C#實現窗體總在最上面或者下面
Pop-under windows are windows that, when created, are immediately shuttled behind all other windows in the z-order. In fact, many times you don''t notice them until you''ve closed or minimized all other open windows. Basically, they''re seen as a less obtrusive means of advertising than pop-ups that require immediate (and usually resentful) attention from the user. With the lines between browser-based Web applications and traditional Windows applications being blurred every day, it should come as no surprise that Windows programmers are looking for ways to emulate the (infamous) pop-under effect utilized by Web marketers. Therefore, in this week''s article, we''ll look at the steps required to pull of this stunt...er...task.
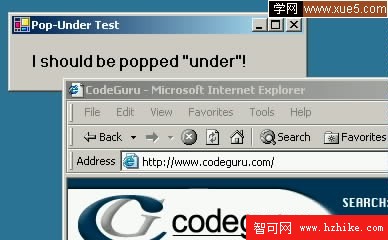
Figure 1
Note: If you also would like to see how pop-under Windows are created in JavaScript, you can read about that in an article by Joe Burns on one of our sister sites—HtmlGoodIEs.com.
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
class Win32
{
[DllImport("user32.dll", EntryPoint = "SetWindowPos")]
public static extern bool SetWindowPos(
int hWnd, // window handle
int hWndInsertAfter, // placement-order handle
int X, // horizontal position
int Y, // vertical position
int cx, // width
int cy, // height
uint uFlags); // window positioning flags
public const int HWND_BOTTOM = 0x1;
public const uint SWP_NOSIZE = 0x1;
public const uint SWP_NOMOVE = 0x2;
public const uint SWP_SHOWWINDOW = 0x40;
}
private void ShoveToBackground()
{
Win32.SetWindowPos((int)this.Handle,
Win32.HWND_BOTTOM,
0, 0, 0, 0,
Win32.SWP_NOMOVE | Win32.SWP_NOSIZE |
Win32.SWP_SHOWWINDOW);
}
private void Form1_Activated(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
ShoveToBackground();
}
private void Form1_Resize(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
ShoveToBackground();
}
Now, when the form is first executed or activated from the task bar or task list, it will always flicker and then immediately get "pushed" to the background as you see in Figure 1.