在多線程(線程同步)中,我們將學習多線程中操作共享資源的技術,學習到的知識點如下所示:
一、執行基本的原子操作
在這一小節中,我們將學習如何在沒有阻塞線程(blocking threads)發生的情況下,在一個對象上執行基本的原子操作並能阻止競爭條件(race condition)的發生。操作步驟如下所示:
1、使用Visual Studio 2015創建一個新的控制台應用程序。
2、雙擊打開“Program.cs”文件,編寫代碼如下所示:
1 using System;
2 using System.Threading;
3 using static System.Console;
4
5 namespace Recipe01
6 {
7 abstract class CounterBase
8 {
9 public abstract void Increment();
10
11 public abstract void Decrement();
12 }
13
14 class Counter : CounterBase
15 {
16 private int count;
17
18 public int Count => count;
19
20 public override void Increment()
21 {
22 count++;
23 }
24
25 public override void Decrement()
26 {
27 count--;
28 }
29 }
30
31 class CounterNoLock : CounterBase
32 {
33 private int count;
34
35 public int Count => count;
36
37 public override void Increment()
38 {
39 Interlocked.Increment(ref count);
40 }
41
42 public override void Decrement()
43 {
44 Interlocked.Decrement(ref count);
45 }
46 }
47
48 class Program
49 {
50 static void TestCounter(CounterBase c)
51 {
52 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
53 {
54 c.Increment();
55 c.Decrement();
56 }
57 }
58
59 static void Main(string[] args)
60 {
61 WriteLine("Incorrect counter");
62
63 var c1 = new Counter();
64
65 var t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
66 var t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
67 var t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
68 t1.Start();
69 t2.Start();
70 t3.Start();
71 t1.Join();
72 t2.Join();
73 t3.Join();
74
75 WriteLine($"Total count: {c1.Count}");
76 WriteLine("--------------------------");
77
78 WriteLine("Correct counter");
79
80 var c2 = new CounterNoLock();
81
82 t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c2));
83 t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c2));
84 t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c2));
85 t1.Start();
86 t2.Start();
87 t3.Start();
88 t1.Join();
89 t2.Join();
90 t3.Join();
91
92 WriteLine($"Total count: {c2.Count}");
93 }
94 }
95 }
3、運行該控制台應用程序,運行效果(每次運行效果可能不同)如下圖所示:
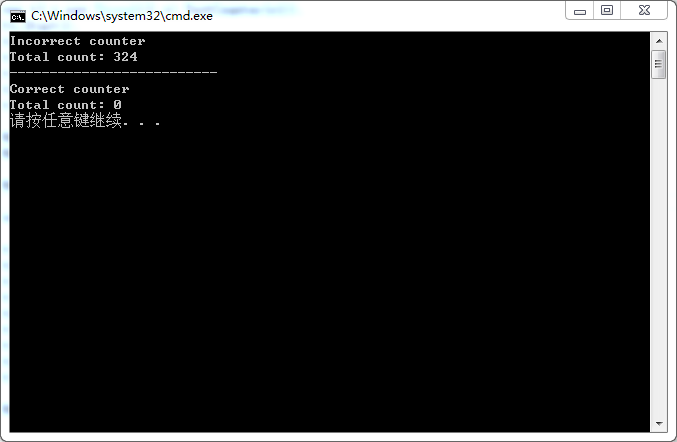
在第63行代碼處,我們創建了一個非線程安全的Counter類的一個對象c1,由於它是非線程安全的,因此會發生競爭條件(race condition)。
在第65~67行代碼處,我們創建了三個線程來運行c1對象的“TestCounter”方法,在該方法中,我們按順序對c1對象的count變量執行自增和自減操作。由於c1不是線程安全的,因此在這種情況下,我們得到的counter值是不確定的,我們可以得到0值,但多運行幾次,多數情況下會得到不是0值得錯誤結果。
在多線程(基礎篇)中,我們使用lock關鍵字鎖定對象來解決這個問題,但是使用lock關鍵字會造成其他線程的阻塞。但是,在本示例中我們沒有使用lock關鍵字,而是使用了Interlocked構造,它對於基本的數學操作提供了自增(Increment)、自減(Decrement)以及其他一些方法。
二、使用Mutex構造
