題外話
以前也用C寫過字符串,主要應用的領域是,大字符串,文件讀取方面.寫的很粗暴,用的湊合著.那時候看見雲風前輩的一個開源的 cstring 串.
當時簡單觀摩了一下,覺得挺好的.也沒細看.過了較長一段時間,想整合一下,將大字符串和雲風的cstring 短簡單的串合在一起變成一種.但是自己
認真復制了一遍後發現.
1.整合不了 雲風(後面都省略前輩二字,覺得雲風兩個字,就已經帥的不行了)簡單cstring.因為處理的領域不一樣.
雲風的 cstring => String , 而自己寫的操作文件的c簡單串 => StringBuilder.
2.技巧太多了,不明覺厲,但是雲風用的技巧,都會解釋,畢竟都是C開發中常用的技巧.
3.自己很菜,只能是瞎子摸象,看見只是部分,更多的需要大家自己參悟.
參考資料
1.雲風博客簡單字符串簡介 http://blog.codingnow.com/2013/09/cstring.html
2.雲風githup cstring https://github.com/cloudwu/cstring
3.gcc inline解釋 在線文檔 https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc-5.3.0/gcc/Inline.html#Inline
4.字符串hash 函數簡介 http://www.cnblogs.com/uvsjoh/archive/2012/03/27/2420120.html#3240817
5. 簡單實現原子操作 http://www.cnblogs.com/life2refuel/p/5024289.html#3326123
6. assert 使用 http://www.cnblogs.com/ggzss/archive/2011/08/18/2145017.html
7. 位運算 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7b7cad23010163vy.html
8.stdarg.h c可變參數詳解 http://www.cnblogs.com/life2refuel/p/4984275.html
前言
這次直接切入正題,也許你會不屑一顧,還是想 分享一個故事
面朝大海,春暖花開
海子 於 1989
從明天起,做一個幸福的人
喂馬、劈柴,周游世界
從明天起,關心糧食和蔬菜
我有一所房子,面朝大海,春暖花開
從明天起,和每一個親人通信
告訴他們我的幸福
那幸福的閃電告訴我的
我將告訴每一個人
給每一條河每一座山取一個溫暖的名字
陌生人,我也為你祝福
願你有一個燦爛的前程
願你有情人終成眷屬
願你在塵世獲得幸福
我只願面朝大海,春暖花開
同名歌曲
面朝大海 http://music.163.com/#/song?id=27946316
正題
首先下載雲風的cstring 源碼 結構如下:
首先 看 cstring.h 文件
#ifndef cstring_h
#define cstring_h
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#define CSTRING_PERMANENT 1
#define CSTRING_INTERNING 2
#define CSTRING_ONSTACK 4
#define CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE 32
#define CSTRING_STACK_SIZE 128
struct cstring_data {
char * cstr;
uint32_t hash_size;
uint16_t type;
uint16_t ref;
};
typedef struct _cstring_buffer {
struct cstring_data * str;
} cstring_buffer[1];
typedef struct cstring_data * cstring;
#define CSTRING_BUFFER(var) \
char var##_cstring [CSTRING_STACK_SIZE] = { '\0' }; \
struct cstring_data var##_cstring_data = { var##_cstring , 0, CSTRING_ONSTACK, 0 }; \
cstring_buffer var; \
var->str = &var##_cstring_data;
#define CSTRING_LITERAL(var, cstr) \
static cstring var = NULL; \
if (var) {} else { \
cstring tmp = cstring_persist(""cstr, (sizeof(cstr)/sizeof(char))-1); \
if (!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&var, NULL, tmp)) { \
cstring_free_persist(tmp); \
} \
}
#define CSTRING(s) ((s)->str)
#define CSTRING_CLOSE(var) \
if ((var)->str->type != 0) {} else \
cstring_release((var)->str);
/* low level api, don't use directly */
cstring cstring_persist(const char * cstr, size_t sz);
void cstring_free_persist(cstring s);
/* public api */
cstring cstring_grab(cstring s);
void cstring_release(cstring s);
cstring cstring_cat(cstring_buffer sb, const char * str);
cstring cstring_printf(cstring_buffer sb, const char * format, ...)
