Tips : here S The box has not been added to the affine transformation , therefore 0x0、0x1 For the fixed point , Can be eliminated after adding 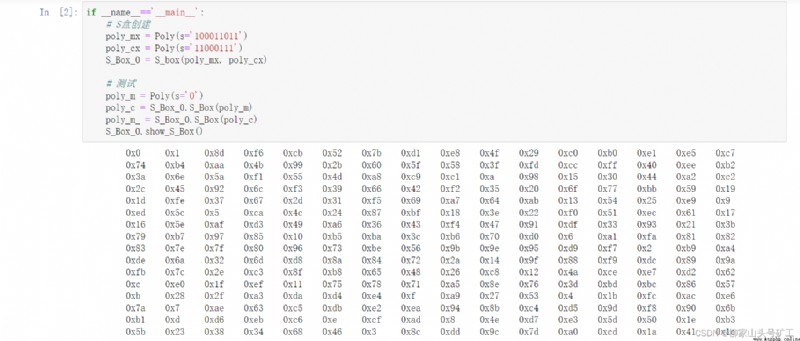
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Polynomial class
class Poly():
def __init__(self, s=None, dex=None, use_String=True):
if use_String:
self.s = s
self.poly, self.length = self.__str2poly()
self.dex = self.__str2dex()
self.hex = hex(self.dex)
else:
self.dex = dex
self.s = str(bin(self.dex))[2:]
self.hex = hex(self.dex)
self.poly, self.length = self.__str2poly()
# target: Receive polynomial , Returns its decimal form
# params: character string
# return: Numbers
def __str2dex(self)-> int:
lt_reversed = self.poly.copy()
lt_reversed.reverse()
ret = 0
for i in range(len(lt_reversed)):
ret += int(lt_reversed[i])<<i
return ret
# target: Receive string , Return to its list form
# params: character string
# return: String list form and its length
def __str2poly(self)-> list:
return list(pd.Series(list(self.s)).map(int)), len(self.s)
# Polynomial operations
class Poly_opera():
def __init__(self, mx):
self.mx = mx
self .m = self.add(self.mx, Poly(''.join(['1',*((self.mx.length-1) * ['0'])])))
# target: Set up mx
# params: mx
# return: nothing
def set_mx(self, mx):
self.mx = mx
self .m = self.add(self.mx, Poly(''.join(['1',*((self.mx.length-1) * ['0'])])))
# target: Add two polynomials
# params: polynomial 0, polynomial 1
# return: Sum of polynomials
def add(self, poly0, poly1):
poly0_lt = poly0.poly
poly1_lt = poly1.poly
align_lt = [0] * abs(poly0.length-poly1.length)
if(poly0.length-poly1.length>=0):
align_lt.extend(poly1_lt)
poly1_lt = align_lt
else:
align_lt.extend(poly0_lt)
poly0_lt = align_lt
xor_res_lt = list((pd.Series(poly0_lt) ^ pd.Series(poly1_lt)).map(str))
return Poly(str(int(''.join(xor_res_lt))))
# target: Calculation poly0 And x^i The product of the
# params: poly0
# return: poly0 And x^i List of product polynomials
def __single_multi(self, poly0):
ret = [poly0]
for i in range(self.mx.length-2):
if(ret[-1].length==self.mx.length-1):
temp_poly_s = Poly(ret[-1].s[1:] + '0')
ret.append(self.add(temp_poly_s, self.m))
else:
temp_poly_s = Poly(ret[-1].s[:] + '0')
ret.append(temp_poly_s)
return ret
# target: Calculation poly0 And poly0 The product of the
# params: poly0,poly1
# return: Product of two polynomials
def multi(self, poly0, poly1):
poly1_lt = poly1.poly.copy()
poly1_lt.reverse()
poly0_single = self.__single_multi(poly0)
ret = Poly('0')
for i in range(len(poly1_lt)):
if(poly1_lt[i]==1):
ret = self.add(ret, poly0_single[i])
return ret
# target: Polynomial division
# paramas: Divisor , Divisor
# return: Quotient and remainder
def div(self, poly_divisor, poly_dividend):
dic_ = {
}
while(poly_divisor.s!='0' and poly_divisor.length >= poly_dividend.length):
extend_length = poly_divisor.length - poly_dividend.length
extend_dividend = Poly(poly_dividend.s + ''.join(['0'] * extend_length))
poly_divisor = self.add(poly_divisor, extend_dividend)
dic_[extend_length+1] = 1
res = []
dic_keys = list(dic_.keys())