在這一小節中,我們將學習如何使用Mutex構造同步兩個單獨的程序,即進程間的同步。具體步驟如下所示:
1、使用Visual Studio 2015創建一個新的控制台應用程序。
2、雙擊打開“Program.cs”文件,編寫代碼如下所示:
1 using System;
2 using System.Threading;
3 using static System.Console;
4
5 namespace Recipe02
6 {
7 class Program
8 {
9 static void Main(string[] args)
10 {
11 const string MutexName = "Multithreading";
12
13 using (var m = new Mutex(false, MutexName))
14 {
15 // WaitOne方法的作用是阻止當前線程,直到收到其他實例釋放的處理信號。
16 // 第一個參數是等待超時時間,第二個是否退出上下文同步域。
17 if (!m.WaitOne(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10), false))
18 {
19 WriteLine("Second instance is running!");
20 ReadLine();
21 }
22 else
23 {
24 WriteLine("Running!");
25 ReadLine();
26 // 釋放互斥資源
27 m.ReleaseMutex();
28 }
29 }
30
31 ReadLine();
32 }
33 }
34 }
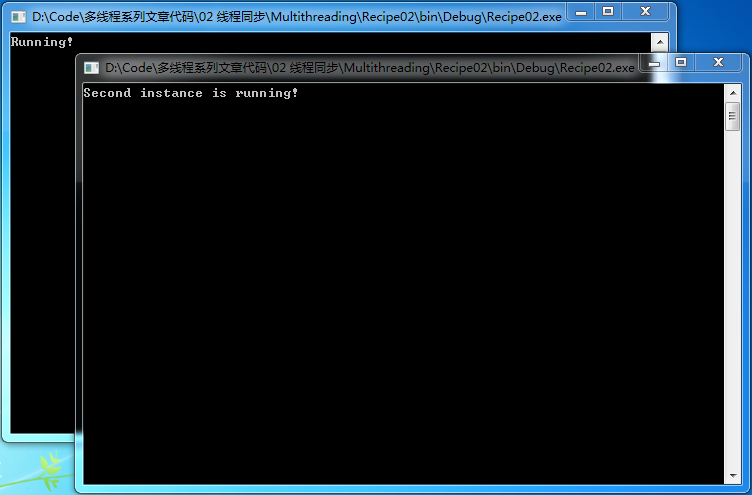
3、編譯代碼,執行兩次該程序,運行效果如下所示:
第一種情況的運行結果:
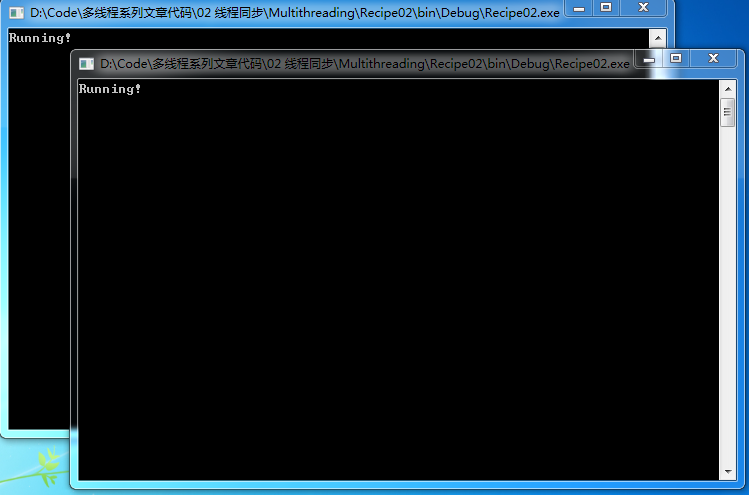
第二種情況的運行結果:
在第11行代碼處,我們定義了一個mutex(互斥量)的名稱為“Multithreading”,並在第13行代碼處將其傳遞給了Mutex類的構造方法,該構造方法的第一個參數initialOwner我們賦值為false,這允許程序獲得一個已經被創建的mutex。如果沒有任何線程鎖定互斥資源,程序只簡單地顯示“Running”,然後等待按下任何鍵以釋放互斥資源。
如果我們啟動該程序的第二個實例,如果在10秒內我們沒有在第一個實例下按下任何按鈕以釋放互斥資源,那麼在第二個實例中就會顯示“Second instance is running!”,如第一種情況的運行結果所示。如果在10內我們在第一個實例中按下任何鍵以釋放互斥資源,那麼在第二個實例中就會顯示“Running”,如第二種情況的運行結果所示。
三、使用SemaphoreSlim構造
在這一小節中,我們將學習如何在SemaphoreSlim構造的幫助下,限制同時訪問資源的線程數量。具體步驟如下所示:
1、使用Visual Studio 2015創建一個新的控制台應用程序。
2、雙擊打開“Program.cs”文件,編寫代碼如下所示:
1 using System;
2 using System.Threading;
3 using static System.Console;
4 using static System.Threading.Thread;
5
6 namespace Recipe03
7 {
8 class Program
9 {
10 static SemaphoreSlim semaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(4);
11
12 static void AccessDatabase(string name, int seconds)
13 {
14 WriteLine($"{name} waits to access a database");
15 semaphore.Wait();
16 WriteLine($"{name} was granted an access to a database");
17 Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds));
18 WriteLine($"{name} is completed");
19 semaphore.Release();
20 }
21
22 static void Main(string[] args)
23 {
24 for(int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
25 {
26 string threadName = "Thread" + i;
27 int secondsToWait = 2 + 2 * i;
28 var t = new Thread(() => AccessDatabase(threadName, secondsToWait));
29 t.Start();
30 }
31 }
32 }
33 }
3、運行該控制台應用程序,運行效果(每次運行效果可能不同)如下圖所示:
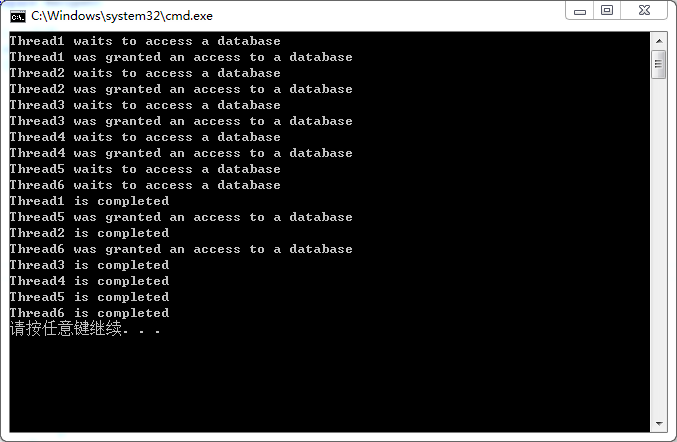
在第10行代碼處,我們創建了一個SemaphoreSlim的實例,並對該構造方法傳遞了參數4,該參數指定了可以有多少個線程同時訪問資源。然後,我們啟動了6個不同名字的線程。每個線程都試著獲取對數據庫的訪問,但是,我們限制了最多只有4個線程可以訪問數據庫,因此,當4個線程訪問數據庫後,其他2個線程必須等待,直到其他線程完成其工作後,調用“Release”方法釋放資源之後才能訪問數據庫。