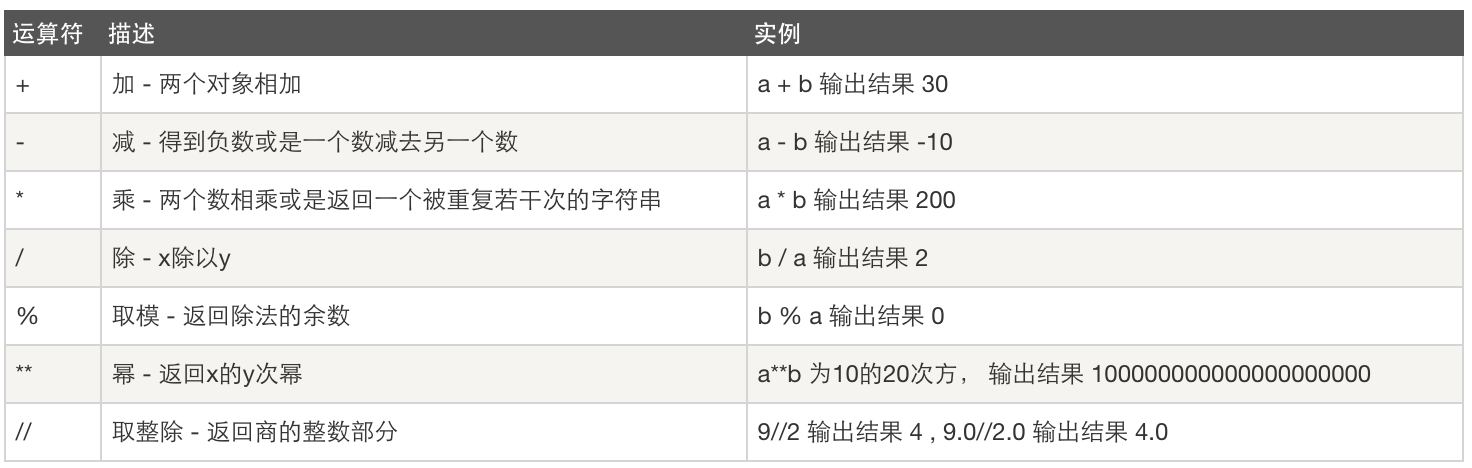
練習:
+ 加法 兩個對象相加 1 + 2得到3;'a' + 'b'得到'ab'。 - 減法 一個數減去另一個數或者是負數 5 - 3得到2;-2得到一個負數 * 乘法 兩個數相乘或者返回一個被重復若干次的字符串 -5.2得到一個負數。50 - 24得到26。 ** 冪 返回x的y次冪 3 ** 4得到81(即3 * 3 * 3 * 3) / 除 x除以y 4/3得到1(整數的除法得到整數結果)。4.0/3或4/3.0得到1.3333333333333333 // 取整除 返回商的整數部分 4 // 3.0得到1.0 % 取模 返回除法的余數 8%3得到2。-25.5%2.25得到1.5
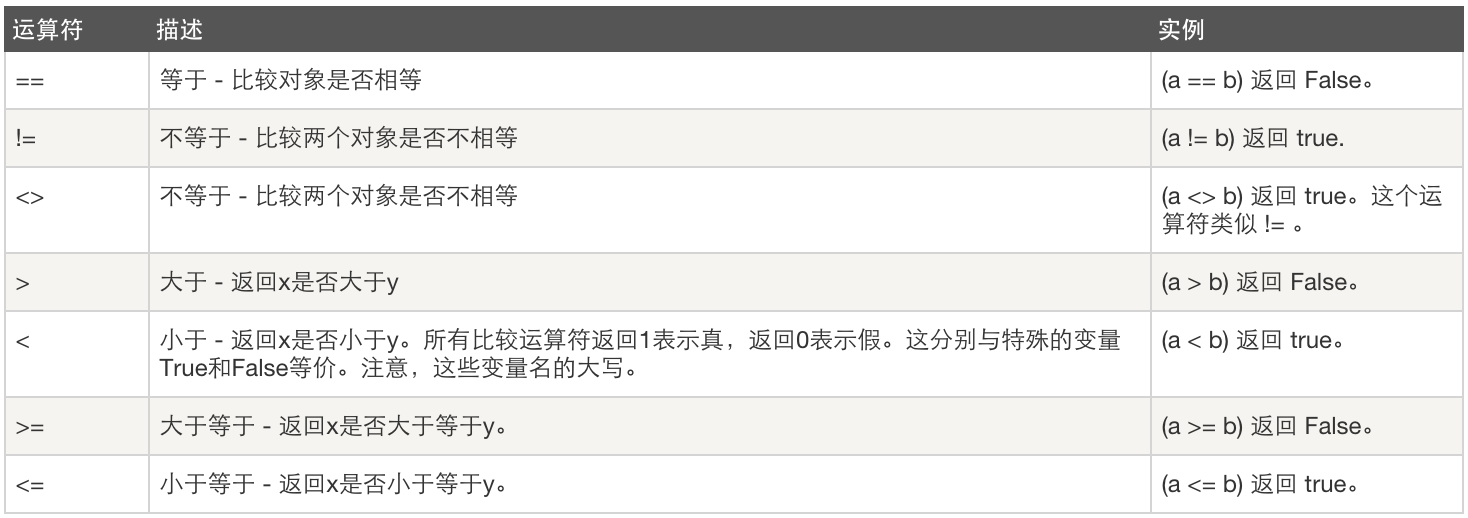
<< 左移 把一個數的比特向左移一定數目(每個數在內存中都表示為比特或二進制數字,即0和1) 2 << 2得到8。——2按比特表示為10 >> 右移 把一個數的比特向右移一定數目 11 >> 1得到5。——11按比特表示為1011,向右移動1比特後得到101,即十進制的5。 ~ 按位翻轉 x的按位翻轉是-(x+1) ~5得到-6 < 小於 返回x是否小於y。所有比較運算符返回1表示真,返回0表示假。這分別與特殊的變量True和False等價。注意,這些變量名的大寫 5 < 3返回0(即False)而3 < 5返回1(即True)。比較可以被任意連接:3 < 5 < 7返回True > 大於 返回x是否大於y 5 > 3返回True。如果兩個操作數都是數字,它們首先被轉換為一個共同的類型。否則,它總是返回False。 <= 小於等 返回x是否小於等於y x = 3; y = 6; x <= y返回True == 等於 比較對象是否相等 x = 2; y = 2; x == y返回True。x = 'str'; y = 'stR'; x == y返回False。x = 'str'; y = 'str'; x == y返回True。 != 不等於 比較兩個對象是否不相等 x = 2; y = 3; x != y返回True
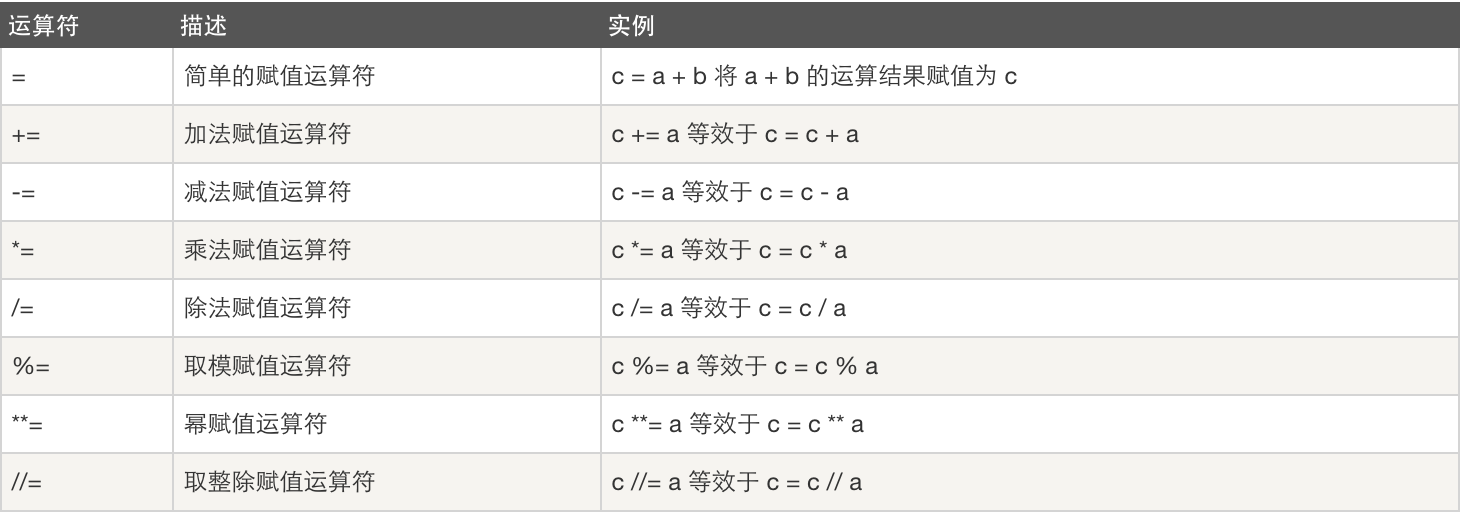
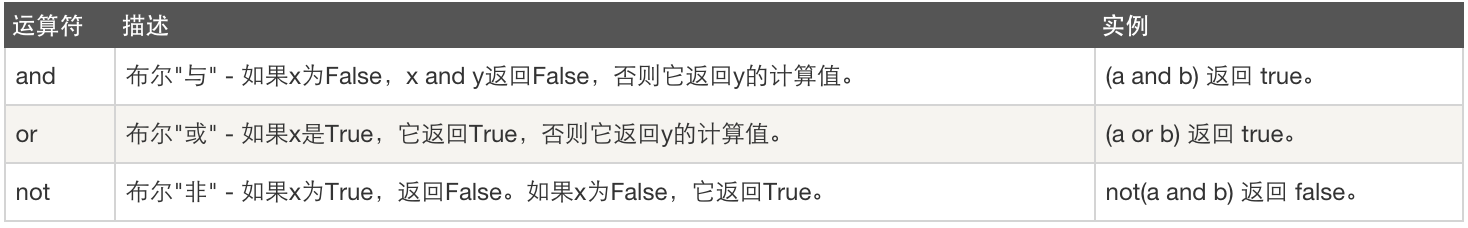
not 布爾“非” 如果x為True,返回False。如果x為False,它返回True。 x = True; not x返回False and 布爾“與” 如果x為False,x and y返回False,否則它返回y的計算值 x = False; y = True; x and y,由於x是False,返回False。在這裡,Python不會計算y,因為它知道這個表達式的值肯定是False(因為x是False)。這個現象稱為短路計算。 or 布爾“或” 如果x是True,它返回True,否則它返回y的計算值。 x = True; y = False; x or y返回True。短路計算在這裡也適用。
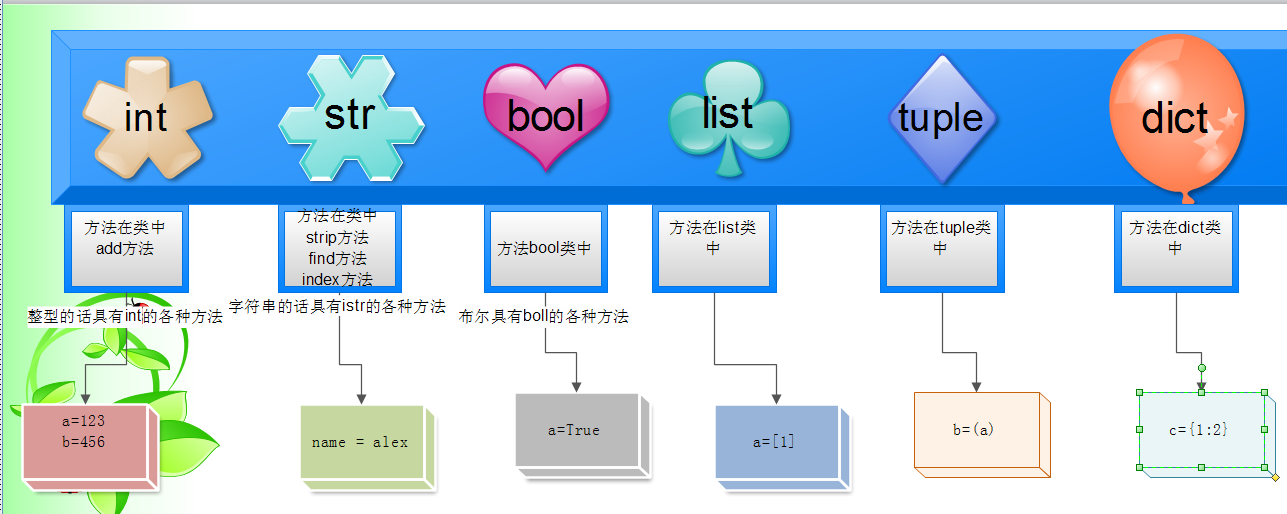
Python可以處理任意大小的正負整數,但是實際中跟我們計算機的內存有關,在32位機器上,整數的位數為32位,取值范圍為-2**31~2**31-1,在64位系統上,整數的位數為64位,取值范圍為-2**63~2**63-1。
a=4
print(a.bit_length()) # 4在二進制中可以用最少3位 100 來表示4,所以輸出3
print(int('4')) #將字符串4轉換成整數4
# int還可下面的將二進制的字符串轉換成整數, base=2 代表前面的字符串是二進制。
print(int('1010',base=2)) # 輸出10
class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self):
""" 返回表示該數字的時占用的最少位數 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回該復數的共轭復數 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass
def __abs__(self):
""" 返回絕對值 """
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __and__(self, y):
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y):
""" 比較兩個數大小 """
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y):
""" 強制生成一個元組 """
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y):
""" 相除,得到商和余數組成的元組 """
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __float__(self):
""" 轉換為浮點類型 """
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 內部調用 __new__方法或創建對象時傳入參數使用 """
pass
def __hash__(self):
"""如果對象object為哈希表類型,返回對象object的哈希值。哈希值為整數。在字典查找中,哈希值用於快速比較字典的鍵。兩個數值如果相等,則哈希值也相等。"""
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __hex__(self):
""" 返回當前數的 十六進制 表示 """
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass
def __index__(self):
""" 用於切片,數字無意義 """
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 構造方法,執行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 時,自動調用,暫時忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self):
""" 轉換為整數 """
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __invert__(self):
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass
def __long__(self):
""" 轉換為長整數 """
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lshift__(self, y):
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __oct__(self):
""" 返回改值的 八進制 表示 """
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass
def __or__(self, y):
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" 冪,次方 """
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rand__(self, y):
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self):
"""轉化為解釋器可讀取的形式 """
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __str__(self):
