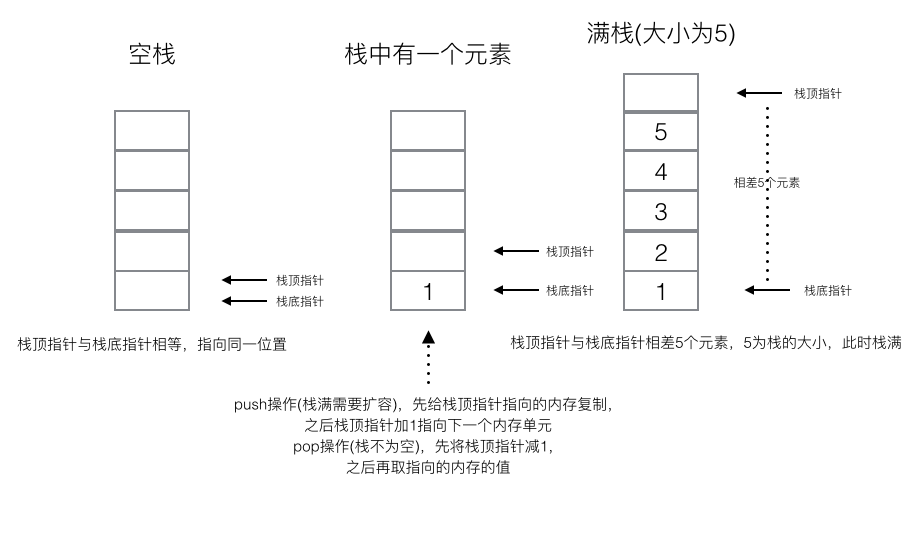
用C語言實現了一個簡單的棧。基本思路是定義一個棧結構體,裡面有兩個指針和一個表示棧大小的int。兩個指針分別指向棧底和棧頂,當棧底指針和棧頂指針重合時,說明棧為空;當棧頂指針減去棧底指針的值大於等於棧的大小,說明棧已滿。
//mystack.h
#ifndef mystack_H
#define mystack_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MYSTACK_INCREASE_NUM 2
typedef int ElementType; //暫定為int
typedef int Bool;
typedef struct
{
ElementType * bottom; //棧底指針
ElementType * top; //棧頂指針
int size; //棧大小
} MyStack;
MyStack * initStack( int size); //初始化
Bool freeStack(MyStack * stack); //釋放內存
Bool push(MyStack * stack, ElementType data);
Bool pop(MyStack *stack, ElementType * outputData);
Bool isEmpty(MyStack *stack);
void makeStackEmpty(MyStack *stack);
void printStack(MyStack *stack);
#endif
//mystack。c
#include "mystack.h"
MyStack* initStack( int size)
{
MyStack* stack = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); //分配內存
if(stack==NULL)
return NULL;
stack->bottom = (ElementType*)malloc(sizeof(ElementType)*size);
if(stack->bottom == NULL)
return NULL;
stack->top = stack->bottom; //初始化為空棧 棧頂指針和棧底指針指向同一位置
stack->size = size; //初始化大小
return stack;
}
Bool freeStack(MyStack * stack)
{
if(stack!=NULL)
{
free(stack->bottom);
free(stack);
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void makeStackEmpty(MyStack *stack)
{
if(stack!=NULL)
stack->top = stack->bottom;
}
Bool isEmpty(MyStack *stack)
{
if(stack != NULL)
{
if(stack->bottom == stack->top)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
else
return 0;
}
Bool push(MyStack * stack, ElementType data)
{
if(stack->top - stack->bottom >= stack->size) //棧滿
{
stack->bottom = (ElementType*)realloc(stack->bottom, //分配內存,增加棧大小
sizeof(ElementType*)*(stack->size + MYSTACK_INCREASE_NUM));
if(stack->bottom == NULL)
return 0;
stack->top = stack->bottom + stack->size; //初始化棧頂指針
stack->size += MYSTACK_INCREASE_NUM;
}
*(stack->top)=data; //先存值
stack->top++; //指針加1,指向下一內存單元
return 1;
}
Bool pop(MyStack *stack, ElementType * outputData)
{
if(isEmpty(stack))
{
printf("stack is empty\n");
return 0;
}
stack->top--; //指針減1後指向棧中最頂上的元素
*outputData = *(stack->top); //取值
return 1;
}
void printStack(MyStack *stack)
{
if(stack!= NULL)
{
if(stack->bottom == stack->top)
{
printf("stack is empty\n");
}
else
{
/*for(int i = 0 ; i < stack->top - stack->bottom ; i++)
printf("%d\n",stack->bottom[i] );*/
ElementType * element = stack->bottom;
for(;element != stack->top ; element++)
printf("%d\n",*element);
}
}
}
//stacktest.c
#include "mystack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
/* code */
int a,b,c;
MyStack* stack = initStack(2);
push(stack,1);
push(stack,2);
printStack(stack); //預期輸出 1 、2
push(stack,3);
printStack(stack); //預期輸出 1、2、3
pop(stack,&a);
pop(stack,&b);
push(stack,4);
pop(stack,&c);
printf("a=%d b=%d c=%d\n",a,b,c ); //預期輸出 a=3 b=2 c=4
makeStackEmpty(stack);
pop(stack,&a); //預期輸出 stack is empty
printf("a=%d\n", a); //預期輸出 a=3
freeStack(stack);
return 0;
}
參考 : 百度文庫
http://blog.csdn.net/mci2004/article/details/7532205