用注解編寫創立表的SQL語句。本站提示廣大學習愛好者:(用注解編寫創立表的SQL語句)文章只能為提供參考,不一定能成為您想要的結果。以下是用注解編寫創立表的SQL語句正文
本文實例講述了SQL Server完成將特定字符串拆分並停止拔出操作的辦法。分享給年夜家供年夜家參考,詳細以下:
--輪回履行添加操作
declare @idx as int
While Len(@UserList) > 0
Begin
Set @idx = Charindex(',', @UserList);
--只要一條數據
If @idx = 0 and Len(@UserList) > 0
Begin
Insert Into BIS_MsgCenterInfo(ID,MsgID,UserID,[State])Values(Newid(),@ID,@UserList,0);
Break;
End
--多條數據
If @idx > 1
Begin
Insert Into BIS_MsgCenterInfo(ID,MsgID,UserID,[State]) Values(Newid(),@ID,left(@UserList, @idx - 1),0);
Set @UserList = right(@UserList, Len(@UserList) - @idx);
End
Else
Set @UserList = right(@UserList, Len(@UserList) - @idx);
End
願望本文所述對年夜家SQL Server數據庫法式設計有所贊助。
ges、types(類、接口、列舉、Annotation類型)、類型成員(辦法、結構辦法、成員變量、列舉值)、辦法參數和當地變量(如輪回變量、catch參數)。在Annotation類型的聲明中應用了target可加倍了了其潤飾的目的。 感化:用於描寫注解的應用規模(即:被描寫的注解可以用在甚麼處所) 取值(ElementType)有: 1.CONSTRUCTOR:用於描寫結構器 2.FIELD:用於描寫域 3.LOCAL_VARIABLE:用於描寫部分變量 4.METHOD:用於描寫辦法 5.PACKAGE:用於描寫包 6.PARAMETER:用於描寫參數 7.TYPE:用於描寫類、接口(包含注解類型) 或enum聲明 @Retention: @Retention界說了該Annotation被保存的時光長短:某些Annotation僅湧現在源代碼中,而被編譯器拋棄;而另外一些卻被編譯在class文件中;編譯在class文件中的Annotation能夠會被虛擬機疏忽,而另外一些在class被裝載時將被讀取(請留意其實不影響class的履行,由於Annotation與class在應用上是被分別的)。應用這個meta-Annotation可以對 Annotation的“性命周期”限制。 感化:表現須要在甚麼級別保留該正文信息,用於描寫注解的性命周期(即:被描寫的注解在甚麼規模內有用) 取值(RetentionPoicy)有: 1.SOURCE:在源文件中有用(即源文件保存) 2.CLASS:在class文件中有用(即class保存) 3.RUNTIME:在運轉時有用(即運轉時保存) Retention meta-annotation類型有獨一的value作為成員,它的取值來自java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy的列舉類型值 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface DBTable { public String name() default ""; }Constraints 束縛注解:
/**
* Project Name:myannotation
* File Name:Constraints.java
* Package Name:com.iflytek.db
* Date:2016-8-28下晝08:27:08
* Copyright (c) 2016, syzhao@iflytek.com All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package com.iflytek.db;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Constraints
{
boolean primaryKey() default false;
boolean allowNull() default true;
boolean unique() default false;
}
SQLInteger int注解:
/**
* Project Name:myannotation
* File Name:SQLInteger.java
* Package Name:com.iflytek.db
* Date:2016-8-29下晝10:24:11
* Copyright (c) 2016, syzhao@iflytek.com All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package com.iflytek.db;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SQLInteger
{
String name() default "";
Constraints constraints() default @Constraints;
}
SQLString 字符注解:
/**
* Project Name:myannotation
* File Name:SQLString.java
* Package Name:com.iflytek.db
* Date:2016-8-29下晝10:28:04
* Copyright (c) 2016, syzhao@iflytek.com All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package com.iflytek.db;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SQLString
{
int value() default 0;
String name() default "";
Constraints constraints() default @Constraints;
}
創立表的處置器:
/**
* Project Name:myannotation
* File Name:TableCreator.java
* Package Name:com.iflytek.table
* Date:2016-8-29下晝10:57:52
* Copyright (c) 2016, syzhao@iflytek.com All Rights Reserved.