"""轉換為人閱讀的形式,如果沒有適於人閱讀的解釋形式的話,則返回解釋器課閱讀的形式"""
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __ror__(self, y):
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass
def __rshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y):
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" 返回數值被截取為整形的值,在整形中無意義 """
pass
def __xor__(self, y):
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虛數,無意義 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 數字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 實屬,無意義 """
"""the real part of a complex number"""
int
可能如:2147483649、9223372036854775807
每個長整型都具備如下功能:


class long(object):
"""
long(x=0) -> long
long(x, base=10) -> long
Convert a number or string to a long integer, or return 0L if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
4L
"""
def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
long.bit_length() -> int or long
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37L)
'0b100101'
>>> (37L).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any long. """
pass
def __abs__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __float__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __hex__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass
def __index__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass
def __init__(self, x=0): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
pass
def __int__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __invert__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass
def __long__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __nonzero__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __oct__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass
def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __pos__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass
def __rshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns size in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __str__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Truncating an Integral returns itself. """
pass
def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the real part of a complex number"""
long
如:3.14、2.88
每個浮點型都具備如下功能:


class float(object):
"""
float(x) -> floating point number
Convert a string or number to a floating point number, if possible.
"""
def as_integer_ratio(self):
""" 獲取改值的最簡比 """
"""
float.as_integer_ratio() -> (int, int)
Return a pair of integers, whose ratio is exactly equal to the original
float and with a positive denominator.
Raise OverflowError on infinities and a ValueError on NaNs.
>>> (10.0).as_integer_ratio()
(10, 1)
>>> (0.0).as_integer_ratio()
(0, 1)
>>> (-.25).as_integer_ratio()
(-1, 4)
"""
pass
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self, the complex conjugate of any float. """
pass
def fromhex(self, string):
""" 將十六進制字符串轉換成浮點型 """
"""
float.fromhex(string) -> float
Create a floating-point number from a hexadecimal string.
>>> float.fromhex('0x1.ffffp10')
2047.984375
>>> float.fromhex('-0x1p-1074')
-4.9406564584124654e-324
"""
return 0.0
def hex(self):
""" 返回當前值的 16 進制表示 """
"""
float.hex() -> string
Return a hexadecimal representation of a floating-point number.
>>> (-0.1).hex()
'-0x1.999999999999ap-4'
>>> 3.14159.hex()
'0x1.921f9f01b866ep+1'
"""
return ""
def is_integer(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return True if the float is an integer. """
pass
def __abs__(self):
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y):
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y):