#ifdef __GNUC__
__attribute__((format(printf, 2, 3)))
#endif
;
int cstring_equal(cstring a, cstring b);
uint32_t cstring_hash(cstring s);
#endif
第一部分 對頭文件 cstring.h 簡單解析如下(對於源碼全部解釋,自己說的不爽,別人看也會不爽,畢竟不是原創)
1.1 字符串類型
#define CSTRING_PERMANENT 1
上面聲明表示一個 永久的串 類型,實現采用static 變量類型聲明
#define CSTRINT_INTERNING 2
上面表示一個 符號表字符串 類型,實現方式 直接 "root" 這麼搞
#define CSTRING_ONSTACK 4
這大家都知道 臨時字符串 類型,實現方式 利用宏嵌到 函數代碼體中
1.2 字符串大小宏
#define CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE 32
上面是符號表串,小於32字節的 都可以聲明為 CSTRINT_INTERNING
#define CSTRING_STACK_SIZE 128
上面是表明小於128字節的都可以放到棧上 類型 CSTRING_ONSTACK
2.1 特殊的結構體
typedef struct cstring_buffer {
struct cstring_data * str;
} cstring_buffer[1];
上面 定義的 cstring_buffer 類型,是C中一個聲明技巧
例如 cstring_buffer cb; 其中 cb 內存分配在 棧上 但是可以當指針使用,傳入到 struct cstring_buffer* 地方.
更簡單一點如下,其它就自己悟吧
cstring_buffer cb; => struct cstring_buffer cb[1];
3.1 函數宏分析
#define CSTRING_BUFFER(var) \
char var##_cstring[CSTRING_STACK_SIZE] = { '\0' }; \
struct cstring_data var##_cstring_data = { var##_cstring, 0, CSTRING_ONSTACK, 0 }; \
cstring_buffer var; \
var->str = &var##cstring_data;
這個宏 也很巧妙, ## 表示鏈接宏 假如 var 是 abc,var只能同變量,不能有雙引號
那麼就聲明了一個
char abc_cstring[128] = { '\0' };
這個變量內存在棧上,通常不需要回收.
這個宏作用是 聲明了一個名為 var 的 cstring_buffer 對象 但是在函數結束時,應該使用 CSTRING_CLOSE(var) 關閉它。
3.2 另一個出彩的函數宏
#define CSTRING_LITERAL(var, cstr) \
static cstring var = NULL; \
if (var) {} else { \
cstring tmp = cstring_persist(""cstr, (sizeof(cstr)/sizeof(char)-1)); \
if(!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&var, NULL, tmp)){ \
cstring_free_persist(tmp); \
} \
}
這個函數宏聲明變量都是 全局存儲區的變量,這裡認為是常量cstring.
但是cstr必須是 引起""引起宏.
這裡這個
cstring_persist(""cstr, (sizeof(cstr)/sizeof(char)-1));
""特別亮,在函數編譯的時候就能找出錯誤!第二參數 常量字符串最後一個字符的索引
後面 __sync_bool_compare_and_swap 是gcc 內置的原子函數,推薦用最新的gcc版本測試
詳細一點介紹是
bool __sync_bool_compare_and_swap (type *ptr, type oldval, type newval, ...);
__sync_bool_compare_and_swap 內置函數比較 oldval 和 *ptr。 如果它們匹配,就把 newval 復制到 *ptr。 此時返回返回值是 true,否則是 false.
這個函數 在並發編程中甩掉互斥鎖N條街.
4.1 函數解析,首先是cstring 如果需要把字符串做參數傳遞,就應該使用 cstring 類型,而不是 cstring_buffer 類型。
CSTRING(var) 可以把 var 這個 cstring_buffer 對象,轉換為 cstring 類型。
但是,在對 cstring_buffer 對象做新的操作後,這個 cstring 可能無效。
所以每次傳遞 cstring_buffer 內的值,最好都重新用 CSTRING 宏取一次。
函數調用的參數以及返回值,都應該使用 cstring 類型。
如果 cstring 是由外部傳入的,無法確定它的數據在棧上還是堆上,所以不能長期持有。
如果需要把 cstring 保存在數據結構中,可以使用這對 API :
cstring cstring_grab(cstring s); void cstring_release(cstring s);
把 cstring 轉化為標准的 const char * ,只需要用 s->cstr 即可。
cstring 的比較操作以及 hash 操作都比 const char * 廉價,所以,請使用以下 API :
int cstring_equal(cstring a, cstring b); uint32_t cstring_hash(cstring s);
這裡還有一個函數聲明
cstring cstring_printf(cstring_buffer sb, const char * format, ...)
