基於C#的socket編程的TCP異步的完成代碼。本站提示廣大學習愛好者:(基於C#的socket編程的TCP異步的完成代碼)文章只能為提供參考,不一定能成為您想要的結果。以下是基於C#的socket編程的TCP異步的完成代碼正文
一、摘要
本篇論述基於TCP通訊協議的異步完成。
二、實驗平台
Visual Studio 2010
三、異步通訊完成原理及常用辦法
3.1 樹立銜接
在同步形式中,在服務器上運用Accept辦法接入銜接懇求,而在客戶端則運用Connect辦法來銜接服務器。絕對地,在異步形式下,服務器可以運用BeginAccept辦法和EndAccept辦法來完成銜接到客戶端的義務,在客戶端則經過BeginConnect辦法和EndConnect辦法來完成與服務器的銜接。
BeginAccept在異步方式下傳入的銜接嘗試,它允許其他舉措而不用等候銜接樹立才持續執行前面順序。在調用BeginAccept之前,必需運用Listen辦法來偵聽能否有銜接懇求,BeginAccept的函數原型為:
BeginAccept(AsyncCallback AsyncCallback, Ojbect state)
參數:
AsyncCallBack:代表回調函數
state:表示形態信息,必需保證state中包括socket的句柄
運用BeginAccept的根本流程是:
(1)創立本地終節點,並新建套接字與本地終節點停止綁定;
(2)在端口上偵聽能否有新的銜接懇求;
(3)懇求開端接入新的銜接,傳入Socket的實例或許StateOjbect的實例。
參考代碼:
//定義IP地址
IPAddress local = IPAddress.Parse("127.0,0,1");
IPEndPoint iep = new IPEndPoint(local,13000);
//創立服務器的socket對象
Socket server = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp);
server.Bind(iep);
server.Listen(20);
server.BeginAccecpt(new AsyncCallback(Accept),server);
當BeginAccept()辦法調用完畢後,一旦新的銜接發作,將調用回調函數,而該回調函數必需包括用來完畢接入銜接操作的EndAccept()辦法。
該辦法參數列表為 Socket EndAccept(IAsyncResult iar)
上面為回調函數的實例:
void Accept(IAsyncResult iar)
{
//復原傳入的原始套接字
Socket MyServer = (Socket)iar.AsyncState;
//在原始套接字上調用EndAccept辦法,前往新的套接字
Socket service = MyServer.EndAccept(iar);
}
至此,服務器端曾經預備好了。客戶端應經過BeginConnect辦法和EndConnect來近程銜接主機。在調用BeginConnect辦法時必需注冊相應的回調函數並且至多傳遞一個Socket的實例給state參數,以保證EndConnect辦法中能運用原始的套接字。上面是一段是BeginConnect的調用:
Socket socket=new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp)
IPAddress ip=IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint iep=new IPEndPoint(ip,13000);
socket.BeginConnect(iep, new AsyncCallback(Connect),socket);
EndConnect是一種阻塞辦法,用於完成BeginConnect辦法的異步銜接诶近程主機的懇求。在注冊了回調函數後必需接納BeginConnect辦法前往的IASynccReuslt作為參數。上面為代碼演示:
void Connect(IAsyncResult iar)
{
Socket client=(Socket)iar.AsyncState;
try
{
client.EndConnect(iar);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
finally
{
}
}
除了采用上述辦法樹立銜接之後,也可以采用TcpListener類外面的辦法停止銜接樹立。上面是服務器端對關於TcpListener類運用BeginAccetpTcpClient辦法處置一個傳入的銜接嘗試。以下是運用BeginAccetpTcpClient辦法和EndAccetpTcpClient辦法的代碼:
public static void DoBeginAccept(TcpListener listner)
{
//開端從客戶端監聽銜接
Console.WriteLine("Waitting for a connection");
//接納銜接
//開端預備接入新的銜接,一旦有新銜接嘗試則調用回調函數DoAcceptTcpCliet
listner.BeginAcceptTcpClient(new AsyncCallback(DoAcceptTcpCliet), listner);
}
//處置客戶端的銜接
public static void DoAcceptTcpCliet(IAsyncResult iar)
{
//復原原始的TcpListner對象
TcpListener listener = (TcpListener)iar.AsyncState;
//完成銜接的舉措,並前往新的TcpClient
TcpClient client = listener.EndAcceptTcpClient(iar);
Console.WriteLine("銜接成功");
}
代碼的處置邏輯為:
(1)調用BeginAccetpTcpClient辦法開開端銜接新的銜接,當銜接視圖發作時,回調函數被調用以完成銜接操作;
(2)下面DoAcceptTcpCliet辦法經過AsyncState屬性取得由BeginAcceptTcpClient傳入的listner實例;
