
大家好,我是小F。
Python在編程語言流行指數PYPL中已多次排名第一。
由於其代碼可讀性和更簡單的語法,它被認為是有史以來最簡單的語言。
NumPy、Pandas、TensorFlow等各種AI和機器學習庫的豐富性,是Python核心需求之一。
如果你是數據科學家或 AI/機器學習的初學者,那麼Python是開始你的旅程的正確選擇。
本次,小F會帶著大家探索一些Python編程的基礎知識,雖然簡單但都很有用。
目錄
數據類型
變量
列表
集合
字典
注釋
基本功能
條件語句
循環語句
函數
異常處理
字符串操作
正則表達式
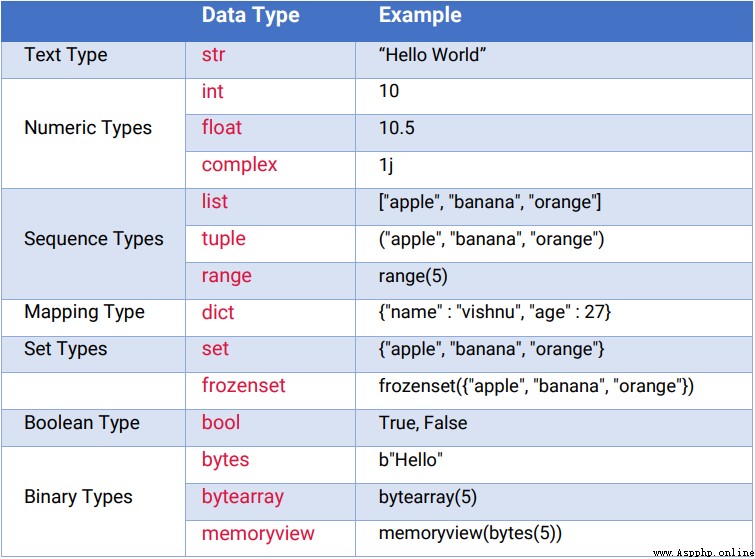
▍1、數據類型
數據類型是可以存儲在變量中的數據規范。解釋器根據變量的類型為變量分配內存。
下面是Python中的各種數據類型。
▍2、變量
變量是存放數據值的容器。
變量可以使用短名稱(如x和y)或更具描述性的名稱(age、carname、total_volume)。
Python 變量命名規則:
變量名必須以字母或下劃線字符開頭
變量名稱不能以數字開頭
變量名只能包含字母數字字符和下劃線(A-z、0-9和_)
變量名稱區分大小寫(age、Age和AGE是三個不同的變量)
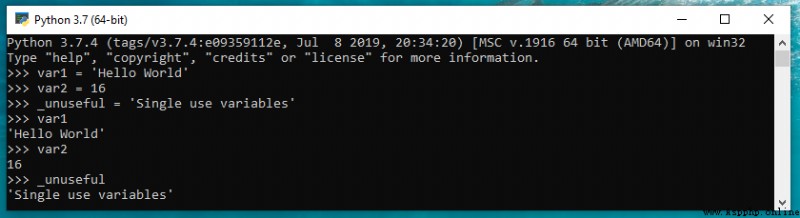
var1 = 'Hello World'
var2 = 16
_unuseful = 'Single use variables'輸出結果如下。
▍3、列表
列表(List)是一種有序和可更改的集合,允許重復的成員。
它可能不是同質的,我們可以創建一個包含不同數據類型(如整數、字符串和對象)的列表。
>>> companies = ["apple","google","tcs","accenture"]
>>> print(companies)
['apple', 'google', 'tcs', 'accenture']
>>> companies.append("infosys")
>>> print(companies)
['apple', 'google', 'tcs', 'accenture', 'infosys']
>>> print(len(companies))
5
>>> print(companies[2])
tcs
>>> print(companies[-2])
accenture
>>> print(companies[1:])
['google', 'tcs', 'accenture', 'infosys']
>>> print(companies[:1])
['apple']
>>> print(companies[1:3])
['google', 'tcs']
>>> companies.remove("infosys")
>>> print(companies)
["apple","google","tcs","accenture"]
>>> companies.pop()
>>> print(companies)
["apple","google","tcs"]▍4、集合
集合(Set)是一個無序和無索引的集合,沒有重復的成員。
對於從列表中刪除重復條目非常有用。它還支持各種數學運算,例如並集、交集和差分。
>>> set1 = {1,2,3,7,8,9,3,8,1}
>>> print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9}
>>> set1.add(5)
>>> set1.remove(9)
>>> print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8}
>>> set2 = {1,2,6,4,2}
>>> print(set2)
{1, 2, 4, 6}
>>> print(set1.union(set2)) # set1 | set2
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
>>> print(set1.intersection(set2)) # set1 & set2
{1, 2}
>>> print(set1.difference(set2)) # set1 - set2
{8, 3, 5, 7}
>>> print(set2.difference(set1)) # set2 - set1
{4, 6}▍5、字典
字典是作為鍵值對的可變無序項集合。
與其他數據類型不同,它以【鍵:值】對格式保存數據,而不是存儲單個數據。此功能使其成為映射JSON響應的最佳數據結構。
>>> # example 1
>>> user = { 'username': 'Fan', 'age': 20, 'mail_id': '[email protected]', 'phone': '18650886088' }
>>> print(user)
{'mail_id': '[email protected]', 'age': 20, 'username': 'Fan', 'phone': '18650886088'}
>>> print(user['age'])
