一、合成(Composite)模式
合成模式有時又叫做部分-整體模式(Part-Whole)。合成模式將對象組織到樹結構中,可以用來描述整體與部分的關系。合成模式可以使客戶端將單純元素與復合元素同等看待。
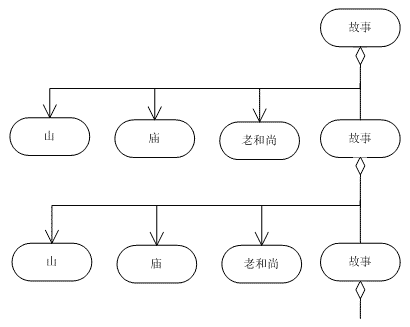
從和尚的故事談起
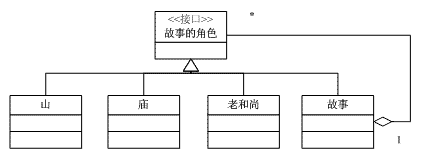
這是小時候我奶奶講的故事:從前有個山,山裡有個廟,廟裡有個老和尚在給小和尚講故事,講的什麼故事呢?從前有個山,山裡有個廟……。奶奶的故事要循環多少次,根據你多長時間睡著而定。在故事中有山、有廟、有和尚、有故事。因此,故事的角色有兩種:一種裡面沒有其它角色;另一種內部有其它角色。
對象的樹結構
一個樹結構由兩種節點組成:樹枝節點和樹葉節點。樹枝節點可以有子節點,而一個樹葉節點不可以有子節點。除了根節點外,其它節點有且只有一個父節點。
注意:一個樹枝節點可以不帶任何葉子,但是它因為有帶葉子的能力,因此仍然是樹枝節點,而不會成為葉節點。一個樹葉節點永遠不可能帶有子節點。
二、合成模式概述
下圖所示的類圖省略了各個角色的細節。
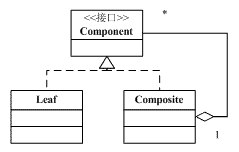
可以看出,上面的類圖結構涉及到三個角色:
抽象構件(Component)角色:這是一個抽象角色,它給參與組合的對象規定一個接口。這個角色給出共有接口及其默認行為。
樹葉構件(Leaf)角色:代表參加組合的樹葉對象。一個樹葉對象沒有下級子對象。
樹枝構件(Composite)角色:代表參加組合的有子對象的對象,並給出樹枝構件對象的行為。
可以看出,Composite類型的對象可以包含其它Component類型的對象。換而言之,Composite類型對象可以含有其它的樹枝(Composite)類型或樹葉(Leaf)類型的對象。
合成模式的實現根據所實現接口的區別分為兩種形式,分別稱為安全模式和透明模式。合成模式可以不提供父對象的管理方法,但合成模式必須在合適的地方提供子對象的管理方法(諸如:add、remove、getChild等)。
透明方式
作為第一種選擇,在Component裡面聲明所有的用來管理子類對象的方法,包括add()、remove(),以及getChild()方法。這樣做的好處是所有的構件類都有相同的接口。在客戶端看來,樹葉類對象與合成類對象的區別起碼在接口層次上消失了,客戶端可以同等同的對待所有的對象。這就是透明形式的合成模式。
這個選擇的缺點是不夠安全,因為樹葉類對象和合成類對象在本質上是有區別的。樹葉類對象不可能有下一個層次的對象,因此add()、remove()以及getChild()方法沒有意義,是在編譯時期不會出錯,而只會在運行時期才會出錯。
安全方式
第二種選擇是在Composite類裡面聲明所有的用來管理子類對象的方法。這樣的做法是安全的做法,因為樹葉類型的對象根本就沒有管理子類對象的方法,因此,如果客戶端對樹葉類對象使用這些方法時,程序會在編譯時期出錯。
這個選擇的缺點是不夠透明,因為樹葉類和合成類將具有不同的接口。
這兩個形式各有優缺點,需要根據軟件的具體情況做出取捨決定。
三、安全式的合成模式的結構
安全式的合成模式要求管理聚集的方法只出現在樹枝構件類中,而不出現在樹葉構件中。
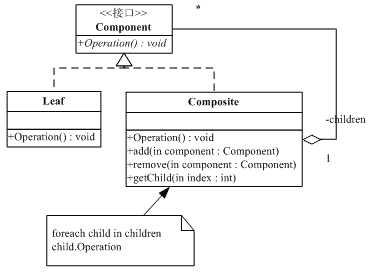
這種形式涉及到三個角色:
抽象構件(Component)角色:這是一個抽象角色,它給參加組合的對象定義出公共的接口及其默認行為,可以用來管理所有的子對象。在安全式的合成模式裡,構件角色並不是定義出管理子對象的方法,這一定義由樹枝構件對象給出。
樹葉構件(Leaf)角色:樹葉對象是沒有下級子對象的對象,定義出參加組合的原始對象的行為。
樹枝構件(Composite)角色:代表參加組合的有下級子對象的對象。樹枝對象給出所有的管理子對象的方法,如add()、remove()、getChild()等。
四、安全式的合成模式實現
以下示例性代碼演示了安全式的合成模式代碼:
// Composite pattern -- Structural example
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
// "Component"
abstract class Component
{
// Fields
protected string name;
// Constructors
public Component( string name )
{
this.name = name;
}
// Operation
public abstract void Display( int depth );
}
// "Composite"
class Composite : Component
{
// Fields
private ArrayList children = new ArrayList();
// Constructors
public Composite( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Methods
public void Add( Component component )
{
children.Add( component );
}
public void Remove( Component component )
{
children.Remove( component );
}
public override void Display( int depth )
{
Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', depth ) + name );
// Display each of the node's children
foreach( Component component in children )
component.Display( depth + 2 );
}
}
// "Leaf"
class Leaf : Component
{
// Constructors
public Leaf( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Methods
public override void Display( int depth )
