前言
建議13、為類型輸出格式化字符串
建議14、正確實現淺拷貝和深拷貝
建議15、使用dynamic來簡化反射實現
建議13、為類型輸出格式化字符串
有兩種方法可以為類型提供格式化的字符串輸出。
一種是意識到類型會產生格式化字符串輸出,於是讓類型繼承接口IFormattable。這對類型來說,是一種主動實現的方式,要求開發者可以預見類型在格式化方面的要求。
更多的時候,類型的使用者需為類型自定義格式化器,這就是第二種方法,也是最靈活多變的方法,可以根據需求的變化為類型提供多個格式化器。
下面我們就來看一下這兩種方式的實現。
最簡單的字符串輸出是為類型重寫ToString()方法,如果沒有為類型重寫該方法,默認會調用Ojbect的ToString方法,它會返回當前類型的類型名稱。但即使是重寫了ToString()方法,提供的字符串輸出也是非常單一的,而通過實現IFormattable接口的ToString()方法,可以讓類型根據用戶的輸入而格式化輸出。
下面我們來看一個簡單的小例子:

public class Person:IFormattable
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 實現接口Iformattable的方法ToString
/// </summary>
/// <param name="format"></param>
/// <param name="formatProvider"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public string ToString(string format, IFormatProvider formatProvider)
{
switch (format)
{
case"Ch":
return this.ToString();
case"Eg":
return string.Format("{0}{1}", this.FirstName, this.LastName);
default:
return
this.ToString();
}
}
///重寫Object的方法ToString()
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}{1}",this.LastName,this.FirstName);
}
}

調用代碼如下所示:

static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person() { FirstName="Kris",LastName="aehyok"};
Console.WriteLine(person);
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString("Ch",null));
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString("Eg", null));
Console.ReadLine();
}

調用執行結果如下:
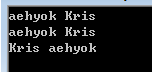
下面我們來繼續介紹第二實現方式——格式化器。如果類型本身沒有提供格式化的功能,那麼格式化器就可以派上用場了。格式化器的好處就是可以根據需求的變化,隨時增加或者修改它。
接下來我們繼續來看另外的一個小例子:
首先定義一個實體類Person:
public class Person
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
一個典型的格式化器應該繼承IFormatProvider和ICustomerFormatter,看代碼:

public class PersonFomatter:IFormatProvider,ICustomFormatter
{
#region IFormatProvider成員
public object GetFormat(Type formatType)
{
if (formatType == typeof(ICustomFormatter))
{
return this;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
#endregion
#region ICustomFormatter成員
public string Format(string format, object arg, IFormatProvider formatProvider)
{
Person person = arg as Person;
if (person == null)
{
return string.Empty;
}
switch (format)
{
case"Ch":
return string.Format("{0} {1}",person.LastName,person.FirstName);
case"":
return string.Format("{0} {1}",person.FirstName,person.LastName);
case"CHM":
return string.Format("{0} {1}:{2}", person.LastName, person.FirstName, person.IDCode);
default:
return string.Format("{0} {1}", person.LastName, person.FirstName);
}
}
#endregion
}

調用代碼如下:

class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person() { FirstName="Kris", LastName="aehyok", IDCode="ID000001"};
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString());
PersonFomatter pFomatter = new PersonFomatter();
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("Ch", person, null));
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("Eg", person, null));
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("CHM", person, null));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}

調用執行結果如下:
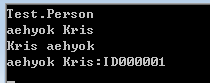
其實還有另外一種變通的形式,就是將這兩種方式合並一起使用的過程,下面來看一下具體的實現代碼:

public class Person:IFormattable
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 實現接口Iformattable的方法ToString
/// </summary>
/// <param name="format"></param>
/// <param name="formatProvider"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public string ToString(string format, IFormatProvider formatProvider)
{
switch (format)
{
case"Ch":
return this.ToString();
case"Eg":
return string.Format("{0}{1}", this.FirstName, this.LastName);
default:
//return this.ToString();
ICustomFormatter customerFormatter = formatProvider as ICustomFormatter;
if (formatProvider == null)
{
return this.ToString();
}
return customerFormatter.Format(format, this, null);
}
}
///重寫Object的方法ToString()
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}{1}",this.LastName,this.FirstName);
}
}

