceptor implements Runnable {
5 private Reactor reactor;
6
7 public Acceptor(Reactor reactor) {
8 this.reactor = reactor;
9 }
10
11 @Override
12 public void run() {
13 try {
14 SocketChannel socketChannel = reactor.serverSocketChannel.accept();
15 if (socketChannel != null){
16 // 調用Handler來處理channel
17 new SocketReadHandler(reactor.selector, socketChannel);
18 }
19 } catch (IOException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }
22 }
23 }
View Code
3. Handler
具體的事件處理者,例如ReadHandler、SendHandler,ReadHandler負責讀取緩存中的數據,然後再調用一個工作處理線程去處理讀取到的數據。具體為一個SocketChannel,Acceptor初始化該Handler時會將SocketChannel注冊到Reactor的Selector中,同時將SelectionKey綁定該Handler,這樣下次就會調用本Handler。
參考代碼如下:

1 import java.io.IOException;
2 import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
3 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
4 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
5 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
6
7 public class SocketReadHandler implements Runnable {
8 private SocketChannel socketChannel;
9
10 public SocketReadHandler(Selector selector, SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException {
11 this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
12 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
13
14 SelectionKey selectionKey = socketChannel.register(selector, 0);
15
16 // 將SelectionKey綁定為本Handler 下一步有事件觸發時,將調用本類的run方法。
17 // 參看dispatch(SelectionKey key)
18 selectionKey.attach(this);
19
20 // 同時將SelectionKey標記為可讀,以便讀取。
21 selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
22 selector.wakeup();
23 }
24
25 /**
26 * 處理讀取數據
27 */
28 @Override
29 public void run() {
30 ByteBuffer inputBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
31 inputBuffer.clear();
32 try {
33 socketChannel.read(inputBuffer);
34 // 激活線程池 處理這些request
35 // requestHandle(new Request(socket,btt));
36 } catch (IOException e) {
37 e.printStackTrace();
38 }
39 }
40 }
View Code
綜上所述,我們可以把上述角色的細化理解為將一份工作的工作量細化了,或者說重新分配了一下,專人做專事,這樣最大化利用了每個角色的價值,提高工作效率。