只看某一個象限 能看到的數 == 一個 象限*4+4
能看到的樹既距離原點的距離 gcd(x,y)==1
a 和 b 一大一小 預處理2000以內的phi函數,枚舉小的一條邊
從1...a 與 a gcd 為 1 的數的個數就是 phi(a)
從 1+a ... 2*a 與 a gcd 為 1 的數的個數 因為 GCD(i,a) = GCD(i+a,a) 所以還是 phi(a)
....
Submit Status
Description
The saying ``You can't see the wood for the trees'' is not only a cliche, but is also incorrect. The real problem is that you can't see the trees for the wood. If you stand in the middle of a wood, the trees tend to obscure each other and the number of distinct trees you can actually see is quite small. This is especially true if the trees are planted in rows and columns, because they tend to line up. The purpose of this problem is to find how many distinct trees one can see if one were standing on the position of a tree in the middle of the wood.
For a mathematically more precise description we assume that you are situated at the origin of a coordinate system in the plane.
Trees are planted at all positions ![]() , with "x|<=a and |y|<=b .
, with "x|<=a and |y|<=b .
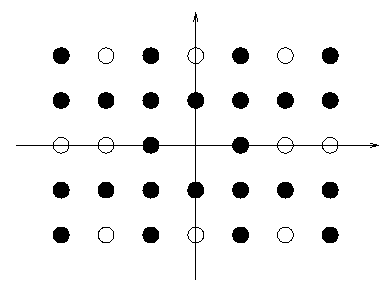
A tree at pZ喎?http://www.Bkjia.com/kf/ware/vc/" target="_blank" class="keylink">vc2l0aW9uICh4LHkpIGNhbiBiZSBzZWVuIGZyb20gdGhlIG9yaWdpbiBpZiB0aGVyZSBhcmUgbm8gb3RoZXIgdHJlZXMgb24gdGhlIHN0cmFpZ2h0IGxpbmUgZnJvbSAoMCwwKSB0byAoeCx5KSAuIEZpbmQgdGhlIG51bWJlciBLIG9mIGFsbCB0aGUgdHJlZXMgaW4gdGhlIHdvb2QgdGhhdCBjYW4gYmUgc2VlbiBmcm9tIHRoZSBvcmlnaW4gYW5kIHRoZSBudW1iZXIgTiBvZiBhbGwgdGhlIHRyZWVzIHRvCiBjb21wdXRlIHRoZSBmcmFjdGlvbiA8aW1nIHNyYz0="https://www.aspphp.online/bianchen/UploadFiles_4619/201701/2017012113182795.gif" width="19" height="29" id="_x0000_i1027" align="top" border="0" alt="\">.
Hint: The Euler phi function ![]() is defined to be the number of integers m in
the range 1≤m≤n relatively prime to n :
is defined to be the number of integers m in
the range 1≤m≤n relatively prime to n :
![]()
Instead of counting (an adequate method for small n !) you could as well use the following identity:
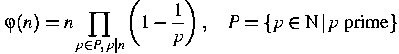
Hint: Remember that gcd (m,n)= gcd (m+n,n)= gcd (m+2n,n)= gcd (m+in,i)
You might be surprised that the fraction ![]() converges to
converges to ![]() 0.607927
for an infinitely large wood.
0.607927
for an infinitely large wood.
Each scenario consists of a line with the two numbers a and b (separated by a white space), with 1 <= a <= 2000 and 1 <= b <= 2000000 Input is terminated by a line with two zeros.
For each scenario print a line containing the fraction ![]() with a precision of 7 digits after the decimal point.
Error less than 2e-7 or 2*10^(-7) will be tolerated.
with a precision of 7 digits after the decimal point.
Error less than 2e-7 or 2*10^(-7) will be tolerated.
3 2
0 0
Source
Root :: AOAPC II: Beginning Algorithm Contests (Second Edition) (Rujia Liu) :: Chapter 10. Maths :: ExamplesSubmit Status
/* *********************************************** Author :CKboss Created Time :2015年02月03日 星期二 22時13分33秒 File Name :UVA10214.cpp ************************************************ */ #include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include