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __eq__(self, y):
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __float__(self):
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, format_spec):
"""
float.__format__(format_spec) -> string
Formats the float according to format_spec.
"""
return ""
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getformat__(self, typestr):
"""
float.__getformat__(typestr) -> string
You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be
used in Python's test suite.
typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. This function returns whichever of
'unknown', 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian' best describes the
format of floating point numbers used by the C type named by typestr.
"""
return ""
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __ge__(self, y):
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y):
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __hash__(self):
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __init__(self, x):
pass
def __int__(self):
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y):
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __long__(self):
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lt__(self, y):
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y):
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self):
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __setformat__(self, typestr, fmt):
"""
float.__setformat__(typestr, fmt) -> None
You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be
used in Python's test suite.
typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. fmt must be one of 'unknown',
'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian', and in addition can only be
one of the latter two if it appears to match the underlying C reality.
Override the automatic determination of C-level floating point type.
This affects how floats are converted to and from binary strings.
"""
pass
def __str__(self):
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return the Integral closest to x between 0 and x. """
pass
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the real part of a complex number"""
float


class str(object):
"""
str(object='') -> str
str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str
Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or
errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer
that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler.
Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined)
or repr(object).
encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding().
errors defaults to 'strict'.
"""
def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" #將 字符串首字母 小寫改大寫
S.capitalize() -> str
Return a capitalized version of S, i.e. make the first character
have upper case and the rest lower case.
"""
return ""
def casefold(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.casefold() -> str
Return a version of S suitable for caseless comparisons.
"""
return ""
def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 可以為字符串 填充自定字符 長度=字符+指定字符
S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str
Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return ""
def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 下面是詳細參數:
子串:是要搜索的子串。
開始:從該指數開始搜索。第一個字符從索引0開始。通過默認搜索引擎從索引0開始。
結束:搜索從該指數結束。第一個字符從索引0開始。默認情況下,搜索結束,在最後一個索引。
S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are
interpreted as in slice notation.