#ifdef __GNUC__
__attribute__((format(printf, 2, 3)))
#endif
重點 是 後面的 __attribute__() 這也是個gcc 內置語法,是對編譯器編譯行為進行一些約定 , 這裡 format (printf, 2, 3)告訴編譯器,
cstring_printf的format相當於printf的format, 而可變參數是從cstring_printf的第3個參數開始。
這樣編譯器就會在編譯時用和printf一樣的check法則來確認可變參數是否正確了.
關於 gcc編譯器的控制行為,還是比較多的.自己可以搜索一下 gcc __attribute__,這些都很死,不是大神推薦不要用太多編譯器指令,不通用技巧性太強,容易東施效颦!
到這裡第一部分 基本就解釋 完畢了.
這裡再擴展一點 對於結構
struct cstring_data {
char * cstr;
uint32_t hash_size;
uint16_t type;
uint16_t ref;
};
後面使用的時候 常出現這樣的代碼
struct cstring_data *p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sz + 1);
// todo: memory alloc error
assert(p);
void * ptr = (void *)(p + 1);
p->cstr = ptr;
p->type = 0;
p->ref = 1;
memcpy(ptr, cstr, sz);
((char*)ptr)[sz] = '\0';
p->hash_size = 0;
這裡的一個技巧是 直接一次 malloc 將兩個 內存都分配好了 .
第一個 sizeof (struct cstring_data) 是給 p用的,
第二個 sizeof (struct cstring_data) + sz + 1 給 p->cstr 用的,.
對於這個技巧還用更 巧的是
struct cstring_data {
uint32_t hash_size;
uint16_t type;
uint16_t ref;
char [] cstr;
};
這種結構 聲明方式和方式一樣
struct cstring_data *p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sz + 1);
下面這種方式和上面比有點 內存更小了, 小了 sizeof (cstr).
不要在C中問出,少了4字節有什麼意義,那只能推薦你去學java吧.
但是 為什麼 雲風沒有這麼干呢. 是這樣的 後面 那種聲明方式為不完全類型, 有點 像
void* arg;
內存只能通過堆分配,不在在棧上分配,而 cstring 需要運用棧內存,具體看下面宏.
#define CSTRING_BUFFER(var) \
char var##_cstring[CSTRING_STACK_SIZE] = { '\0' }; \
struct cstring_data var##_cstring_data = { var##_cstring, 0, CSTRING_ONSTACK, 0 }; \
cstring_buffer var; \
var->str = &var##_cstring_data;
這裡 再擴展一下,吐槽一下 雲風前輩
struct cstring_data *p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sz + 1);
// todo: memory alloc error
assert(p);
第一次見這樣代碼,看一遍覺得好,屌.
看第二遍 有點不對吧.
看第三遍 確定 這樣是 用錯了assert, assert 在 開啟 NDEBUG 會失效.
假如 程序正式跑了,設置了
gcc -Wall -INDEBUG -o $^ $@
上面代碼 assert 就等同於
#ifdef NDEBUG
#define assert(expression) ((void)0)
#endif
那麼程序 假如 另一個 BUG,將 內存吃完了,這裡 就是 未定義 修改 未知內存,基本是返回NULL,操作NULL,程序崩了.
服務器當了,查原因 還沒日志...... 這是 不好的, 反正是 他用錯了
還是用下面這樣質樸的代碼吧
struct cstring_data *p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sz + 1);
// todo: memory alloc error
if(NULL == p) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d][%s][error:malloc struct cstring_data return NULL!]",__FILE__, __LINE__, __func__) ;
return NULL;
}
上面寫的比較簡單,還需要錯誤輸出需要考慮時間.