(3)在失掉listener對象後,用它調用EndAcceptTcpClient辦法,該辦法前往新的包括客戶端信息的TcpClient。
BeginConnect辦法和EndConnect辦法可用於客戶端嘗試樹立與服務端的銜接,這裡和第一種辦法並無區別。上面看實例:
public void doBeginConnect(IAsyncResult iar)
{
Socket client=(Socket)iar.AsyncState;
//開端與近程主機停止銜接
client.BeginConnect(serverIP[0],13000,requestCallBack,client);
Console.WriteLine("開端與服務器停止銜接");
}
private void requestCallBack(IAsyncResult iar)
{
try
{
//復原原始的TcpClient對象
TcpClient client=(TcpClient)iar.AsyncState;
//
client.EndConnect(iar);
Console.WriteLine("與服務器{0}銜接成功",client.Client.RemoteEndPoint);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
finally
{
}
}
以上是樹立銜接的兩種辦法。可依據需求選擇運用。
3.2 發送與承受數據
在樹立了套接字的銜接後,就可以服務器端和客戶端之間停止數據通訊了。異步套接字用BeginSend和EndSend辦法來擔任數據的發送。留意在調用BeginSend辦法前要確保單方都曾經樹立銜接,否則會出異常。上面演示代碼:
private static void Send(Socket handler, String data)
{
// Convert the string data to byte data using ASCII encoding.
byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data);
// Begin sending the data to the remote device.
handler.BeginSend(byteData, 0, byteData.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), handler);
}
private static void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the socket from the state object.
Socket handler = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete sending the data to the remote device.
int bytesSent = handler.EndSend(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Sent {0} bytes to client.", bytesSent);
handler.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
handler.Close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
接納數據是經過BeginReceive和EndReceive辦法:
private static void Receive(Socket client)
{
try
{
// Create the state object.
StateObject state = new StateObject();
state.workSocket = client;
// Begin receiving the data from the remote device.
client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
private static void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the state object and the client socket
// from the asynchronous state object.
StateObject state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState;
Socket client = state.workSocket;
// Read data from the remote device.
int bytesRead = client.EndReceive(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0)
{
// There might be more data, so store the data received so far.
state.sb.Append(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(state.buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// Get the rest of the data.
client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state);
}
else
{
// All the data has arrived; put it in response.
if (state.sb.Length > 1)
{
response = state.sb.ToString();
}
// Signal that all bytes have been received.
