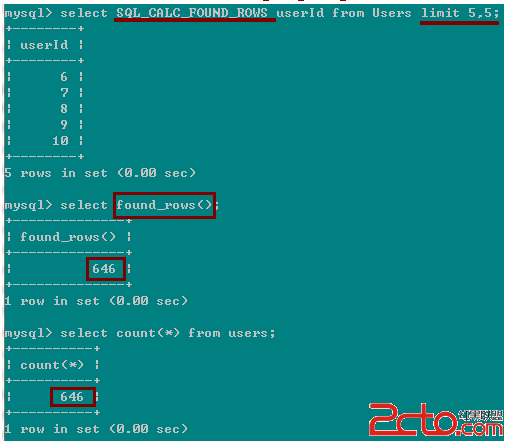
 此種情況下,select found_rows() 和 select count(*) 有一個很小的區別:如果userId允許為null,那麼select found_rows() 的結果可能要比select count(*) 要小一些。因為前者等價於:select count(userId) from Users; 而該語句不會計算userId 為null的行在內。而count(*)會計算在內。
2)found_rows() 的第二種/第三中使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS):
In the absence of the SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS option in the most recent successful SELECT statement, FOUND_ROWS() returns the number of rows in the result set returned by that statement. If the statement includes a LIMIT clause, FOUND_ROWS() returns the number of rows up to the limit. For example, FOUND_ROWS() returns 10 or 60, respectively, if the statement includes LIMIT 10 or LIMIT 50, 10.
The row count available through FOUND_ROWS() is transient and not intended to be available past the statement following the SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS statement. If you need to refer to the value later, save it:
mysql> SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS * FROM ... ;
mysql> SET @rows = FOUND_ROWS();
If you are using SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS, MySQL must calculate how many rows are in the full result set. However, this is faster than running the query again without LIMIT, because the result set need not be sent to the client.
1> 第二種使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,也沒有帶 limit ):
此種情況下,select found_rows() 和 select count(*) 有一個很小的區別:如果userId允許為null,那麼select found_rows() 的結果可能要比select count(*) 要小一些。因為前者等價於:select count(userId) from Users; 而該語句不會計算userId 為null的行在內。而count(*)會計算在內。
2)found_rows() 的第二種/第三中使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS):
In the absence of the SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS option in the most recent successful SELECT statement, FOUND_ROWS() returns the number of rows in the result set returned by that statement. If the statement includes a LIMIT clause, FOUND_ROWS() returns the number of rows up to the limit. For example, FOUND_ROWS() returns 10 or 60, respectively, if the statement includes LIMIT 10 or LIMIT 50, 10.
The row count available through FOUND_ROWS() is transient and not intended to be available past the statement following the SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS statement. If you need to refer to the value later, save it:
mysql> SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS * FROM ... ;
mysql> SET @rows = FOUND_ROWS();
If you are using SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS, MySQL must calculate how many rows are in the full result set. However, this is faster than running the query again without LIMIT, because the result set need not be sent to the client.
1> 第二種使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,也沒有帶 limit ):
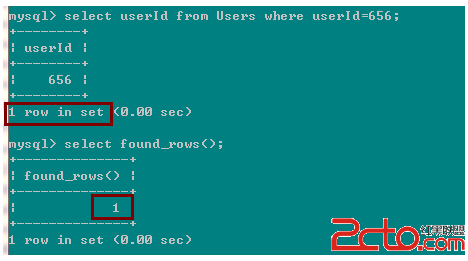 如果前面的select語句沒有帶 SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,也沒有帶 limit ,那麼後面的 SELECT FOUND_ROWS(); 返回的結果就是前面的select返回的行數;