第二部分 寫一個簡單例子 直接用雲風 的 test.c
#include "cstring.h"
#include <stdio.h>
static cstring
foo(cstring t) {
CSTRING_LITERAL(hello, "hello");
CSTRING_BUFFER(ret);
if (cstring_equal(hello,t)) {
cstring_cat(ret, "equal");
} else {
cstring_cat(ret, "not equal");
}
return cstring_grab(CSTRING(ret));
}
static void
test() {
CSTRING_BUFFER(a);
cstring_printf(a, "%s", "hello");
cstring b = foo(CSTRING(a));
printf("%s\n", b->cstr);
cstring_printf(a, "very long string %01024d",0);
printf("%s\n", CSTRING(a)->cstr);
CSTRING_CLOSE(a);
cstring_release(b);
}
int
main() {
test();
return 0;
}
我們采用 Ubuntu 測試一下
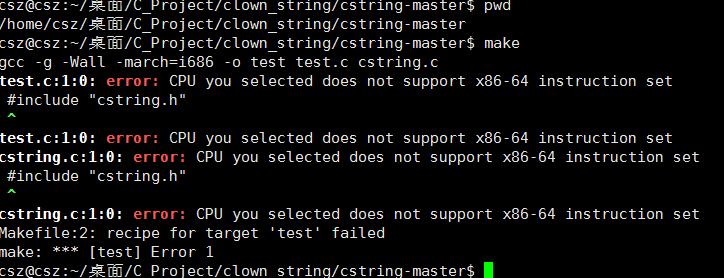
編譯失敗,按照下面改
vim Makefile gcc -g -Wall -march=native -o test test.c cstring.c Esc wq!
最後結果如下
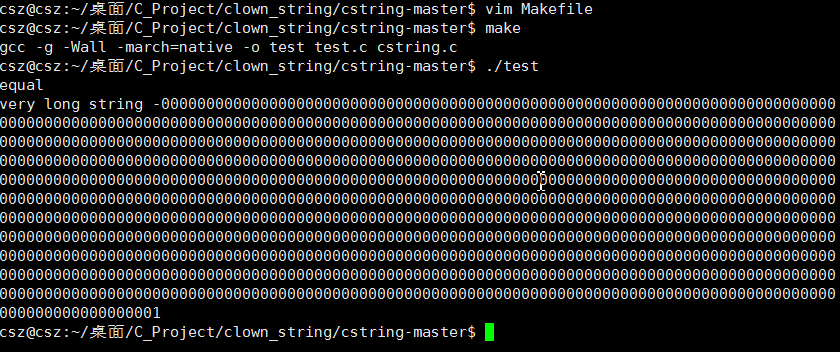
到這裡 我們 代碼 已經跑起來了. 對於 test.c中
我們簡單 解釋一下 其中 test.c使用到的 api
CSTRING_BUFFER(a);
cstring_printf(a, "%s", "hello");
一開a字符串在棧上,後面輸出的串比較小,仍然在棧上.後面有個
CSTRING_CLOSE(a);
關閉這個內存,本質是
#define CSTRING_CLOSE(var) \
if ((var)->str->type != 0) {} else \
cstring_release((var)->str);
因為 a->str->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK != 0 所以 cstring_release執行後沒有反應,可有可無.
但是 推薦 CSTRING_BUFFER 和 CSTRING_CLOSE 成對出現.
還有就是 foo 函數裡面
CSTRING_LITERAL(hello, "hello");
CSTRING_BUFFER(ret);
hello 相當於 符號表中字符串,生存周期是 和程序同生共死的.ret 目前在棧上.
後面
if (cstring_equal(hello,t)) {
cstring_cat(ret, "equal");
} else {
cstring_cat(ret, "not equal");
}
這個二者 執行 的 cstring_cat(ret, "equal"); 結果是 塞得字符串小 ret仍然是棧上的.
後面返回
return cstring_grab(CSTRING(ret));
變成運行時串 既
cs->type = CSTRING_INTERNING;
cs->ref = 0;
所以最後 就不需要 CSTRING_CLOSE (ret);
到了
cstring_printf(a, "very long string %01024d",0);
變成待釋放的臨時串 r->type = 0; r->ref = 1;
技巧很多,主要還是需要看 源碼, 將在第三部剖析一下 實現 string.c中的一些技巧!
