今天在看LinkedList的源代碼的時候,遇到了一個坑。我研究源碼時,發現LinkedList是一個直線型的鏈表結構,但是我在baidu搜索資料的時候,關於這部分的源碼解析,全部都說LinkedList是一個環形鏈表結構。。我糾結了好長時間,還以為我理解錯了,最後還是在Google搜到了結果:因為我看的源碼是1.7的而baidu出來的幾乎全部都是1.6的。而且也沒有對應的說明。在1.7之後,oracle將LinkedList做了一些優化,將1.6中的環形結構優化為了直線型了鏈表結構。這裡要提示一下朋友們,看源碼的時候,一定要看版本,有的情況是屬於小改動,有的地方可能有大改動,這樣只會越看越迷糊。
好,言歸正傳。我們來分析一下Java中LinkedList的部分源碼。(本文針對的是1.7的源碼)
 在LinkedList中,我們把鏈子的“環”叫做“節點”,每個節點都是同樣的結構。節點與節點之間相連,構成了我們LinkedList的基本數據結構,也是LinkedList的核心。
我們再來看一下LinkedList在jdk1.6和1.7直接結構的區別
首先看1.7中的結構
在LinkedList中,我們把鏈子的“環”叫做“節點”,每個節點都是同樣的結構。節點與節點之間相連,構成了我們LinkedList的基本數據結構,也是LinkedList的核心。
我們再來看一下LinkedList在jdk1.6和1.7直接結構的區別
首先看1.7中的結構
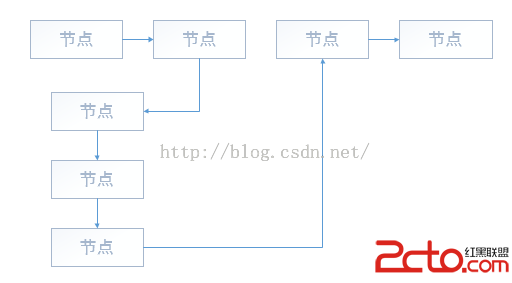
 再來看1.6中的結構
再來看1.6中的結構
 對比一下,知道區別在哪裡了吧?在1.7中,去掉了環形結構,自然在代碼中的也會有部分的改變。
理解了上邊的結構,在分析的時候就會容易許多。
對比一下,知道區別在哪裡了吧?在1.7中,去掉了環形結構,自然在代碼中的也會有部分的改變。
理解了上邊的結構,在分析的時候就會容易許多。
// 什麼都沒做,是一個空實現
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
// 檢查傳入的索引值是否在合理范圍內
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 將給定的Collection對象轉為Object數組
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
// 數組為空的話,直接返回false
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
// 數組不為空
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
// 構造方法調用的時候,index = size = 0,進入這個條件。
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
// 鏈表非空時調用,node方法返回給定索引位置的節點對象
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
// 遍歷數組,將數組的對象插入到節點中
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred; // 將當前鏈表最後一個節點賦值給last
} else {
// 鏈表非空時,將斷開的部分連接上
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
// 記錄當前節點個數
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
這裡要說明一下,Node是LinkedList的內部私有類,它的組成很簡單,只有一個構造方法。
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
構造方法的參數順序是:前繼節點的引用,數據,後繼節點的引用。
有了上邊的說明,我們來看LinkedList的構造方法。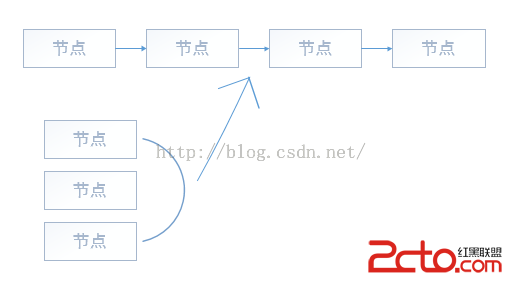
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); // 創建新的節點,新節點的後繼指向原來的頭節點,即將原頭節點向後移一位,新節點代替頭結點的位置。
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
其實只要理解了上邊的數據結構,這段代碼是很好理解的。
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
這段代碼即不需要解析了吧。。很簡單的。
public E get(int index) {
// 校驗給定的索引值是否在合理范圍內
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
一開始我很費解,這是要干嘛?後來我才明白,代碼要做的是:判斷給定的索引值,若索引值大於整個鏈表長度的一半,則從後往前找,若索引值小於整個鏈表的長度的一般,則從前往後找。這樣就可以保證,不管鏈表長度有多大,搜索的時候最多只搜索鏈表長度的一半就可以找到,大大提升了效率。
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
摘掉頭結點,將原來的第二個節點變為頭結點,改變frist的指向,若之前僅剩一個節點,移除之後全部置為了null。