receiveDone.Set();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
上述代碼的處置邏輯為:
(1)首先處置銜接的回調函數裡失掉的通訊套接字client,接著開端接納數據;
(2)當數據發送到緩沖區中,BeginReceive辦法試圖從buffer數組中讀取長度為buffer.length的數據塊,並前往接納到的數據量bytesRead。最後接納並打印數據。
除了上述辦法外,還可以運用基於NetworkStream相關的異步發送和接納辦法,上面是基於NetworkStream相關的異步發送和接納辦法的運用引見。
NetworkStream運用BeginRead和EndRead辦法停止讀操作,運用BeginWreite和EndWrete辦法停止寫操作,上面看實例:
static void DataHandle(TcpClient client)
{
TcpClient tcpClient = client;
//運用TcpClient的GetStream辦法獲取網絡流
NetworkStream ns = tcpClient.GetStream();
//反省網絡流能否可讀
if(ns.CanRead)
{
//定義緩沖區
byte[] read = new byte[1024];
ns.BeginRead(read,0,read.Length,new AsyncCallback(myReadCallBack),ns);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("無法從網絡中讀取流數據");
}
}
public static void myReadCallBack(IAsyncResult iar)
{
NetworkStream ns = (NetworkStream)iar.AsyncState;
byte[] read = new byte[1024];
String data = "";
int recv;
recv = ns.EndRead(iar);
data = String.Concat(data, Encoding.ASCII.GetString(read, 0, recv));
//接納到的音訊長度能夠大於緩沖區總大小,重復循環直到讀完為止
while (ns.DataAvailable)
{
ns.BeginRead(read, 0, read.Length, new AsyncCallback(myReadCallBack), ns);
}
//打印
Console.WriteLine("您收到的信息是" + data);
}
3.3 順序阻塞與異步中的同步問題
.Net裡提供了EventWaitHandle類來表示一個線程的同步事情。EventWaitHandle即事情等候句柄,他允許線程經過操作零碎互發信號和等候彼此的信號來到達線程同步的目的。這個類有2個子類,辨別為AutoRestEevnt(自動重置)和ManualRestEvent(手動重置)。上面是線程同步的幾個辦法:
(1)Rset辦法:將事情形態設為非終止形態,招致線程阻塞。這裡的線程阻塞是指允許其他需求等候的線程停止阻塞即讓含WaitOne()辦法的線程阻塞;
(2)Set辦法:將事情形態設為終止形態,允許一個或多個等候線程持續。該辦法發送一個信號給操作零碎,讓處於等候的某個線程從阻塞形態轉換為持續運轉,即WaitOne辦法的線程不在阻塞;
(3)WaitOne辦法:阻塞以後線程,直到以後的等候句柄收到信號。此辦法將不斷使本線程處於阻塞形態直到收到信號為止,即當其他非阻塞進程調用set辦法時可以持續執行。
public static void StartListening()
{
// Data buffer for incoming data.
byte[] bytes = new Byte[1024];
// Establish the local endpoint for the socket.
// The DNS name of the computer
// running the listener is "host.contoso.com".
//IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve(Dns.GetHostName());
//IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0];
IPAddress ipAddress = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, 11000);
// Create a TCP/IP socket.
Socket listener = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// Bind the socket to the local
//endpoint and listen for incoming connections.
try
{
listener.Bind(localEndPoint);
listener.Listen(100);
while (true)
{
// Set the event to nonsignaled state.
allDone.Reset();
// Start an asynchronous socket to listen for connections.
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for a connection...");
listener.BeginAccept(new AsyncCallback(AcceptCallback),listener);
// Wait until a connection is made before continuing.
allDone.WaitOne();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
Console.WriteLine("\nPress ENTER to continue...");
Console.Read();
}
上述代碼的邏輯為:
(1)試用了ManualRestEvent對象創立一個等候句柄,在調用BeginAccept辦法前運用Rest辦法允許其他線程阻塞;
(2)為了避免在銜接完成之前對套接字停止讀寫操作,務必要在BeginAccept辦法後調用WaitOne來讓線程進入阻塞形態。
當有銜接接入後零碎會自動調用會調用回調函數,所以當代碼執行到回調函數時闡明銜接曾經成功,並在函數的第一句就調用Set辦法讓處於等候的線程可以持續執行。
四、實例
上面是一個實例,客戶端懇求銜接,服務器端偵聽端口,當銜接樹立之後,服務器發送字符串給客戶端,客戶端收到後並回發給服務器端。
服務器端代碼:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
// State object for reading client data asynchronously
public class StateObject
{
// Client socket.
public Socket workSocket = null;
// Size of receive buffer.
public const int BufferSize = 1024;
// Receive buffer.
public byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize];
// Received data string.
public StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
}
public class AsynchronousSocketListener
{
// Thread signal.
public static ManualResetEvent allDone = new ManualResetEvent(false);
public AsynchronousSocketListener()
{
}
public static void StartListening()
{
// Data buffer for incoming data.
byte[] bytes = new Byte[1024];
// Establish the local endpoint for the socket.
