框架的源碼分析,有些代碼可以暫時忽略,如Spring如何進行XML模式校驗的、XML解析的細節等,這些代碼可以在了解了整體的原理之後,再做針對性的分析,關注重點內容即可,切記在一開始就去深挖每個細節,這樣不僅會耗費很長時間,而且容易陷入某個坑裡出不來。
以《深入理解Spring系列之一:開篇》示例中的ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationgContext.xml")為入口,進入源碼內部,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext類圖如下。
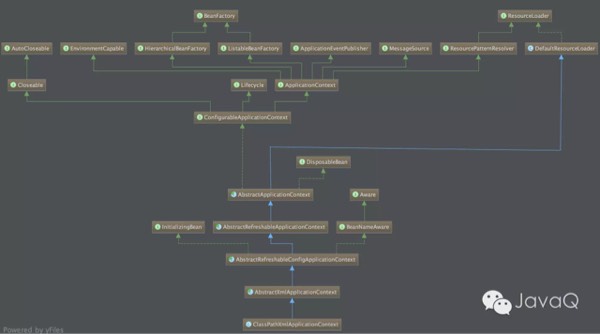
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext有多個構造方法,跟蹤代碼可以發現,最終使用的是下面這個方法,
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
方法的參數很容易理解,configLocations指Spring的xml配置文件;refresh指是否需要刷新,這個refresh決定了是否進行bean解析、注冊及實例化;parent指父ApplicationContext。setConfigLocations方法就是設置框架要加載的資源文件的位置。進入refresh方法,這個方法繼承自AbstractApplicationContext,所以具體實現在AbstractApplicationContext類中,具體代碼如下。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//容器預先准備,記錄容器啟動時間和標記
prepareRefresh();
//創建bean工廠,裡面實現了BeanDefinition的裝載
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//配置bean工廠的上下文信息,如類裝載器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//在BeanDefinition被裝載後,提供一個修改BeanFactory的入口
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//在bean初始化之前,提供對BeanDefinition修改入口,PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer在這裡被調用
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注冊各種BeanPostProcessors,用於在bean被初始化時進行攔截,進行額外初始化操作
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
//初始化上下文事件廣播
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//模板方法
onRefresh();
//注冊監聽器
registerListeners();
//初始化所有未初始化的非懶加載的單例Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//發布事件通知
finishRefresh();
}catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
這個方法裡面就是IOC容器初始化的大致步驟了。上面步驟的第二步完成了BeanDefinition的裝載,進入obtainFreshBeanFactory方法,這個方法的具體實現也在AbstractApplicationContext類中,代碼如下所示。
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
這裡面主要關注refreshBeanFactory方法,這個方法在AbstractApplicationContext類中並未實現,具體實現在子類AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中,代碼如下。
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
這個方法使用了final修飾,也就是不能被重寫了。首先檢查BeanFactory是否已經存在,如果存在則銷毀並關閉,然後新建一個BeanFactory,其實就是一個DefaultListableBeanFactory,這個DefaultListableBeanFactory就是《深入理解Spring系列之一:開篇》說的那個。然後進行BeanFactory的屬性設置,設置是否允許重寫BeanDefinition、是否允許循環引用,接著loadBeanDefinitions方法就是BeanDefinition載入的入口了,這個方法在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext本類中並未實現,具體在其子類中實現,根據用途不同有多個實現子類,下一篇內容將分析基於最基本的解析xml方式的AbstractXmlApplicationContext類中的實現。