PersonFomatter自定義格式化器的代碼並沒有發生任何的改變。
調用代碼如下:

static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person person = new Person() { FirstName="Kris", LastName="aehyok", IDCode="ID000001"};
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString());
PersonFomatter pFomatter = new PersonFomatter();
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("Ch", person, null));
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("Eg", person, null));
Console.WriteLine(pFomatter.Format("CHM", person, null));
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString("Ch",pFomatter));
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString("Eg", pFomatter));
Console.WriteLine(person.ToString("CHM", pFomatter));
Console.ReadLine();
}

調用執行結果如下所示:
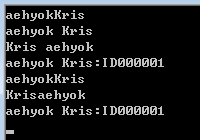
建議14、正確實現淺拷貝和深拷貝
為對象創建副本的技術成為拷貝(也叫克隆)。我們將拷貝分為淺拷貝和深拷貝。
淺拷貝 將對象中的所有字段復制到新的對象(副本)中。其中,值類型字段的值被復制到副本中後,在副本中的修改不會影響到源對象對應的值。 而引用類型的字段被復制到副本中的是引用類型的引用,而不是引用的對象,在副本中對引用類型的字段值做修改會影響到源對象本身。
深拷貝 同樣,將對象中的所有字段復制到新的對象中。不過無論是對象的值類型字段,還是引用類型字段,都會被重新創建並賦值,對於副本的修改,不會影響到源對象本身。
無論是淺拷貝還是深拷貝,微軟都建議用類型繼承ICloneable接口的方式明確告訴調用者:該類型可以被拷貝。當然,ICloneable接口只提供了一個聲明為Clone的方法,我們可根據需求在Clone方法內實現淺拷貝或深拷貝。一個簡答的淺拷貝的實現代碼如下所示:
首先定義實體類:

public class Employee:ICloneable
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public Department Department { get; set; }
#region OCloneable成員
public object Clone()
{
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
#endregion
}
public class Department
{
public string Name{get;set;}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.Name;
}
}

然後進行調用代碼如下:

static void Main(string[] args)
{
Employee Niki = new Employee()
{
IDCode = "IDaehyok",
Age = 25,
Department = new Department() { Name="Depart1" }
};
Employee Kris = Niki.Clone() as Employee;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("IDCode:{0}\tAge:{1}\tDepartment:{2}", Kris.IDCode, Kris.Age, Kris.Department));
///開始改變Niki的值
Niki.IDCode = "IDNiki";
Niki.Age = 23;
Niki.Department.Name = "Depart2";
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("IDCode:{0}\tAge:{1}\tDepartment:{2}", Kris.IDCode, Kris.Age, Kris.Department));
Console.ReadLine();
}

調用執行結果如下
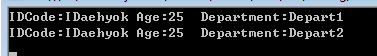
注意到Employee的IDCode屬string類型。理論上string類型是引用類型,但是由於該引用類型的特殊性(無論是實際還是語義),Object.MemberwiseClone方法仍舊為其創建了副本。也就是說,在淺拷貝過程,我們應該將字符串看成是值類型。Employee的Department屬性是一個引用類型,所以,如果改變了源對象Niki中的值,那麼副本Kris中的值也會隨之一起變動。
Employee的深拷貝有多種實現方法,最簡單的方式是手動的對字段進行逐個的賦值。但是這種方法容易出錯,也就是說,如果類型的字段發生變化或有增減,那麼該拷貝方法也要發生相應的變化,所以,建議使用序列化的形式來進行深拷貝。Employee深拷貝的一種實現方式如下:

[Serializable]
public class Employee:ICloneable
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public Department Department { get; set; }
#region OCloneable成員
public object Clone()
{
using (Stream objectstream = new MemoryStream())
{
IFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(objectstream, this);
objectstream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
return formatter.Deserialize(objectstream) as Employee;
}
}
#endregion
}
[Serializable]
public class Department
{
public string Name{get;set;}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.Name;
}
}

調用方法如下所示:

Employee Niki = new Employee()
{
IDCode = "IDaehyok",
Age = 25,
Department = new Department() { Name="Depart1" }
};
Employee Kris = Niki.Clone() as Employee;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("IDCode:{0}\tAge:{1}\tDepartment:{2}", Kris.IDCode, Kris.Age, Kris.Department));
///開始改變Niki的值
Niki.IDCode = "IDNiki";
Niki.Age = 23;
Niki.Department.Name = "Depart2";
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("IDCode:{0}\tAge:{1}\tDepartment:{2}", Kris.IDCode, Kris.Age, Kris.Department));
Console.ReadLine();

最終代碼調用結果如下
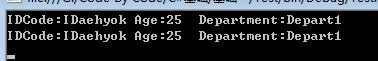
可以發現再次改變Niki的值,不會對副本Kris產生影響。
由於接口ICloneable,只有一個模稜兩可的方法,所以,如果要在一個類中進行淺拷貝和深拷貝,只能由我們額外的實現兩個方法。聲明為DeepClone和Shallow。那麼最終代碼如下所示:

[Serializable]
public class Employee:ICloneable
{
public string IDCode { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public Department Department { get; set; }
#region OCloneable成員
public object Clone()
{
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
#endregion
public Employee DeeptClone()
{
using (Stream objectstream = new MemoryStream())
{
IFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(objectstream, this);
objectstream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
return formatter.Deserialize(objectstream) as Employee;
}
}
public Employee Shallow()
{
return Clone() as Employee;
}
}

建議15、使用dynamic來簡化反射實現
Dynamic是Framework4.0的新特性。dynamic的出現讓C#具有了弱類型的特性。編譯器在編譯的時候不再對類型進行檢查,編譯器默認dynamic對象支持開發者想要的任何類型。如果運行時不包含指定的特性,運行時程序會拋出一個RuntimeBinderException異常。
下面我們先來看一個簡單的例子

public class DynamicSample
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}

現在我們想調用上面實體類的Add方法,實現方式可以是這樣的:
DynamicSample dynamicSample = new DynamicSample();
var addMethod = typeof(DynamicSample).GetMethod("Add");
int re = (int)addMethod.Invoke(dynamicSample, new object[] { 1, 2 });
Console.WriteLine(re);
下面我們再通過使用dynamic來實現一下:
dynamic dynamic = new DynamicSample();
int re2 = dynamic.Add(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine(re2);
可以發現dynamic的實現方式很簡潔,而且性能也有所提升,當然上面一次的調用我們是看不出什麼效果的,假如上面的代碼我們進行調用了10000000次。

int times = 10000000;
////第一種調用方式
DynamicSample reflectSample = new DynamicSample();
var addMethod = typeof(DynamicSample).GetMethod("Add");
Stopwatch watch1 = Stopwatch.StartNew();///用於測試運行時間
for (var i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
addMethod.Invoke(reflectSample, new object[] { 1, 2 });
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("普通方法反射耗時:{0} 毫秒", watch1.ElapsedMilliseconds));
////第二種調用方式
dynamic dynamicSample = new DynamicSample();
Stopwatch watch2 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
dynamicSample.Add(1, 2);
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("dynamic方式耗時:{0} 毫秒", watch2.ElapsedMilliseconds));
////第三種調用方式
DynamicSample reflectSampleBetter = new DynamicSample();
var addMethod2 = typeof(DynamicSample).GetMethod("Add");
var delg = (Func<DynamicSample, int, int, int>)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Func<DynamicSample, int, int, int>), addMethod2);
Stopwatch watch3 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (var i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
delg(reflectSampleBetter, 1, 2);
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("優化的反射耗時:{0} 毫秒", watch3.ElapsedMilliseconds));
Console.ReadLine();

調用執行後的結果為
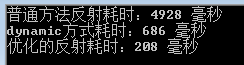
現在可以看出很明顯的區別,普通方法調用發射執行效率遠遠的低於使用dynamic。第三種方式是我們優化了發射之後的執行時間,比使用dynamic也有所提升,但是並不是特別明顯,雖然帶來了性能的提升,不過卻犧牲了代碼的整潔性。這種實現方式在我看來是得不償失的。所以建議大家使用dynamic來優化發射。
到這裡為止,第一章的內容暫時已經整理完畢,感覺自己學了不少知識,繼續加油,接下來繼續進行第二章集合和LINQ的學習。