第三部分 string.c 源碼 觀察
#include "cstring.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#define FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE 1024
#define INTERNING_POOL_SIZE 1024
// HASH_START_SIZE must be 2 pow
#define HASH_START_SIZE 16
struct string_node {
struct cstring_data str;
char buffer[CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE];
struct string_node * next;
};
struct string_pool {
struct string_node node[INTERNING_POOL_SIZE];
};
struct string_interning {
int lock;
int size;
struct string_node ** hash;
struct string_pool * pool;
int index;
int total;
};
static struct string_interning S;
static inline void
LOCK() {
while (__sync_lock_test_and_set(&(S.lock),1)) {}
}
static inline void
UNLOCK() {
__sync_lock_release(&(S.lock));
}
static void
insert_node(struct string_node ** hash, int sz, struct string_node *n) {
uint32_t h = n->str.hash_size;
int index = h & (sz-1);
n->next = hash[index];
hash[index] = n;
}
static void
expand(struct string_interning * si) {
int new_size = si->size * 2;
if (new_size < HASH_START_SIZE) {
new_size = HASH_START_SIZE;
}
assert(new_size > si->total);
struct string_node ** new_hash = malloc(sizeof(struct string_node *) * new_size);
memset(new_hash, 0, sizeof(struct string_node *) * new_size);
int i;
for (i=0;i<si->size;i++) {
struct string_node *node = si->hash[i];
while (node) {
struct string_node * tmp = node->next;
insert_node(new_hash, new_size, node);
node = tmp;
}
}
free(si->hash);
si->hash = new_hash;
si->size = new_size;
}
static cstring
interning(struct string_interning * si, const char * cstr, size_t sz, uint32_t hash) {
if (si->hash == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
int index = (int)(hash & (si->size-1));
struct string_node * n = si->hash[index];
while(n) {
if (n->str.hash_size == hash) {
if (strcmp(n->str.cstr, cstr) == 0) {
return &n->str;
}
}
n = n->next;
}
// 80% (4/5) threshold
if (si->total * 5 >= si->size * 4) {
return NULL;
}
if (si->pool == NULL) {
// need not free pool
// todo: check memory alloc error
si->pool = malloc(sizeof(struct string_pool));
assert(si->pool);
si->index = 0;
}
n = &si->pool->node[si->index++];
memcpy(n->buffer, cstr, sz);
n->buffer[sz] = '\0';
cstring cs = &n->str;
cs->cstr = n->buffer;
cs->hash_size = hash;
cs->type = CSTRING_INTERNING;
cs->ref = 0;
n->next = si->hash[index];
si->hash[index] = n;
return cs;
}
static cstring
cstring_interning(const char * cstr, size_t sz, uint32_t hash) {
cstring ret;
LOCK();
ret = interning(&S, cstr, sz, hash);
if (ret == NULL) {
expand(&S);
ret = interning(&S, cstr, sz, hash);
}
++S.total;
UNLOCK();
assert(ret);
return ret;
}
static uint32_t
hash_blob(const char * buffer, size_t len) {
const uint8_t * ptr = (const uint8_t *) buffer;
size_t h = len;
size_t step = (len>>5)+1;
size_t i;
for (i=len; i>=step; i-=step)
h = h ^ ((h<<5)+(h>>2)+ptr[i-1]);
if (h == 0)
return 1;
else
return h;
}
void
cstring_free_persist(cstring s) {
if (s->type == CSTRING_PERMANENT) {
free(s);
}
}
static cstring
cstring_clone(const char * cstr, size_t sz) {
if (sz < CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE) {
return cstring_interning(cstr, sz, hash_blob(cstr,sz));
}
struct cstring_data * p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sz + 1);
// todo: memory alloc error
assert(p);
void * ptr = (void *)(p + 1);
p->cstr = ptr;
p->type = 0;
p->ref = 1;
memcpy(ptr, cstr, sz);
((char *)ptr)[sz] = '\0';
p->hash_size = 0;
return p;
}
cstring
cstring_persist(const char * cstr, size_t sz) {
cstring s = cstring_clone(cstr, sz);
if (s->type == 0) {
s->type = CSTRING_PERMANENT;
s->ref = 0;
}
return s;
}
cstring
cstring_grab(cstring s) {
if (s->type & (CSTRING_PERMANENT | CSTRING_INTERNING)) {
return s;
}
if (s->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK) {
cstring tmp = cstring_clone(s->cstr, s->hash_size);
return tmp;
} else {
if (s->ref == 0) {
s->type = CSTRING_PERMANENT;
} else {
__sync_add_and_fetch(&s->ref,1);
}
return s;
}
}
void
cstring_release(cstring s) {
if (s->type != 0) {
return;
}
if (s->ref == 0) {
return;
}
if (__sync_sub_and_fetch(&s->ref,1) == 0) {