"""
return 0
def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 編碼 上面有介紹
S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes
Encode S using the codec registered for encoding. Default encoding
is 'utf-8'. errors may be given to set a different error
handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
"""
return b""
def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 以 某個字符結束
suffix -- 該參數可以是一個字符串或者是一個元素。
start -- 字符串中的開始位置。
end -- 字符中結束位置。
返回值
如果字符串含有指定的後綴返回True,否則返回False。
S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False
def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 把tab轉換成空格
S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str
Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
"""
return ""
def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
find(str, pos_start, pos_end)
解釋:
str:被查找“字串”
pos_start:查找的首字母位置(從0開始計數。默認:0)
pos_end: 查找的末尾位置(默認-1)
返回值:如果查到:返回查找的第一個出現的位置。否則,返回-1。
S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0
def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
""" 占位符 類似變量引用
s = "print hell {0} ,age {1}"
print(s.format('alex',19))
S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
"""
pass
def format_map(self, mapping): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""字符串格式化,動態參數,將函數式編程時細說
S.format_map(mapping) -> str
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
"""
return ""
def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" #跟find類似但是 沒有找到的話會報錯。 而find是返回-1
S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0
def isalnum(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" #判斷是否是數字和字母
S.isalnum() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isalpha(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""是否是字母
S.isalpha() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isdecimal(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isdecimal() -> bool
Return True if there are only decimal characters in S,
False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isdigit(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否是數字
S.isdigit() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are digits
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isidentifier(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isidentifier() -> bool
Return True if S is a valid identifier according
to the language definition.
Use keyword.iskeyword() to test for reserved identifiers
such as "def" and "class".
"""
return False
def islower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""是否小寫字母
S.islower() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isnumeric(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isnumeric() -> bool
Return True if there are only numeric characters in S,
False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isprintable(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.isprintable() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are considered
printable in repr() or S is empty, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isspace(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""是否是空格
S.isspace() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def istitle(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否是標題 字符串開頭是大寫 後面是小寫
S.istitle() -> bool
Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
character in S, i.e. upper- and titlecase characters may only
follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones.
Return False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isupper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否是大寫
S.isupper() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 拼接 後面有例子
S.join(iterable) -> str
Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
iterable. The separator between elements is S.
"""
return ""
def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 內容左對齊,右側填充
ljust()方法語法:
str.ljust(width[, fillchar])
參數
width -- 指定字符串長度。
fillchar -- 填充字符,默認為空格。
返回值
返回一個原字符串左對齊,並使用空格填充至指定長度的新字符串。如果指定的長度小於原字符串的長度則返回原字符串。
S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str Return S left-justified in a Unicode string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space). """ return "" def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 轉換為小寫 S.lower() -> str Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase. """ return "" def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 去除左側開頭空白 S.lstrip([chars]) -> str Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed. If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead. """ return "" def maketrans(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return a translation table usable for str.translate(). If there is only one argument, it must be a dictionary mapping Unicode ordinals (integers) or characters to Unicode ordinals, strings or None. Character keys will be then converted to ordinals. If there are two arguments, they must be strings of equal length, and in the resulting dictionary, each character in x will be mapped to the character at the same position in y. If there is a third argument, it must be a string, whose characters will be mapped to None in the result. """ pass def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 以指定 字符 開始分割 指定的字符也顯示 S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return S and two empty strings. """ pass def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 替換
old -- 將被替換的子字符串。
new -- 新字符串,用於替換old子字符串。
max -- 可選字符串, 替換不超過 max 次
返回值
返回字符串中的 old(舊字符串) 替換成 new(新字符串)後生成的新字符串,如果指定第三個參數max,則替換不超過 max 次。
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
"""
return ""
def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 從右開始查找
S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0
def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 顧名思義從右側匹配
S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0
def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 從右側 填充
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
"""
return ""
def rpartition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 從右側開始找到 分割 分割字符也顯示
S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
"""
pass
def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 從右側開始分割 sep是指定幾個
S.rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and
working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified, any whitespace string
is a separator.
"""
return []
def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 從右側 去除結尾的空格
S.rstrip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
"""
return ""
def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 分割 sep是幾個算分割符
S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are
removed from the result.
"""
return []
def splitlines(self, keepends=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.splitlines([keepends]) -> list of strings
Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
is given and true.
"""
return []
def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 指定以什麼開始
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False
def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 去除兩端空格
S.strip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
"""
return ""
def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 大寫轉小寫小寫轉大寫
S.swapcase() -> str
Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase
and vice versa.
"""
return ""
def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.title() -> str
Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case
characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case.
"""
return ""
def translate(self, table): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
轉換,需要先做一個對應表,最後一個表示刪除字符集合
intab = "aeiou"
outtab = "12345"
trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"print str.translate(trantab, 'xm')
S.translate(table) -> str
Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped
through the given translation table. The table must implement
lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list,
mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If
this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched.
Characters mapped to None are deleted.
"""
return ""
def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 大寫顯示
S.upper() -> str
Return a copy of S converted to uppercase.
"""
return ""
def zfill(self, width): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 方法返回指定長度的字符串,原字符串右對齊,前面填充0。
S.zfill(width) -> str
Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
"""
return ""
def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self+value. """
pass
def __contains__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return key in self. """
pass
def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
pass
def __format__(self, format_spec): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.__format__(format_spec) -> str
Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
"""
return ""
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass
def __getitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self[key]. """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
pass
def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
pass
def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return hash(self). """
pass
def __init__(self, value='', encoding=None, errors='strict'): # known special case of str.__init__
"""
str(object='') -> str
str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str
Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or
errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer
that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler.
Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined)
or repr(object).
encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding().