{
Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', depth ) + name );
}
}
/**//// <summary>
/// Client test
/// </summary>
public class Client
{
public static void Main( string[] args )
{
// Create a tree structure
Composite root = new Composite( "root" );
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf A" ));
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf B" ));
Composite comp = new Composite( "Composite X" );
comp.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf XA" ) );
comp.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf XB" ) );
root.Add( comp );
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf C" ));
// Add and remove a leaf
Leaf l = new Leaf( "Leaf D" );
root.Add( l );
root.Remove( l );
// Recursively display nodes
root.Display( 1 );
}
}
五、透明式的合成模式結構
與安全式的合成模式不同的是,透明式的合成模式要求所有的具體構件類,不論樹枝構件還是樹葉構件,均符合一個固定的接口。
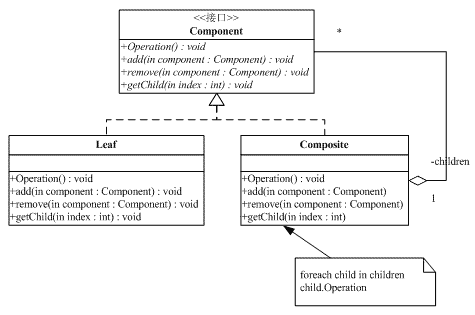
這種形式涉及到三個角色:
抽象構件(Component)角色:這是一個抽象角色,它給參加組合的對象規定一個接口,規范共有的接口及默認行為。
樹葉構件(Leaf)角色:代表參加組合的樹葉對象,定義出參加組合的原始對象的行為。樹葉類會給出add()、remove()以及getChild()之類的用來管理子類對對象的方法的平庸實現。
樹枝構件(Composite)角色:代表參加組合的有子對象的對象,定義出這樣的對象的行為。
六、透明式的合成模式實現
以下示例性代碼演示了安全式的合成模式代碼:
// Composite pattern -- Structural example
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
// "Component"
abstract class Component
{
// Fields
protected string name;
// Constructors
public Component( string name )
{ this.name = name; }
// Methods
abstract public void Add(Component c);
abstract public void Remove( Component c );
abstract public void Display( int depth );
}
// "Composite"
class Composite : Component
{
// Fields
private ArrayList children = new ArrayList();
// Constructors
public Composite( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Methods
public override void Add( Component component )
{ children.Add( component ); }
public override void Remove( Component component )
{ children.Remove( component ); }
public override void Display( int depth )
{
Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', depth ) + name );
// Display each of the node's children
foreach( Component component in children )
component.Display( depth + 2 );
}
}
// "Leaf"
class Leaf : Component
{
// Constructors
public Leaf( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Methods
public override void Add( Component c )
{ Console.WriteLine("Cannot add to a leaf"); }
public override void Remove( Component c )
{ Console.WriteLine("Cannot remove from a leaf"); }
public override void Display( int depth )
{ Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', depth ) + name ); }
}
/**//// <summary>
/// Client test
/// </summary>
public class Client
{
public static void Main( string[] args )
{
// Create a tree structure
Composite root = new Composite( "root" );