for i in range(1, dic_keys[0]+1):
if(i in dic_keys):
res.insert(0, '1')
else:
res.insert(0, '0')
return Poly(''.join(res)), poly_divisor
# target: division
# params: Divisor , Divisor
# return: Quotient and remainder
def get_QR(self, poly_divisor, poly_dividend):
Q_lt = []
R_lt = []
while(poly_dividend.s != '0'):
poly_Q, poly_R = self.div(poly_divisor, poly_dividend)
Q_lt.append(poly_Q)
R_lt.append(poly_R)
poly_divisor = poly_dividend
poly_dividend = poly_R
return Q_lt, R_lt
# target: Finding the inverse of a polynomial ( Prerequisite :gcd(mx,fx)=1)
# paramas: mx,fx
# return: fx mod mx The inverse of
def Euclid_inv(self, poly_fx):
Q_lt, R_lt = self.get_QR(self.mx, poly_fx)
mx_inv = Poly('1')
fx_inv = Poly('0')
Q_lt.reverse()
R_lt.reverse()
for q, r in zip(Q_lt, R_lt):
mx_inv, fx_inv = fx_inv, self.add(mx_inv, self.multi(q, fx_inv))
return fx_inv
# S Box of transformation
class S_box:
def __init__(self, mx, cx):
self.mx = mx
self.cx = cx
self.np_arr_cx = self.__poly2narray(cx)
self.s_box = self.__get_S_box()
self.transform_mat = self.__get_transform_matrix()
# obtain S box
def __get_S_box(self)-> np.ndarray:
S_box_lt = []
for i in range(16):
temp = []
for j in range(16):
temp.append(Poly(dex=i*16+j, use_String=False))
S_box_lt.append(temp)
# Seeking inverse
poly_opera = Poly_opera(self.mx)
func_inv = lambda x: poly_opera.Euclid_inv(x)
for i in range(16):
for j in range(16):
S_box_lt[i][j] = func_inv(S_box_lt[i][j])
return np.array(S_box_lt)
# Obtain the affine transformation matrix
def __get_transform_matrix(self)-> np.ndarray:
arr1 = np.eye(N=7, dtype=np.int16)
arr2 = np.zeros((7,1), dtype=np.int16)
arr3 = np.zeros((1,8), dtype=np.int16)
arr3[0,-1] = 1
arr4 = np.concatenate((arr3, np.concatenate((arr1,arr2),axis=1)),axis=0)
eye = np.eye(N=8, dtype=np.int16)
arr = eye + arr4 @ (eye + arr4 @ (eye + arr4 @ (eye + arr4)))
return arr
# Polynomial to np matrix shape=(1, 8)
def __poly2narray(self, poly0)-> np.ndarray:
poly_lt = poly0.poly.copy()
extend_poly = (8 - poly0.length) * [0] + list(map(int, poly_lt))
return np.array(extend_poly).reshape((8,1))
# np Matrix to polynomial
def __narray2poly(self, arr: np.ndarray):
return Poly(''.join(list(map(str,list(map(int,list(arr)))))))
# The bytes are S Box of transformation & Affine transformation
def S_Box(self, poly0):
# Address the query
m_arr = self.__poly2narray(poly0)
row = self.__narray2poly(m_arr[:4]).dex
col = self.__narray2poly(m_arr[4:]).dex
# S Box of transformation
temp = self.s_box[row, col]
# Affine transformation
poly_opera = Poly_opera(self.mx)
poly_ret = Poly(self.cx.s)
for i in range(8):
poly_ret = poly_opera.add(poly_ret, poly_opera.multi(self.__narray2poly(self.transform_mat[i,:]),temp))
return poly_ret
# s Box view
def show_S_Box(self):
for i in range(16):
for j in range(16):
print(f'\t{
self.s_box[i, j].hex}', end='')
print()
if __name__=='__main__':
# S Box creation
poly_mx = Poly(s='100011011')
poly_cx = Poly(s='11000111')
S_Box_0 = S_box(poly_mx, poly_cx)
# test
poly_m = Poly(s='0')
poly_c = S_Box_0.S_Box(poly_m)
poly_m_ = S_Box_0.S_Box(poly_c)
S_Box_0.show_S_Box()