該程序在屏幕上畫出指定的函數的圖像,函數的自變量的取值范圍由用戶指定,程序自動計算該區間內函數的值的取值范圍。首先,讓我們來看一幅正弦函數: f(x) = sin(x) 的圖像:
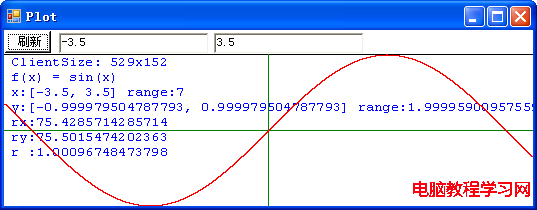
這幅圖像中,ClientSize: 529x152 表示該程序畫圖區寬度為 529 個像素,高度為 152 個像素。該函數自變量 x 的取值范圍從 -3.5 到 3.5,函數值 y 的取值范圍應該是從 -1 到 1,但因為浮點數運算誤差的關系,程序計算出來的是從 -0.999979504787793 到 0.999979504787793。接下來的 rx 表示函數自變量每單位值用多少個象素表示,ry 表示函數的值每單位值用多少個象素表示,r 值如果小於1表示圖形縱向被壓扁,反之則被拉伸。
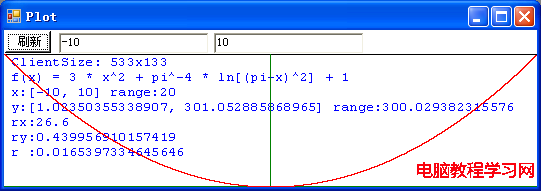
這是拋物線的圖像嗎?不,這就是我們要討論的病態函數: f(x) = 3 * x2 + π-4 * ln[(π-x)2] + 1 在 x 位於區間 [-10, 10] 之間的圖像。程序計算出來的函數在這區間的取值范圍是從 1.02350355338907 到 301.052885868965。r 值是 0.0165397334645646,表明該圖像被極大地壓扁,也就是,實際的圖像要高得多。但是,由於這個函數是病態的,程序的計算實際上是錯誤的,在該區間內,函數的最小值應該是負無窮大,並且,在 π - 10-667 到 π + 10-667 這一極小區間內方程 f(x) = 0 有兩個實根。讓我們在 π 值附近放大圖像看一看:
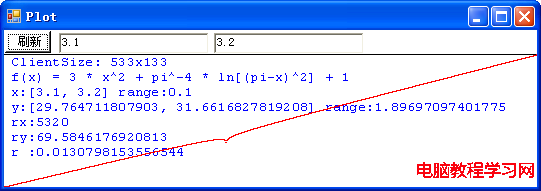
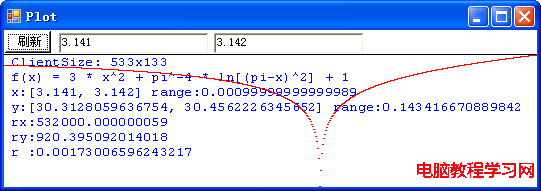
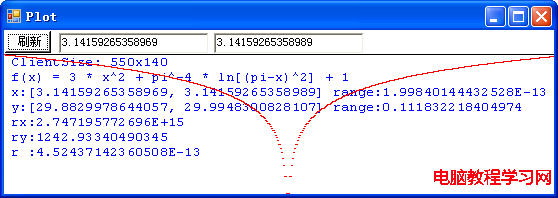
這下看得比較清楚了吧!
實際上這個病態函數是《C數值算法(第二版)》第三章“內插法和外推法”中提到的:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
可以很容易地構造一些病態函數使內插法失敗。例如,考慮函數
f(x) = 3 * x2 + π-4 * ln[(π-x)2] + 1
它除了 x = π 之外都有定義,而 x = π 時無定義,其它情況,值有正有負。而這函數在任何基於數值 x = 3.13, 3.14, 3.15, 3.16 的插值法,都肯定在 x = 3.1416 處得到一個錯誤的解,盡管通過這五個點所畫的曲線確實相當平滑!(用計算器試試看。)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
這個畫函數圖形的C#程序有一個嚴重的缺點,就是函數表達式是直接寫的源程序中的,不能象SciLab和Matlab那樣交互式地輸入。不知道用 System.Reflection.Emit.ILGenerator 類能不能動態地生成用戶輸入的函數表達式?好了,下面就是該程序的源代碼:

// plot.cs: 畫函數圖形, 編譯方法: csc /t:winexe plot.cs

using System;

using System.Drawing;

using System.
Windows.Forms;


namespace Skyiv.Ben.Plot
{

sealed class PlotForm : Form

{

// 要畫的函數,如果能在 TextBox 中輸入函數的表達式就更好了

double Function(double x)



