學習C#線程。本站提示廣大學習愛好者:(學習C#線程)文章只能為提供參考,不一定能成為您想要的結果。以下是學習C#線程正文
2016-12-17
有意間看到了關於C#線程的解說。經過一下午的學習後,漸漸的對線程也有了一定的了解。這裡解說的是最根底的內容,包括線程的創立、睡眠、等候、終止。
實驗環境:Visual studio 2010.
運用言語:C#
內容:創立、睡眠、等候、中止線程
1.創立新線程對象 Thread t=new Thread();
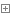

1 using System;
2 using System.Threading;
3 using System.Collections.Generic;
4 using System.Linq;
5 using System.Text;
6
7 namespace 線程學習
8 {
9 class Program
10 {
11 static void PrintNumbers()
12 {
13
14 Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
15 for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
16 {
17 Console.WriteLine(i);
18 }
19 }
20
21 static void Main(string[] args)
22 {
23 Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbers);
24 t.Start();
25 PrintNumbers();
26 }
27 }
28 }
View Code
經過Thread t=new Thread創立新對象後,t為子線程,t.Start()開端執行子線程,子線程執行結構對象中的PrintNumber()函數,父線程執行下一行的PrintNumbers()函數,兩線程並發,所以後果不定。
2.線程睡眠 調用Slee()函數,選擇讓線程暫時“睡眠“


using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace 線程學習
{
class Program
{
static void PrintNumbers()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i+"父線程");
}
}
static void PrintNumbersWithDelay()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
Console.WriteLine(i+"子線程");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbersWithDelay);
t.Start();
PrintNumbers();
}
}
}
View Code
創立線程後,子線程t執行PrintNumbersWithDelay()函數,其中每循環一次就睡眠一秒,父線程執行下一行的PrintNumbers()函數,兩線程並發執行。
3.線程等候 調用join()函數,讓線程依照想要的順序執行


1 using System;
2 using System.Threading;
3 using System.Collections.Generic;
4 using System.Linq;
5 using System.Text;
6 namespace 線程學習
7 {
8 class Program
9 {
10 static void PrintNumberWithDelay()
11 {
12 Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
13 for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
14 {
15 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
16 Console.WriteLine(i);
17 }
18 }
19 static void PrintNumbers()
20 {
21 Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
22 for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
23 {
24 Console.WriteLine(i);
25 }
26 }
27 static void Main(string[] args)
28 {
29 Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
30 Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumberWithDelay);
31 t.Start();
32 t.Join();
33 PrintNumbers();
34 Console.WriteLine("Thread completed");
35 }
36 }
37 }
View Code
創立線程後,t.join()之後的語句(即父線程)必需等候之前的語句執行完後,才干執行。
4.線程終止 調用Abort()函數,殺死該線程。


using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace 線程學習
{
class Program
{
static void PrintNumbers()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
static void PrintNumberWithDelay()
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting...");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting Program..");
Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumberWithDelay);
t.Start();
t.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("A thread has been aborted");
t = new Thread(PrintNumbers);
t.Start();
PrintNumbers();
}
}
}
View Code
運用Abort()完畢子線程。前面的代碼跟後面例一相似