// The DNS name of the computer
// running the listener is "host.contoso.com".
//IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve(Dns.GetHostName());
//IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0];
IPAddress ipAddress = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, 11000);
// Create a TCP/IP socket.
Socket listener = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// Bind the socket to the local
//endpoint and listen for incoming connections.
try
{
listener.Bind(localEndPoint);
listener.Listen(100);
while (true)
{
// Set the event to nonsignaled state.
allDone.Reset();
// Start an asynchronous socket to listen for connections.
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for a connection...");
listener.BeginAccept(new AsyncCallback(AcceptCallback),listener);
// Wait until a connection is made before continuing.
allDone.WaitOne();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
Console.WriteLine("\nPress ENTER to continue...");
Console.Read();
}
public static void AcceptCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
// Signal the main thread to continue.
allDone.Set();
// Get the socket that handles the client request.
Socket listener = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
Socket handler = listener.EndAccept(ar);
// Create the state object.
StateObject state = new StateObject();
state.workSocket = handler;
handler.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReadCallback), state);
}
public static void ReadCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
String content = String.Empty;
// Retrieve the state object and the handler socket
// from the asynchronous state object.
StateObject state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState;
Socket handler = state.workSocket;
// Read data from the client socket.
int bytesRead = handler.EndReceive(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0)
{
// There might be more data, so store the data received so far.
state.sb.Append(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(state.buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// Check for end-of-file tag. If it is not there, read
// more data.
content = state.sb.ToString();
if (content.IndexOf("<EOF>") > -1)
{
// All the data has been read from the
// client. Display it on the console.
Console.WriteLine("Read {0} bytes from socket. \n Data : {1}", content.Length, content);
// Echo the data back to the client.
Send(handler, content);
}
else
{
// Not all data received. Get more.
handler.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReadCallback), state);
}
}
}
private static void Send(Socket handler, String data)
{
// Convert the string data to byte data using ASCII encoding.
byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data);
// Begin sending the data to the remote device.
handler.BeginSend(byteData, 0, byteData.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), handler);
}
private static void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the socket from the state object.
Socket handler = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete sending the data to the remote device.
int bytesSent = handler.EndSend(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Sent {0} bytes to client.", bytesSent);
handler.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
handler.Close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
public static int Main(String[] args)
{
StartListening();
return 0;
}
}
客戶端代碼:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Threading;
using System.Text;
// State object for receiving data from remote device.
public class StateObject
{
// Client socket.
public Socket workSocket = null;
// Size of receive buffer.
public const int BufferSize = 256;
// Receive buffer.
public byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize];
// Received data string.
public StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
}
public class AsynchronousClient
{
// The port number for the remote device.
private const int port = 11000;
// ManualResetEvent instances signal completion.
private static ManualResetEvent connectDone = new ManualResetEvent(false);
private static ManualResetEvent sendDone = new ManualResetEvent(false);
private static ManualResetEvent receiveDone = new ManualResetEvent(false);
// The response from the remote device.
private static String response = String.Empty;
private static void StartClient()
{
// Connect to a remote device.
try
{
// Establish the remote endpoint for the socket.
// The name of the
// remote device is "host.contoso.com".
//IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve("user");
//IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0];
IPAddress ipAddress = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint remoteEP = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, port);
// Create a TCP/IP socket.
Socket client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// Connect to the remote endpoint.
client.BeginConnect(remoteEP, new AsyncCallback(ConnectCallback), client);
connectDone.WaitOne();
// Send test data to the remote device.