*
*/
package com.iflytek.table;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.iflytek.db.Constraints;
import com.iflytek.db.DBTable;
import com.iflytek.db.SQLInteger;
import com.iflytek.db.SQLString;
public class TableCreator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
createTable(Member.class);
}
//創立表SQL語句
private static void createTable(Class<?> cl)
{
//獲得DBTable注解
DBTable dbTable = cl.getAnnotation(DBTable.class);
//斷定DBTable注解能否存在
if (dbTable == null)
{
System.out.println("沒有找到關於DBTable");
return;
}
//假如@DBTable注解存在獲得注解
String tableName = dbTable.name();
//斷定表名能否存在
if (tableName.length() < 1)
{
//不存在,解釋默許就是類名,經由過程 cl.getSimpleName()獲得類名而且年夜寫
tableName = cl.getSimpleName().toUpperCase();
}
//界說獲得column的容器
List<String> columnDefs = new ArrayList<String>();
//輪回屬性字段
//解釋:getDeclaredFields()取得某個類的一切聲名的字段,即包含public、private和proteced,然則不包含父類的聲名字段。
//getFields()取得某個類的一切的公共(public)的字段,包含父類。
for (Field field : cl.getDeclaredFields())
{
//界說表字段稱號變量
String columnName = null;
//獲得字段上的注解(如今字段許可多個注解,是以前往的是數組)
Annotation[] anns = field.getDeclaredAnnotations();
//斷定屬性能否存在注解
if (anns.length < 1)
continue;
//斷定能否是我們界說的數據類型
if (anns[0] instanceof SQLInteger)
{
//獲得SQLInteger 注解
SQLInteger sInt = (SQLInteger)anns[0];
//斷定能否注解的name能否有值
if (sInt.name().length() < 1)
{
//假如沒有值,解釋是類的屬性字段,獲得屬性並轉換年夜寫
columnName = field.getName().toUpperCase();
}
else
{ //假如有值,獲得設置的name值
columnName = sInt.name();
}
//放到屬性的容器內
columnDefs.add(columnName + " INT " + getConstraints(sInt.constraints()));
}
//同上SQLInteger,這裡不寫正文了
if (anns[0] instanceof SQLString)
{
SQLString sString = (SQLString)anns[0];
if (sString.name().length() < 1)
{
columnName = field.getName().toUpperCase();
}
else
{
columnName = sString.name();
}
columnDefs.add(columnName + " VARCHAR(" + sString.value() + ")" + getConstraints(sString.constraints()));
}
//界說生成創立表的SQL語句
StringBuilder createCommand = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE " + tableName + "(");
//輪回下面屬性容器,
for (String columnDef : columnDefs)
{
//把屬性添加到sql語句中
createCommand.append("\n " + columnDef + ",");
//去失落最初一個逗號
String tableCreate = createCommand.substring(0, createCommand.length() - 1) + ");";
//打印
System.out.println("Table creation SQL for " + cl.getName() + " is :\n" + tableCreate);
}
}
}
private static String getConstraints(Constraints con)
{
String constraints = "";
//斷定能否為null
if (!con.allowNull())
{
constraints += " NOT NULL ";
}
//斷定能否是主鍵
if (con.primaryKey())
{
constraints += " PRIMARY KEY ";
}
//能否獨一
if (con.unique())
{
constraints += " UNIQUE ";
}
return constraints;
}
}
以上代碼拷貝出來,便可以運轉了!
下面固然是簡略的創立表語句,但我們可以舒展到hibernate的domain類裡的注解,各類CURD ,未嘗不是如許處置的呢,只是hibernate有許多器械,然則萬變不離其宗,今後無機會研討一下hibernate 。
收成:
讀了今後,關於注解曉得為何要這麼用了,其實望文生義就是一個注解,只是有一個處置器來處置這個注解,這對我今後用到注解方面應當有贊助的,
時光不早了,就寫到這裡!
成果:
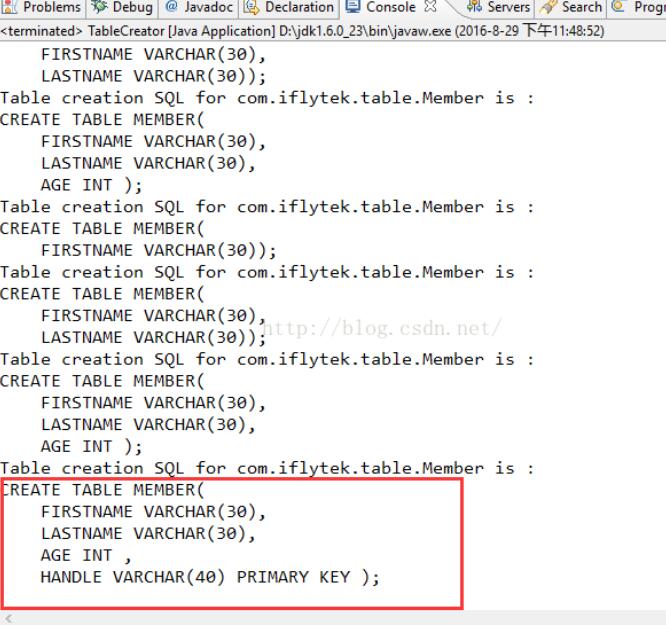
以上就是本文的全體內容,願望對年夜家的進修有所贊助,也願望年夜家多多支撐。