free(s);
}
}
uint32_t
cstring_hash(cstring s) {
if (s->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK)
return hash_blob(s->cstr, s->hash_size);
if (s->hash_size == 0) {
s->hash_size = hash_blob(s->cstr, strlen(s->cstr));
}
return s->hash_size;
}
int
cstring_equal(cstring a, cstring b) {
if (a == b)
return 1;
if ((a->type == CSTRING_INTERNING) &&
(b->type == CSTRING_INTERNING)) {
return 0;
}
if ((a->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK) &&
(b->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK)) {
if (a->hash_size != b->hash_size) {
return 0;
}
return memcmp(a->cstr, b->cstr, a->hash_size) == 0;
}
uint32_t hasha = cstring_hash(a);
uint32_t hashb = cstring_hash(b);
if (hasha != hashb) {
return 0;
}
return strcmp(a->cstr, b->cstr) == 0;
}
static cstring
cstring_cat2(const char * a, const char * b) {
size_t sa = strlen(a);
size_t sb = strlen(b);
if (sa + sb < CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE) {
char tmp[CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE];
memcpy(tmp, a, sa);
memcpy(tmp+sa, b, sb);
tmp[sa+sb] = '\0';
return cstring_interning(tmp, sa+sb, hash_blob(tmp,sa+sb));
}
struct cstring_data * p = malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + sa + sb + 1);
// todo: memory alloc error
assert(p);
char * ptr = (char *)(p + 1);
p->cstr = ptr;
p->type = 0;
p->ref = 1;
memcpy(ptr, a, sa);
memcpy(ptr+sa, b, sb);
ptr[sa+sb] = '\0';
p->hash_size = 0;
return p;
}
cstring
cstring_cat(cstring_buffer sb, const char * str) {
cstring s = sb->str;
if (s->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK) {
int i = (int)s->hash_size;
while (i < CSTRING_STACK_SIZE-1) {
s->cstr[i] = *str;
if (*str == '\0') {
return s;
}
++s->hash_size;
++str;
++i;
}
s->cstr[i] = '\0';
}
cstring tmp = s;
sb->str = cstring_cat2(tmp->cstr, str);
cstring_release(tmp);
return sb->str;
}
static cstring
cstring_format(const char * format, va_list ap) {
static char * cache = NULL;
char * result;
char * temp = cache;
// read cache buffer atomic
if (temp) {
temp = __sync_val_compare_and_swap(&cache, temp, NULL);
}
if (temp == NULL) {
temp = (char *)malloc(FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE);
// todo : check malloc
assert(temp);
}
int n = vsnprintf(temp, FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE, format, ap);
if (n >= FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE) {
int sz = FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE * 2;
for (;;) {
result = malloc(sz);
// todo : check malloc
assert(result);
n = vsnprintf(result, sz, format, ap);
if (n >= sz) {
free(result);
sz *= 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
} else {
result = temp;
}
cstring r = (cstring)malloc(sizeof(struct cstring_data) + n + 1);
// todo : check malloc
assert(r);
r->cstr = (char *)(r+1);
r->type = 0;
r->ref = 1;
r->hash_size = 0;
memcpy(r->cstr, result, n+1);
if (temp != result) {
free(result);
}
// save temp atomic
if (!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&cache, NULL, temp)) {
free(temp);
} else {
}
return r;
}
cstring
cstring_printf(cstring_buffer sb, const char * format, ...) {
cstring s = sb->str;
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, format);
if (s->type == CSTRING_ONSTACK) {
int n = vsnprintf(s->cstr, CSTRING_STACK_SIZE, format, ap);
if (n >= CSTRING_STACK_SIZE) {
s = cstring_format(format, ap);
sb->str = s;
} else {
s->hash_size = n;
}
} else {
cstring_release(sb->str);
s = cstring_format(format, ap);
sb->str = s;
}
va_end(ap);
return s;
}
上面就是 cstring.c的源碼 . 總的而言還是比較短的容易理解 ,我們依次分析. 扯一點,
他這些技巧我都會,還敲了兩三遍. 因為他用的比我熟練.假如你看到這, 你需要 敲更多,才能掌握,C的技巧也挺難的.真的
搞起來就和算術公式一樣.
首先分析數據結構,基本就是流水賬了
/**
* todo insert explain
*
* FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE 是後面函數 cstring_format 分配內存初始化大小 1k
*
* INTERNING_POOL_SIZE 表示 符號表池的大小 1k
*
* HASH_START_SIZE hash操作在expand中使用,插入hash使用,是 a mod b 中b的初始化值
*/
#define FORMAT_TEMP_SIZE 1024
#define INTERNING_POOL_SIZE 1024
// HASH_START_SIZE must be 2 pow
#define HASH_START_SIZE 16
/**
* todo insert explain
*
* 這是一個字符串鏈表, hash采用桶和鏈表實現,這就是鏈表.