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf A" ));
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf B" ));
Composite comp = new Composite( "Composite X" );
comp.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf XA" ) );
comp.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf XB" ) );
root.Add( comp );
root.Add( new Leaf( "Leaf C" ));
// Add and remove a leaf
Leaf l = new Leaf( "Leaf D" );
root.Add( l );
root.Remove( l );
// Recursively display nodes
root.Display( 1 );
}
}
七、使用合成模式時考慮的幾個問題
明顯的給出父對象的引用。在子對象裡面給出父對象的引用,可以很容易的遍歷所有父對象。有了這個引用,可以方便的應用責任鏈模式。
在通常的系統裡,可以使用享元模式實現構件的共享,但是由於合成模式的對象經常要有對父對象的引用,因此共享不容易實現。
有時候系統需要遍歷一個樹枝結構的子構件很多次,這時候可以考慮把遍歷子構件的結果暫時存儲在父構件裡面作為緩存。
關於使用什麼數據類型來存儲子對象的問題,在示意性的代碼中使用了ArrayList,在實際系統中可以使用其它聚集或數組等。
客戶端盡量不要直接調用樹葉類中的方法,而是借助其父類(Component)的多態性完成調用,這樣可以增加代碼的復用性。
八、和尚的故事
九、一個實際應用Composite模式的例子
下面是一個實際應用中的程序,演示了通過一些基本圖像元素(直線、園等)以及一些復合圖像元素(由基本圖像元素組合而成)構建復雜的圖形樹的過程。
// Composite pattern -- Real World example
using System;
using System.Collections;
// "Component"
abstract class DrawingElement
{
// Fields
protected string name;
// Constructors
public DrawingElement( string name )
{ this.name = name; }
// Operation
abstract public void Display( int indent );
}
// "Leaf"
class PrimitiveElement : DrawingElement
{
// Constructors
public PrimitiveElement( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Operation
public override void Display( int indent )
{
Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', indent ) +
" draw a {0}", name );
}
}
// "Composite"
class CompositeElement : DrawingElement
{
// Fields
private ArrayList elements = new ArrayList();
// Constructors
public CompositeElement( string name ) : base( name ) {}
// Methods
public void Add( DrawingElement d )
{ elements.Add( d ); }
public void Remove( DrawingElement d )
{ elements.Remove( d ); }
public override void Display( int indent )
{
Console.WriteLine( new String( '-', indent ) +
"+ " + name );
// Display each child element on this node
foreach( DrawingElement c in elements )
c.Display( indent + 2 );
}
}
/**//// <summary>
/// CompositeApp test
/// </summary>
public class CompositeApp
{
public static void Main( string[] args )
{
// Create a tree structure
CompositeElement root = new
CompositeElement( "Picture" );
root.Add( new PrimitiveElement( "Red Line" ));
root.Add( new PrimitiveElement( "Blue Circle" ));
root.Add( new PrimitiveElement( "Green Box" ));
CompositeElement comp = new
CompositeElement( "Two Circles" );
comp.Add( new PrimitiveElement( "Black Circle" ) );
comp.Add( new PrimitiveElement( "White Circle" ) );
root.Add( comp );
// Add and remove a PrimitiveElement
PrimitiveElement l = new PrimitiveElement( "Yellow Line" );
root.Add( l );
root.Remove( l );
// Recursively display nodes
root.Display( 1 );
}
}
合成模式與很多其它模式都有聯系,將在後續內容中逐步介紹。