errors defaults to 'strict'.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement iter(self). """
pass
def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return len(self). """
pass
def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
pass
def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
pass
def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self%value. """
pass
def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self*value.n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value%self. """
pass
def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self*value. """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return str(self). """
pass
官方文檔str
s="abcdef ghg k"
print(s.title()) #將字符串轉換成標題,輸出 Abcdef Ghg K
print(s.capitalize()) #將字符串首字母大寫,輸出 Abcdef ghg k
print(s.count('d',0,len(s))) #計算出子串 'd'在母串中出現的次數,默認是在整個母串中查找,
#可以在後面跟兩個參數指定起始位置查找,這裡我指定了在(0,len(s))中查找,
#其中len(s)代表獲取字符串長度
print(s.startswith('a')) #判斷字符串是否以什麼開頭,這裡輸出True,
print(s.find('g',0,len(s))) #查找子串第一次在母串中出現的位置,這裡輸出7,同樣可以自己指定位置范圍來搜查
print(s.upper()) #將字符串轉換成大寫,這裡輸出ABCDEF GHG K
print(s.join(['a','b','c'])) #用字符串 s 來連接列表['a','b','c'] 輸出 aabcdef ghg kbabcdef ghg kc
print(s.strip()) #移除兩側空格
print(s.split()) #分割字符串,返回一個列表 這裡輸出['abcdef', 'ghg', 'k']
print(s.replace('g','G',1)) #替換,默認全部替換,可以設置為1,只替換一次,這裡只替換一次輸出abcdef Ghg k
print(s[0:4]) #切片,[0:4]代表將字符串s的前面4位取出來,這裡輸出 abcd
注:strip()
s = n.strip("o")
print(s)==>"hell"
列表的基本操作:
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'taobao']


class list(object):
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
"""
def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.append(object) -- append object to end """
pass
def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """
return 0
def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.extend(iterable) -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable """
pass
def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
return 0
def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index """
pass
def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
"""
pass
def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.remove(value) -- remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
pass
def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """
pass
def sort(self, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -- stable sort *IN PLACE*;
cmp(x, y) -> -1, 0, 1
"""
pass
def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass
def __delslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__delslice__(i, j) <==> del x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __iadd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iadd__(y) <==> x+=y """
pass
def __imul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__imul__(y) <==> x*=y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of list.__init__
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __reversed__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass
def __setslice__(self, i, j, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__setslice__(i, j, y) <==> x[i:j]=y
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
list官方文檔
l=['a','b','cc',4] #定義一個列表
l.append(5) #添加一個元素,l=['a', 'b', 'cc', 4, 5]
l.pop() #從尾部刪除一個元素,l=['a', 'b', 'cc', 4]
l.remove('a') #從列表中移除 'a',l=['b', 'cc', 4]
l.extend(['gg','kk']) #添加一個列表['gg','kk'], l=['b', 'cc', 4, 'gg', 'kk']
l.reverse() #反轉一個列表,l=['kk', 'gg', 4, 'cc', 'b']
print(l.count('kk')) #某元素出現的次數 輸出 1
print(l.index('gg')) #元素出現的位置,輸出 1
for i in l: #循環輸出列表元素
print(i)
print(l[0:4:2]) #列表切片,以步長2遞增,輸出['kk', 4]
 列表的練習
列表的練習
元組是一個固定的不可變(元組一旦創建 不等增加也不能減少),tuple也是有序的,tuple使用的是小括號標識
基本操作:


class tuple(object):
"""
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
"""
def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """
return 0
def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
return 0
def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of tuple.__init__
"""
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items
If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__sizeof__() -- size of T in memory, in bytes """
pass
tuple的官方文檔
t=('a','b','b','c') #定義一個元組
print(t.index('b')) #索引出元素第一次出現的位置,還可以指定在某一范圍裡查找,這裡默認在整個元組裡查找輸出1
print(t.count('b')) #計算元素出現的次數,這裡輸出2
print(len(t)) #輸出遠組的長度,這裡輸出4
for i in t:
print(i) #循環打印出元組數據
print(t[1:3]) #切片 輸出('b','b')
元組的其他例子:


############### 元組 #################
name_tuple = ('alex', 'eric')
# 索引
print(name_tuple[0])
# len
print(name_tuple[len(name_tuple)-1])
# 切片
print(name_tuple[0:1])
# for
for i in name_tuple:
print(i)
# 刪除
# del name_tuple[0] 不支持
# count,計算元素出現的個數
print(name_tuple.count('alex'))
# index 獲取指定元素的索引位置
print(name_tuple.index('alex'))
元組
pc = {'host': '2.2.2.2', 'port': 80]}
ps:循環時,默認循環key
常用操作:


class dict(object):
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
"""
def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 清除內容 """
""" D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """
pass
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 淺拷貝 """
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """
pass
@staticmethod # known case
def fromkeys(S, v=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
dict.fromkeys(S[,v]) -> New dict with keys from S and values equal to v.
v defaults to None.
"""
pass
def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 根據key獲取值,d是默認值 """
""" D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. """
pass
def has_key(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 是否有key """
""" D.has_key(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有項的列表形式 """
""" D.items() -> list of D's (key, value) pairs, as 2-tuples """
return []
def iteritems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 項可迭代 """
""" D.iteritems() -> an iterator over the (key, value) items of D """
pass
def iterkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" key可迭代 """
""" D.iterkeys() -> an iterator over the keys of D """
pass
def itervalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" value可迭代 """
""" D.itervalues() -> an iterator over the values of D """
pass
def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的key列表 """
""" D.keys() -> list of D's keys """
return []
def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 獲取並在字典中移除 """
"""
D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised
"""
pass
def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 獲取並在字典中移除 """
"""
D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
"""
pass
def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 如果key不存在,則創建,如果存在,則返回已存在的值且不修改 """
""" D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D """
pass
def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update
""" 更新
{'name':'alex', 'age': 18000}
[('name','sbsbsb'),]
"""
"""
D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
"""
pass
def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有的值 """
""" D.values() -> list of D's values """
return []
def viewitems(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 所有項,只是將內容保存至view對象中 """
""" D.viewitems() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """
pass
def viewkeys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewkeys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """
pass
def viewvalues(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.viewvalues() -> an object providing a view on D's values """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __contains__(self, k): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__contains__(k) -> True if D has a key k, else False """
return False
def __delitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__delitem__(y) <==> del x[y] """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __setitem__(self, i, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__setitem__(i, y) <==> x[i]=y """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
dict的官方文檔
d = {'Michael': 95, 'Bob': 75, 'Tracy': 85}
d.get('Bob') #根據key獲取values,如果不存在返回None,這裡輸出75
d.pop('Bob') #根據鍵刪除某一元素 d={'Michael': 95, 'Tracy': 85}
d['Jason']=99 #新增元素 d={'Michael': 95, 'Tracy': 85, 'Jason': 99}
print(len(d)) #輸出字典長度,這裡輸出3
print('Jason' in d) #python3 中移除了 has_key,要判斷鍵是否存在用in
for i in d:
print(i) #循環默認按鍵輸出
for i in d.values(): #循環按值輸出
print(i)
for k,v in d.items(): #循環按鍵值輸出
print(k,v)


value末尾不要忘記加逗號
contact = {
'222' : ['dfas','fdas','hjgkj'],
'gkgj' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
'3333' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
'324234' : ['dsaf','fdasfsa']
}
print contact['222'] #打印字典的key為222的value
contact['222'][2] = '12314' #將該key的第二個value改為12314
print contact['222'] #打印字典的key為222的value
執行結果
C:\Python27\python.exe //192.168.92.131/Share/py_training/seminar6/day2/dict.py
['dfas', 'fdas', 'hjgkj']
['dfas', 'fdas', '12314']
contact = {
'222' : ['alex','it','num'],
'3333' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
'324234' : ['dsaf','fdasfsa']
}
字典的內置函數
>>> contact = {
... '222' : ['alex','it','num'],
... '3333' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
... '324234' : ['dsaf','fdasfsa']
... }
>>> import tab
>>> contact.