* char buffer[CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE];內存在棧上 ,直接 給 string_node.str.cstr
* struct string_node保存運行中字符串,直接和 程序同生存周期
*/
struct string_node {
struct cstring_data str;
char buffer[CSTRING_INTERNING_SIZE];
struct string_node * next;
};
/*
* todo insert explain
*
* string_node 的 池,這個吃的大小是固定的,1k,過了程序會異常
*/
struct string_pool {
struct string_node node[INTERNING_POOL_SIZE];
};
/**
* 這是 字符串 池
*
* lock 加鎖用的
* size hash的大小,圍繞他取余做hash
* hash 保存字符串的對象
* pool 符號表存儲的地方
* index 內部指示 pool使用到哪了
* total 指示當前 string_interning 中保存了多少 字符串運行時常量
*/
struct string_interning {
int lock;
int size;
struct string_node ** hash;
struct string_pool * pool;
int index;
int total;
};
// 全局臨時用的 字符串池對象
static struct string_interning S;
// 加鎖
static inline void
LOCK() {
while (__sync_lock_test_and_set(&(S.lock), 1)) {}
}
//解鎖 具體參照 原子參照
static inline void
UNLOCK() {
__sync_lock_release(&(S.lock));
}
這裡擴展一下 就相當於吐槽,首先 關於
S.index 用法 局限性很大
if (si->pool == NULL) {
// need not free pool
//todo : check memory alloc error
si->pool = malloc(sizeof(struct string_pool));
assert(si->pool);
si->index = 0;
}
n = &si->pool->node[si->index++];
全局只用++,相當於只生產字符串,只增不減. 超過了 1024 程序就崩了. 內存訪問越界. 這裡 我們在下一篇博文中
重構這個字符串.思路有兩個
1. 打錯誤日志, 加大錯誤 警報作用
2. 改變 string_interning 結構, 讓其也支持自動擴容處理.
吐槽一下, 他這裡 寫的不好, 這樣的代碼 , 根本不敢掛上服務器跑. 到時候再優化,保證讓其從玩具變成高級玩具.
這裡 再吐槽一下 關於 gcc inline 用法. 具體看 推薦的 參照資料. inline 只能用於簡單的 順序結構函數.
否則 這樣聲明編譯器也還是讓其 變為 普通函數.
測試如下,采用window 匯編,linux 也一樣 通過 gcc -S 看 匯編.
測試 main.c 如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int g_cut = 0;
__inline void cnotcplusplus(void)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
++g_cut;
//測試三 VS能夠使用內聯
//++ g_cut;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("g_cut = %d\n", g_cut);
/*
*測試一
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
++g_cut;
/*
* 測試二 內聯函數 匯編代碼對比
*/
cnotcplusplus();
printf("g_cut = %d\n", g_cut);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
編譯環境是
這裡運行打斷點 查看 匯編 如下
--- h:\vs_project\clouwu_string\test_inline\main.c -----------------------------
printf("g_cut = %d\n", g_cut);
012A1040 push dword ptr [g_cut (012A3374h)]
012A1046 push offset string "g_cut = %d\n" (012A2108h)
012A104B call printf (012A1010h)
/*
*測試一
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
++g_cut;
012A1050 mov eax,dword ptr [g_cut (012A3374h)]
/*
* 測試二 內聯函數 匯編代碼對比
*/
cnotcplusplus();
012A1055 add eax,14h
printf("g_cut = %d\n", g_cut);
012A1058 push eax
012A1059 push offset string "g_cut = %d\n" (012A2108h)
/*
* 測試二 內聯函數 匯編代碼對比
*/
cnotcplusplus();
012A105E mov dword ptr [g_cut (012A3374h)],eax
printf("g_cut = %d\n", g_cut);
012A1063 call printf (012A1010h)
system("pause");
012A1068 push offset string "pause" (012A2114h)
system("pause");
012A106D call dword ptr [__imp__system (012A2064h)]
012A1073 add esp,14h
return 0;
012A1076 xor eax,eax
}
大家可以自己測試測試,這裡測試結果 關於 inline 函數中出現 while 編譯器 會將這個 inline函數當做 普通函數處理.
這是一個失誤,如果 一定要這麼干, 可以用 宏代替,下一個版本再搞. 這個字符串博文拖得太長了,准備就當下 草草干掉了. 爭取下一個版本
帶來一個高級的玩具.