2> 第三中使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,但是有帶 limit ):
如果前面的select語句沒有帶 SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,但是帶有 limit,那麼後面的 SELECT FOUND_ROWS(); 返回的結果就是limit語句到達的最大的行數,比如:select * from xxx limit 10; 到達的最大的行數為10,所以 found_rows() 返回10;比如 select * from xxx limit 50,10; 它要從第50行開始,再掃描10行,所以到達的最大的行數為60,所以found_rows() 返回60。
如果前面的select語句沒有帶 SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,也沒有帶 limit ,那麼後面的 SELECT FOUND_ROWS(); 返回的結果就是前面的select返回的行數;
2> 第三中使用情況(不帶有SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,但是有帶 limit ):
如果前面的select語句沒有帶 SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS,但是帶有 limit,那麼後面的 SELECT FOUND_ROWS(); 返回的結果就是limit語句到達的最大的行數,比如:select * from xxx limit 10; 到達的最大的行數為10,所以 found_rows() 返回10;比如 select * from xxx limit 50,10; 它要從第50行開始,再掃描10行,所以到達的最大的行數為60,所以found_rows() 返回60。
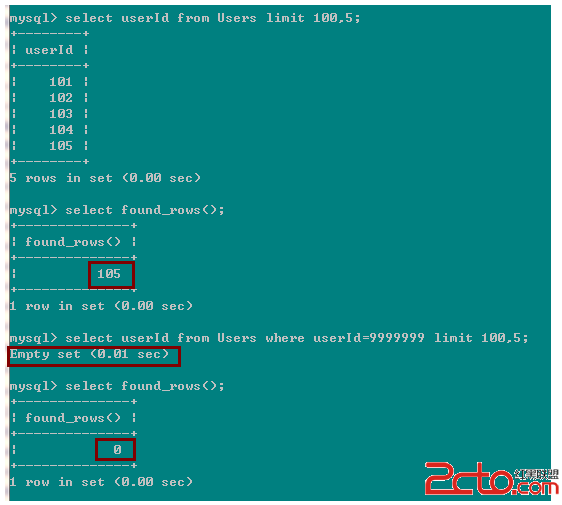 這裡第一個select found_rows() 返回105,因為他是從偏移100的地方,再掃描5行,所以返回105;但是第二個掃描的結果為空,select found_rows()返回了0!而不是105,因為 where userId=999999的結果為空,所以後面的 limit 100,5根本就沒有執行。所以select found_rows()返回了0。
再看一個例子,更深入的理解其中情況下的 found_rows():
這裡第一個select found_rows() 返回105,因為他是從偏移100的地方,再掃描5行,所以返回105;但是第二個掃描的結果為空,select found_rows()返回了0!而不是105,因為 where userId=999999的結果為空,所以後面的 limit 100,5根本就沒有執行。所以select found_rows()返回了0。
再看一個例子,更深入的理解其中情況下的 found_rows():
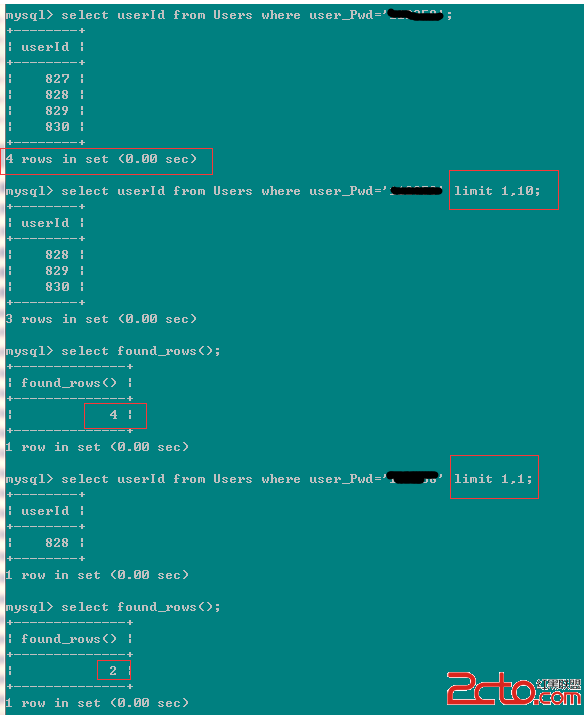 上面sql中 user_Pwd=xx 的值都是一樣的。可以看到這種情況下的found_rows() 是對的select語句的中間結果,再 limit 時,此時的limit的掃描到的最大的行數。和原始表中的數據的行數,是沒有關系的。他是對select的中間結果的limit,然後才得到最後的結果集,再返回。
3)SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS and FOUND_ROWS() 適合使用的場景
SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS and FOUND_ROWS() can be useful in situations when you want to restrict the number of rows that a query returns, but also determine the number of rows in the full result set without running the query again. An example is a Web script that presents a paged display containing links to the pages that show other sections of a search result. Using FOUND_ROWS() enables you to determine how many other pages are needed for the rest of the result.
1> SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROW + limit + found_rows() 可以使用在分頁的場合。
2> 不帶SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROW 的 found_rows() 可以使用在存儲過程中判斷前面的select是否為空:
上面sql中 user_Pwd=xx 的值都是一樣的。可以看到這種情況下的found_rows() 是對的select語句的中間結果,再 limit 時,此時的limit的掃描到的最大的行數。和原始表中的數據的行數,是沒有關系的。他是對select的中間結果的limit,然後才得到最後的結果集,再返回。
3)SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS and FOUND_ROWS() 適合使用的場景
SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS and FOUND_ROWS() can be useful in situations when you want to restrict the number of rows that a query returns, but also determine the number of rows in the full result set without running the query again. An example is a Web script that presents a paged display containing links to the pages that show other sections of a search result. Using FOUND_ROWS() enables you to determine how many other pages are needed for the rest of the result.
1> SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROW + limit + found_rows() 可以使用在分頁的場合。
2> 不帶SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROW 的 found_rows() 可以使用在存儲過程中判斷前面的select是否為空:
DELIMITER //
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS loginandreg //
CREATE PROCEDURE loginandreg(
OUT userId BIGINT,
IN user_Pwd VARCHAR(32),
IN user_MobileCode VARCHAR(16),
IN user_RegIP VARCHAR(16)
)
BEGIN
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM Users u WHERE u.user_MobileCode=user_MobileCode) THEN
SELECT u.userId INTO userId FROM Users u WHERE u.user_MobileCode=user_MobileCode AND u.user_Pwd=user_Pwd;
IF FOUND_ROWS() < 1 THEN
SELECT -1 INTO userId;
END IF;
ELSE
INSERT INTO Users(user_Pwd,user_MobileCode,user_Visibility,user_Level,user_RegTime,user_RegIP,user_Collecter,user_Collected)
VALUES (user_Pwd,user_MobileCode,6,6,NOW(),user_RegIP,0,0);
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() INTO userId;
END IF;
END //
DELIMITER ;
上面存儲過程中的: SELECT u.userId INTO userId FROM Users u WHERE u.user_MobileCode=user_MobileCode AND u.user_Pwd=user_Pwd; IF FOUND_ROWS() < 1 THEN SELECT -1 INTO userId; END IF; 就是一個很好的使用的例子。 這種存儲過程的場景中就可以使用 mysql 的 FOUND_ROWS() 替換 sql server 存儲過程中的 IF @@ROWCOUNT < 1 語句。 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2. row-count() 函數 文檔地址:http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/information-functions.html#function_row-count 一句話,row_count() 函數一般用於返回被 update, insert, delete 實際修改的行數。 In MySQL 5.6, ROW_COUNT() returns a value as follows: DDL statements: 0. This applies to statements such as CREATE TABLE or DROP TABLE. DML statements other than SELECT: The number of affected rows. This applies to statements such as UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE (as before), but now also to statements such as ALTER TABLE and LOAD DATA INFILE. SELECT: -1 if the statement returns a result set, or the number of rows “affected” if it does not. For example, for SELECT * FROM t1, ROW_COUNT() returns -1. For SELECT * FROM t1 INTO OUTFILE 'file_name', ROW_COUNT() returns the number of rows written to the file. SIGNAL statements: 0. For UPDATE statements, the affected-rows value by default is the number of rows actually changed. If you specify the CLIENT_FOUND_ROWS flag to mysql_real_connect() when connecting to mysqld, the affected-rows value is the number of rows “found”; that is, matched by the WHERE clause. 也就是說對於update語句,row_count() 默認返回的是實際被修改的行數;但是通過參數設置,也可以返回找到的行數(或者說匹配的行數,受影響的行數),這樣設置就能兼容於Oracle ps/sql中 sql%rowcount 和 sql server 中的 @@RowCount。 但是 row_count() 的結果和 mysql 的JDBC driver的默認行為卻是不一致的,mysql jdbc中的 Connection.getUpdateCount() 函數返回的是被找到的行數,而不是實際被修改的行數,如果要返回被實際修改的行,要使用存儲過程,相關鏈接說明: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17544782/how-to-tell-number-of-rows-changed-from-jdbc-execution http://mybatis-user.963551.n3.nabble.com/Return-number-of-changed-rows-td3888464.html#a3903155 http://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/en/connector-j-reference-configuration-properties.html (這裡包含了所有mysql jdbc 鏈接可設置的參數) useAffectedRows Don't set the CLIENT_FOUND_ROWS flag when connecting to the server (not JDBC-compliant, will break most applications that rely on "found" rows vs. "affected rows" for DML statements), but does cause "correct" update counts from "INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE" statements to be returned by the server. Default: false Since version: 5.1.7 關於對mysql復制的影響: Important FOUND_ROWS() is not replicated reliably using statement-based replication. This function is automatically replicated using row-based replication. Important ROW_COUNT() is not replicated reliably using statement-based replication. This function is automatically replicated using row-based replication. 注意:found_rows() 和 row_count() 在基於 語句的復制 環境中是不可靠的,它們自動使用 基於行的復制行為。