contact.clear(
contact.copy(
contact.fromkeys(
contact.get(
contact.has_key(
contact.items(
contact.iteritems(
contact.iterkeys(
contact.itervalues(
contact.keys(
contact.pop(
contact.popitem(
contact.setdefault(
contact.update(
contact.values(
contact.viewitems(
contact.viewkeys(
contact.viewvalues(
字典練習一


2版本python 查看字典有沒有這個key
>>> contact['4343']
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: '4343'
>>> contact.has_key('343')
False
>>> contact.has_key('3333')
True
清空字典contact.clear()
>>> contact.clear()
字典做列表contact.items()
>>> contact.items()
[('3333', ['dsfa', 'dsfa']), ('222', ['alex', 'it', 'num']), ('324234', ['dsaf', 'fdasfsa'])]
實驗操作 一個參數只打印key
contact = {
'222' : ['alex','it','num'],
'3333' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
'324234' : ['dsaf','fdasfsa']
}
for i in contact:
print i,contact[i]
C:\Python27\python.exe //192.168.92.131/Share/py_training/seminar6/day2/dict.py
3333 ['dsfa', 'dsfa']
222 ['alex', 'it', 'num']
324234 ['dsaf', 'fdasfsa']
contact.items() Key和value都打印
contact = {
'222' : ['alex','it','num'],
'3333' : ['dsfa','dsfa'],
'324234' : ['dsaf','fdasfsa']
}
for k,v in contact.items():
print k,v
C:\Python27\python.exe //192.168.92.131/Share/py_training/seminar6/day2/dict.py
3333 ['dsfa', 'dsfa']
222 ['alex', 'it', 'num']
324234 ['dsaf', 'fdasfsa']
注意
Contact.item()會把一個字典轉換成列表,但是大數據的話,會花費一定時間的,那種情況下就會慢,特別大的數據不建議循環。如果非要在大數據循環用如下辦法:
for i in contact:
print i,contact[i]
幾萬條數據沒關系
字典增加、修改數據
a.get('key') 來確定這個key是否存在而不報錯
>>> a = {'name':'alex','age':'29'}
>>> a['sex']
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError: 'sex'
>>> b=a.get('sex') #字典沒有sex
>>> b
>>> print b #查看為None
None
>>> b=a.get('name')
>>> b
'alex'
>>> print b
alex
> a.iteritems() 迭代器介紹 後面介紹
>>> a.iteritems()
<dictionary-itemiterator object at 0x7ff61e25b680>
>>> print '這是一個迭代器 加速搜索過程'
這是一個迭代器 加速搜索過程
> a.keys()顯示字典的key
>>> a.keys()
['age', 'name']
> a.values()顯示字典value
>>> a.values()
['29', 'alex']
a.pop() 刪除key
>>> a.pop()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: pop expected at least 1 arguments, got 0
>>> a.pop('age')
'29'
>>> a
{'name': 'alex'}
> a['age']=29 > a['sex']='Feale' 增加更改字典的內容
>>> a['age']=29
>>> a['sex']='Male'
>>> a
{'age': 29, 'name': 'alex', 'sex': 'Male'}
>>> a['sex']='Feale'
>>> a
{'age': 29, 'name': 'alex', 'sex': 'Feale'}
字典是無序的
>>> a['birthday']=0624
>>> a
{'age': 29, 'birthday': 404, 'name': 'alex', 'sex': 'Feale'}
>>> a['country']='CN'
>>> a
{'country': 'CN', 'age': 29, 'birthday': 404, 'name': 'alex', 'sex': 'Feale'}
>>> print '字典是無序的'
字典是無序的
a.popitem()也是無序刪除的
>>> a.popitem()
('country', 'CN')
>>> a.popitem()
('age', 29)
>>> a.popitem()
('birthday', 404)
注意 a.popitem()也是無序刪除的
>a.setdefault保護字典的數據
>>> a.setdefault('Occupation')
>>> a
{'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Occupation': None}
>>> a.setdefault('Occupation','IT')
>>> a
{'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Occupation': None}
>>> a.setdefault('Height','170')
'170'
>>> a
{'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> a.setdefault('Height','190')
'170'
>>> a
{'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>>
聚合字典a.update()
>>> a.update()
>>> a
{'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b={1:2,2:3,3:4}
>>> a.update(b)
>>> a
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 4, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b={1:2,2:3,3:66}
>>> b
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66}
>>> a.update(b)
>>> a
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> a.values()
[2, 3, 66, 'alex', 'CN', 'Feale', 404, '170', None]
>>> a.keys()
[1, 2, 3, 'name', 'country', 'sex', 'birthday', 'Height', 'Occupation']
>>> a.viewitems()
dict_items([(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 66), ('name', 'alex'), ('country', 'CN'), ('sex', 'Feale'), ('birthday', 404), ('Height', '170'), ('Occupation', None)])
>>> a.viewkeys()
dict_keys([1, 2, 3, 'name', 'country', 'sex', 'birthday', 'Height', 'Occupation'])
>>> v
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'v' is not defined
>>> b
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66}
清楚列表b.clear()
>>> b.clear()
>>> b
{}
>>> b['asdfa']=232
>>> b['sdf']='dfasf'
>>> b
{'asdfa': 232, 'sdf': 'dfasf'}
>>> b
b bool( bytearray(
basestring( break bytes(
bin( buffer(
刪除字典 del b
>>> del b
>>> b
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'b' is not defined
>>> b = {}
>>> b['sdf']='dfasf'
>>> b
{'sdf': 'dfasf'}
>>> b.copy()
{'sdf': 'dfasf'}
淺復制a.copy() b字典 a字典一樣,修改a ,b不變
>>> b=a.copy()
>>> a
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> a[2]='T' ##改a字典的 key 2
>>> a
{1: 2, 2: 'T', 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b #查看b 不變
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> c=b #賦值字典的方法改一個都被改了
>>> c
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b['2']='fasdfa'
>>> c
{1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, '2': 'fasdfa', 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>> b[2]=123
>>> c
{1: 2, 2: 123, 3: 66, 'name': 'alex', 'country': 'CN', 'sex': 'Feale', 'birthday': 404, '2': 'fasdfa', 'Height': '170', 'Occupation': None}
>>>
字典練習二
set是一個無序且不重復的元素集合


class set(object):
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object
Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
"""
def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 添加 """
"""
Add an element to a set.