{

double u = Math.PI - x;

double pi2 = Math.PI * Math.PI;

return 3 * x * x + Math.Log(u * u) / pi2 / pi2 + 1;
}


// 僅僅用來顯示在屏幕上

string FunctionString()



{

return "f(x) = 3 * x^2 + pi^-4 * ln[(pi-x)^2] + 1";
}


const int yBase = 24; // 屏幕保留區域的高度


TextBox tbxX0, tbxX1; // 函數自變量的取值范圍


PlotForm()



{

SuspendLayout();


Button btnSubmit = new Button();

btnSubmit.Text = "刷新";

btnSubmit.Location = new Point(0, 0);

btnSubmit.Size = new Size(48, 24);

btnSubmit.Click += new EventHandler(BtnSubmit_Click);


tbxX0 = new TextBox();

tbxX0.Text = "-10";

tbxX0.Location = new Point(55, 3);

tbxX0.Size = new Size(150, 20);


tbxX1 = new TextBox();

tbxX1.Text = "10";

tbxX1.Location = new Point(210, 3);

tbxX1.Size = new Size(150, 20);



Controls.AddRange(new Control[]

{btnSubmit, tbxX0, tbxX1});

Text = "Plot";

BackColor = Color.White;

ClientSize = new Size(600, 600 + yBase);

// WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized;


ResumeLayout(false);
}


void BtnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)



{

Invalidate();
}


protected override void OnSizeChanged(EventArgs e)



{

Invalidate();

base.OnSizeChanged(e);
}


protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)



{

double x0 = double.Parse(tbxX0.Text);

double x1 = double.Parse(tbxX1.Text);

Graphics gc = e.Graphics;

Size size = ClientSize;

int i0 = 0;

int i1 = size.Width - 1;

int j0 = yBase;

int j1 = size.Height - 1;

Pen pen = new Pen(Color.Black, 1);

gc.DrawLine(pen, i0, j0, i1, j0); // 畫圖區和保留區的分界線

double rx = (x1 - x0) / (i1 - i0);

double y0, y1;

GetFunctionValueRange(x0, rx, i0, i1, out y0, out y1);

double ry = (y1 - y0) / (j1 - j0);

Out(gc, 0, "ClientSize: {0}x{1}", i1 - i0 + 1, j1 - j0 + 1);

Out(gc, 1, FunctionString());

Out(gc, 2, "x:[{0}, {1}] range:{2}", x0, x1, x1 - x0);

Out(gc, 3, "y:[{0}, {1}] range:{2}", y0, y1, y1 - y0);

Out(gc, 4, "rx:{0}", 1 / rx); // 函數自變量每單位值用多少個象素表示

Out(gc, 5, "ry:{0}", 1 / ry); // 函數的值每單位值用多少個象素表示

Out(gc, 6, "r :{0}", rx / ry); // 該值如果小於1表示圖形縱向被壓扁,反之則被拉伸

pen.Color = Color.Green;

int j = j1 + (int)(y0 / ry);

if (j >= j0 && j <= j1) gc.DrawLine(pen, i0, j, i1, j); // x坐標軸

int i = i0 - (int)(x0 / rx);

if (i >= i0 && i <= i1) gc.DrawLine(pen, i, j0, i, j1); // y坐標軸

pen.Color = Color.Red;

for (i = i0; i <= i1; i++)



{

double x = x0 + (i - i0) * rx;

double y = Function(x);

if (double.IsInfinity(y) || double.IsNaN(y)) continue;

j = j1 - (int)((y - y0) / ry);

if (j > j1 || j < j0) continue;

gc.DrawLine(pen, i, j, i + 1, j); // 畫函數的圖形
}

base.OnPaint(e);
}


// 函數值的取值范圍

void GetFunctionValueRange(double x0, double rx, int i0, int i1, out double y0, out double y1)



{

y0 = double.MaxValue;

y1 = double.MinValue;

for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++)



{

double x = x0 + (i - i0) * rx;

double y = Function(x);

if (double.IsInfinity(y) || double.IsNaN(y)) continue;

if (y0 > y) y0 = y;

if (y1 < y) y1 = y;
}
}


// 在指定的位置寫字符串

void Out(Graphics gc, int line, string fmt, params object [] args)



{

gc.DrawString(string.Format(fmt, args), new Font("Courier New", 10), Brushes.Blue, new PointF(5, yBase + 15 * line));
}


static void Main()



{

Application.Run(new PlotForm());
}
}
}