/* * 將字符串結點n 插入 到 字符串hash表中 * * h & (sz -1) => h mod sz, 當然 sz 必須 是 2 正整數次冪 */ static inline void insert_node(struct string_node ** hash, int sz, string_node *n) ; /* * 對 S 中初始化或 擴容的函數 * 會重新hash操作,調整結構 */ static void expand(struct string_interning * si); /* * 插入 一個字符串到 字符串池中,線程安全,運行時不安全 */ static cstring cstring_interning(const char * cstr, size_t sz, uint32_t hash); /* * js hash 命中率 為 80%左右 * 這裡 對於 h == 0,即hash_size == 0做特殊處理,待定,沒有比較久不需要生成 */ static uint32_t hash_blob(const char * buffer, size_t len);
這裡簡單說一下對於 expand 中
int new_size = si->size * 2;
if (new_size < HASH_START_SIZE) {
new_size = HASH_START_SIZE;
}
第二個判斷可以省略,放在 S 的聲明的初始化中. 其它的改進不提了,自己看,多看看都能有見解. 這裡擴展一下, 剛對 他的寫的代碼.
還是 能感覺一股鋪面而來的代碼 美感, 能感覺都很多都是手工敲的. 他的美感 多於他的失誤. 但是 這樣的代碼是不能用在實戰中,為什麼呢,
你用這個代碼,你看幾遍這個源碼.用起來內存洩露的都無法控制了. 這也是很多開源的代碼,不是領頭羊,很少敢直接用於 核心模塊中,除非 別無選擇.
因為 維護的人沒時間, 而自己不是作者,改起來成本比開發一個更高.總而言之,開源和封閉 是 兩種模式 最鮮明對比就是 安卓 與 ios.
繼續,
/* * 釋放永久串, 相當於 釋放 'static' string */ void cstring_free_persist(cstring s) ; /* * 這裡 復制一份字符串, * type =0 , 表示 未初始化, 這樣串可以可以被 cstring_release釋放 */ static cstring cstring_clone(const char * cstr, size_t sz) ; /* * 申請這樣的永久的串 */ cstring cstring_persist(const char * cstr, size_t sz) ; /* * 將棧上串 搞一份出來到 普通串中需要調用 釋放函數 CSTRING_CLOSE * 如果 是 永久串 直接 變成 引用加1 */ cstring cstring_grab(cstring s) ; /* * 釋放函數.只有 type == 0 && s->ref == 1才去釋放 */ void cstring_release(cstring s);
這裡再擴展一下 看 cstring.h 中宏
#define CSTRING_LITERAL(var, cstr) \
static cstring var = NULL; \
if (var) {} else { \
cstring tmp = cstring_persist(""cstr, (sizeof(cstr)/sizeof(char)-1)); \
if(!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&var, NULL, tmp)){ \
cstring_free_persist(tmp); \
} \
}
這也是個技巧,如何創建 靜態 堆上 常用變量. 相當於 通過 CSTRING_LITERAL 創建 靜態的字符串 var 變量
並聲明了內存. 雲風就是在秀技巧的. 反正也是學到了,下次自己也用用.
後面還有字符串拼接,這就是 相當於 字符串重構,性能差. 也是為什麼要有 StringBuilder 的原因
/** * * 就是一個簡單的字符串拼接函數,比較低效 * * 這裡有個優化 是 如果串比較直接放在棧上 */ static cstring cstring_cat2(const char *a, const char * b) ; /* * 先自己拼接一下 啥也沒解決 最後給 cstring_cat2 */ cstring cstring_cat(cstring_buffer sb, const char *str) ;
更多的細節 需要看 源碼. 最後 分析 string_printf 函數
/* * 找到固定大小 塞數據進來 */ static cstring cstring_format(const char * format, va_list ap) ; /* * 按照標准輸出到 sb中,sb內存不夠會給它分配 通過 cstring_format */ cstring cstring_printf(cstring_buffer sb, const char *format, ...) ;
到這裡 源碼 是看完了.
多寫幾遍都明白了. 不好意思 太晚了不擴展了,(後面有點忽悠了, 明天還要上班.)
後記
到這裡 錯誤是難免的,歡迎指正立馬改. 下一篇中 會對cstring 進行重構. 解決 雲風的坑.
最後想說一句, char * 夠用了, 真的,C開發沒有那麼多復雜的.
我很水,但我 會改正的, 歡迎批評.