This has no effect if the element is already present.
"""
pass
def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements from this set. """
pass
def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return a shallow copy of a set. """
pass
def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set.
(i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)
"""
pass
def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 刪除當前set中的所有包含在 new set 裡的元素 """
""" Remove all elements of another set from this set. """
pass
def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 移除元素 """
"""
Remove an element from a set if it is a member.
If the element is not a member, do nothing.
"""
pass
def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 取交集,新創建一個set """
"""
Return the intersection of two or more sets as a new set.
(i.e. elements that are common to all of the sets.)
"""
pass
def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 取交集,修改原來set """
""" Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. """
pass
def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 如果沒有交集,返回true """
""" Return True if two sets have a null intersection. """
pass
def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 是否是子集 """
""" Report whether another set contains this set. """
pass
def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 是否是父集 """
""" Report whether this set contains another set. """
pass
def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 移除 """
"""
Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
Raises KeyError if the set is empty.
"""
pass
def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 移除 """
"""
Remove an element from a set; it must be a member.
If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError.
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 差集,創建新對象"""
"""
Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set.
(i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 差集,改變原來 """
""" Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. """
pass
def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 並集 """
"""
Return the union of sets as a new set.
(i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
"""
pass
def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 更新 """
""" Update a set with the union of itself and others. """
pass
def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __contains__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x. """
pass
def __eq__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __ge__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __iand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iand__(y) <==> x&=y """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=()): # known special case of set.__init__
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object
Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __ior__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ior__(y) <==> x|=y """
pass
def __isub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__isub__(y) <==> x-=y """
pass
def __iter__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__iter__() <==> iter(x) """
pass
def __ixor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ixor__(y) <==> x^=y """
pass
def __len__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass
def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
__hash__ = None
set的官方文檔
s = set()
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
#添加元素
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.add('The knife girl')
print(a)
#更新
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.update(b)
print(a)
#a中存在。b中不存在,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.difference(b)
print(set)
#a中存在。b中不存在,並更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.difference_update(b)
print(a)
#交集,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.intersection(b)
print(set)
#交集,更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.intersection_update(b)
print(a)
#對稱交集
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.symmetric_difference(b)
print(set)
#對稱交集,更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.symmetric_difference_update(b)
print(a)
#並集,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.union(b)
print(set)
#如果沒有交集,返回True,否則返回False
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.isdisjoint(b)
print(set)
#是否是子序列
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny'}
set = a.issubset(b)
print(set)
#是否是父序列
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny'}
set = a.issuperset(b)
print(set)
#移除指定元素,不存在不報錯
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.discard('suo')
print(a)
#移除指定元素,不存在則報錯
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.remove('suo')
print(a)
a.remove('suo')
print(a)
#移除隨機元素,並賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
set = a.pop()
print(set)
#清空
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.clear()
print(a)
循環可以迭代的對象裡面的內容:
name = ('nick','jenney')
for i in name:
print(i)
為一個可迭代的對象添加序號,可迭代的對象你可以理解成能用for循環的就是可迭代的。默認是編號是從0開始,可以設置從1開始
li = ["手機", "電腦", '鼠標墊', '游艇']
for k, i in enumerate(li,1):
print(k,i)
1 手機
2 電腦
3 鼠標墊
4 游艇
迭代循環
不會先在內存中創建,而是每次循環就創建一次,(節約內存)
for i in range(10): #循環輸出所生成的 0-9
print(i)
for i in range(1,10,2): #輸出所生成的 1 3 5 7 9
print(i)
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],將所有大於 66 的值保存至字典的第一個key中,將小於 66 的值保存至第二個key的值中。
即: {'k1': 大於66的所有值, 'k2': 小於66的所有值}
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
list_a=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,111]
dic = { "k1":[],"k2":[]}
for i in list_a:
if i <= 66:
dic["k1"].append(i)
else:
dic["k2"].append(i)
print("小於66的值:%s 大於66的值:%s " % (dic["k1"],dic["k2"]))
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
li = ["alec", " aric", "Alec", "Tony", "rain"]