Send(client, "This is a test<EOF>");
sendDone.WaitOne();
// Receive the response from the remote device.
Receive(client);
receiveDone.WaitOne();
// Write the response to the console.
Console.WriteLine("Response received : {0}", response);
// Release the socket.
client.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
client.Close();
Console.ReadLine();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
private static void ConnectCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the socket from the state object.
Socket client = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete the connection.
client.EndConnect(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Socket connected to {0}", client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
// Signal that the connection has been made.
connectDone.Set();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
private static void Receive(Socket client)
{
try
{
// Create the state object.
StateObject state = new StateObject();
state.workSocket = client;
// Begin receiving the data from the remote device.
client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
private static void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the state object and the client socket
// from the asynchronous state object.
StateObject state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState;
Socket client = state.workSocket;
// Read data from the remote device.
int bytesRead = client.EndReceive(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0)
{
// There might be more data, so store the data received so far.
state.sb.Append(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(state.buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// Get the rest of the data.
client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state);
}
else
{
// All the data has arrived; put it in response.
if (state.sb.Length > 1)
{
response = state.sb.ToString();
}
// Signal that all bytes have been received.
receiveDone.Set();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
private static void Send(Socket client, String data)
{
// Convert the string data to byte data using ASCII encoding.
byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data);
// Begin sending the data to the remote device.
client.BeginSend(byteData, 0, byteData.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), client);
}
private static void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
// Retrieve the socket from the state object.
Socket client = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete sending the data to the remote device.
int bytesSent = client.EndSend(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Sent {0} bytes to server.", bytesSent);
// Signal that all bytes have been sent.
sendDone.Set();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
}
}
public static int Main(String[] args)
{
StartClient();
return 0;
}
}
五、實驗後果
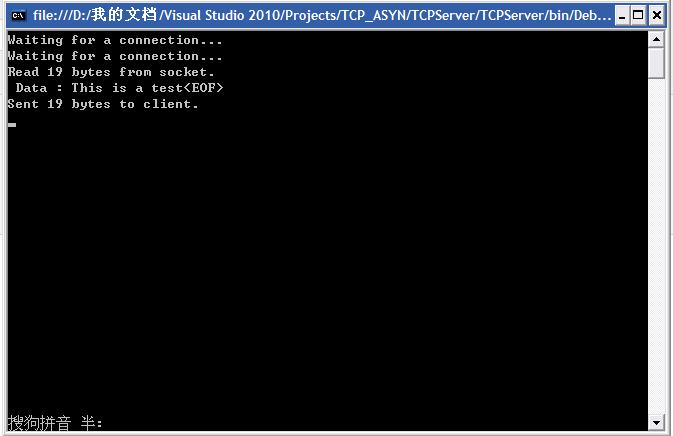 圖1 服務器端界面
圖1 服務器端界面
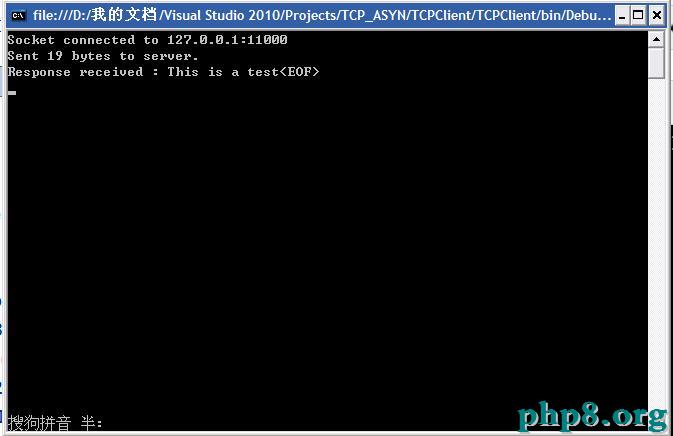 圖2 客戶端界面
圖2 客戶端界面