tu = ("adnc", " arlc", "Amx", "Tony", "rain")
dic = {'k1': "arm", 'k2': ' apec', "k3": "Alc", "k4": "Tony"}
a=[]
b=[]
c=[]
for i in li:
key_a=i.strip()
if (key_a.startswith("a") or key_a.startswith("A")) and key_a.endswith("c"):
a.append(key_a)
for tup in tu:
key_b = tup.strip()
if (key_b.startswith("a") or key_b.startswith("A")) and key_b.endswith("c"):
b.append(key_b)
for key in dic.keys():
key_c = dic[key].strip()
if (key_c.startswith("a") or key_c.startswith("A")) and key_c.endswith("c"):
c.append(key_c)
print("列表內的符合元素為:",a)
print("元組內的符合元素為:",b)
print("字典內內的符合元素為:",c)
#方法一
l1=[1,2,3,4]
l2=["手機", "電腦", '鼠標墊', '游艇']
d=dict(zip(l1,l2))
print(d)
num=input("請輸入商品編號:")
print("你選擇的商品為 %s" %d[int(num)])
#方法二
li = ["手機", "電腦", '鼠標墊', '游艇']
for k, i in enumerate(li):
print(k,i)
k=input("請輸入商品編號:")
print("你選擇的商品為 %s" % li[int(k)])
功能要求:
goods = [
{"name": "電腦", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠標", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "美女", "price": 998},
]
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
while True:
salary = input("\033[33;1m請輸入你的工資:\033[0m").strip()
if len(salary) == 0:
print("\033[31;1m工資不能為空重新輸入~~\033[0m")
continue
elif salary.isdigit() != True:
print("\033[31;1m輸入必須是數字~~~\033[0m")
continue
else:
break
salary = int(salary)
goods = [
{"name": "電腦", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠標", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "美女", "price": 998},
]
def list_goods():
print("\033[32;1m歡迎來到商城 ,商品列表:\033[0m")
n = 1
for i in goods:
print(n, i["name"], i["price"])
n += 1
list_goods()
shop_list = []
while True:
chose = input("\033[33;1m輸入選中的商品 輸入 quit 離開:\033[0m").strip()
if len(chose) == 0:
print("\033[31;1m選擇不能為空重新輸入~~\033[0m")
continue
elif chose == 'quit':
while True:
print("\033[34;1m購物車列表,如果要移除請選擇序列號\033[0m")
for x in enumerate(shop_list, 1):
print(x[0], x[1])
del_list = input("\033[33;1m你可以移除商品,輸入你的購物車商品編號, 輸入 quit 離開:\033[0m")
if len(del_list) == 0:
print("\033[31;1m不能為空~~\033[0m")
continue
elif del_list == 'quit':
break
elif del_list.isdigit() != True:
print("\033[31;1m必須是個數字\033[0m")
continue
elif int(del_list) > len(shop_list):
print("\033[31;1m物品不存在\033[0m")
continue
del_list = int(del_list)
for i in goods:
if shop_list[del_list - 1] == i["name"]:
salary += i["price"]
print(
"\033[35;1m移除了商品:%s 返回現金:%s 元,目前余額:%s 元\033[0m" % (shop_list[del_list - 1], i["price"], salary))
del shop_list[del_list - 1]
break
elif chose.isdigit() != True:
print("\033[31;1m輸入必須是數字~~~\033[0m")
continue
chose = int(chose)
if chose > len(goods):
print("\033[31;1m你選擇的商品不存在!!\033[0m")
continue
if goods[chose - 1]["price"] <= salary:
salary -= goods[chose - 1]["price"]
shop_list.append(goods[chose - 1]["name"])
print("\033[35;1m你選擇了:%s 還剩下工資:%s 你的購物車內有:%s\033[0m" % (goods[chose - 1]["name"], salary, shop_list))
continue
else:
print("\033[31;1m余額不夠\033[0m")
ans = input("你是否想充值?yes=充值 no=返回商城列表:")
if ans == 'yes':
while True:
add_salary = input("輸入你的充值額數:").strip()
if len(add_salary) == 0:
add_salary = 0
break
elif add_salary.isdigit() != True:
print("\033[31;1m輸入必須是數字~~~")
continue
else:
break
add_salary = int(add_salary)
salary += add_salary
print("充值金額:%s 現在工資:%s 元 " % (add_salary, salary))
elif ans == 'no':
list_goods()
continue
balance = salary
if len(shop_list) < 1:
shop_list = "0件"
print(購買的商品: %s 余額是:%s" % (shop_list, balance))
dic = {
"河北": {
"石家莊": ["鹿泉", "藁城", "元氏"],
"邯鄲": ["永年", "涉縣", "磁縣"],
},
"湖南": {
"長沙":['a','b','c'],
"株洲":['d','e','f']
},
"湖北": {
"武漢":['g','h','i'],
"黃石":['j','k','l']
}
}
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
chinamap = {
"山東省":{
"濟南":["市中區","歷下區","天橋區","槐蔭區","歷城區","長清區","章丘市","平陰縣","濟陽縣","商河縣","其他"],
"青島":["市南區","市北區","城陽區","四方區","李滄區","黃島區","崂山區","膠南市","膠州市","平度市","萊西市","即墨市","其他"]
},
"北京市":{
"北京":["東城區","西城區","崇文區","宣武區","朝陽區","海澱區","豐台區","石景山區","房山區","通州區","順義區","昌平區","大興區","懷柔區","平谷區","門頭溝區","密雲縣","延慶縣","其他"],
},
"廣東省":{
"廣州":["越秀區","荔灣區","海珠區","天河區","白雲區","黃埔區","番禺區","花都區","南沙區","蘿崗區","增城市","從化市","其他"],
"深圳":["福田區","羅湖區","南山區","寶安區","龍崗區","鹽田區","其他"]
},
"河北省":{
"邯鄲":[
"成安縣","磁縣","大名縣","肥鄉縣","館陶縣","廣平縣","邯鄲市","邯鄲縣","雞澤縣","臨漳縣","邱縣","曲周縣","涉縣","魏縣","武安市","永年縣"
],
"衡水":[
"安平縣","阜城縣","故城縣","衡水市","冀州市","景縣","饒陽縣","深州市","武強縣","武邑縣","棗強縣"
],
"石家莊":[
"高邑縣","晉州市","井陉縣","靈壽縣","鹿泉市","平山縣","深澤縣","石家莊市","無極縣","辛集市","新樂市","行唐縣","元氏縣","贊皇縣","趙縣","正定縣","藁城市","栾城縣"
]
}
}
chose=[]
def zero():
print("\033[31;1m選擇不能為空,清重新輸入~~\033[0m")
def crre():
print("\033[31;1m你的選擇不正確,清重新輸入~~\033[0m")
print("\033[32;1m省列表如下:\033[0m\033[0m")
for key in chinamap.keys():
print(key)
while True:
sheng=input("\033[33;1m請輸入省,quit for leave:\033[0m").strip()
if len(sheng) == 0:
zero()
continue
elif sheng == 'quit':
break
elif sheng not in chinamap.keys():
crre()
continue
else:
chose.append(sheng)
print("\033[32;1m市列表如下:\033[0m")
for key_shi in chinamap[sheng].keys():
print(key_shi)
while True:
shi=input("\033[33;1m請輸入市:quit for leave:\033[0m").strip()
if len(shi) == 0:
zero()
elif shi == 'quit':
print("\033[35;1m你選擇的省:%s \033[0m"%(chose[0]))
exit()
elif shi not in chinamap[sheng].keys():
crre()
else:
chose.append(shi)
print("\033[32;1m縣區列表如下:\033[0m")
for key_xian in enumerate(chinamap[sheng][shi],1):
print(key_xian[0],key_xian[1])
while True:
xian=input("\033[33;1m請輸入縣序號,quti for leave:\033[0m").strip()
if len(xian) == 0:
zero()
elif xian == 'quit':
print("\033[35;1m你選擇的省:%s 市是:%s \033[0m"%(chose[0],chose[1]))
exit()
elif xian.isdigit() != True:
print("\033[31;1m必須是 數字\033[0m")
continue
elif int(xian) > len(chinamap[sheng][shi]):
print("\033[31;1m選擇不存在\033[0m")
continue
else:
xian=int(xian)
chose.append(chinamap[sheng][shi][xian-1])
break
break
break
if len(chose) < 1:
print("\033[35;1m你什麼也沒選~~!!\033[0m")
else:
print("\033[35;1m你選擇的省:%s 市是:%s 縣是:%s\033[0m"%(chose[0],chose[1],chose[2]))