20
>>> for key in user.keys():
>>> print(key)
mail_id
age
username
phone
>>> for value in user.values():
>>> print(value)
[email protected]
20
Fan
18650886088
>>> for item in user.items():
>>> print(item)
('mail_id', '[email protected]')
('age', 20)
('username', 'Fan')
('phone', '18650886088')
>>> # example 2
>>> user = {
>>> 'username': "Fan",
>>> 'social_media': [
>>> {
>>> 'name': "Linkedin",
>>> 'url': "https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022"
>>> },
>>> {
>>> 'name': "Github",
>>> 'url': "https://github.com/codemaker2022"
>>> },
>>> {
>>> 'name': "QQ",
>>> 'url': "https://codemaker2022.qq.com"
>>> }
>>> ],
>>> 'contact': [
>>> {
>>> 'mail': [
>>> "[email protected]",
>>> "[email protected]"
>>> ],
>>> 'phone': "18650886088"
>>> }
>>> ]
>>> }
>>> print(user)
{'username': 'Fan', 'social_media': [{'url': 'https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022', 'name': 'Linkedin'}, {'url': 'https://github.com/codemaker2022', 'name': 'Github'}, {'url': 'https://codemaker2022.qq.com', 'name': 'QQ'}], 'contact': [{'phone': '18650886088', 'mail': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]']}]}
>>> print(user['social_media'][0]['url'])
https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022
>>> print(user['contact'])
[{'phone': '18650886088', 'mail': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]']}]▍6、注釋
單行注釋,以井字符(#)開頭,後面帶有消息並在行尾結束。
# 定義用戶年齡
age = 27
dob = '16/12/1994' # 定義用戶生日多行注釋,用特殊引號(""")括起來,你可以將消息放在多行中。
"""
Python小常識
This is a multi line comment
"""▍7、基本功能
print()函數在控制台中打印提供的消息。此外你還可以提供文件或緩沖區輸入作為在屏幕上打印的參數。
print(object(s), sep=separator, end=end, file=file, flush=flush)
print("Hello World") # prints Hello World
print("Hello", "World") # prints Hello World?
x = ("AA", "BB", "CC")
print(x) # prints ('AA', 'BB', 'CC')
print("Hello", "World", sep="---") # prints Hello---Worldinput()函數用於收集來自控制台的用戶輸入 。
這裡需要注意,input()會把你輸入的任何內容轉換為字符串。
因此,如果你將年齡作為整數值提供,但input()方法將其作為字符串返回,此時就需要手動將其轉換為整數。
>>> name = input("Enter your name: ")
Enter your name: Codemaker
>>> print("Hello", name)
Hello Codemakerlen()可以查看對象的長度。如果你輸入一個字符串,則可以獲取指定字符串中的字符數。
>>> str1 = "Hello World"
>>> print("The length of the string is ", len(str1))
The length of the string is 11str()用於將其他數據類型轉換為字符串值。
>>> str(123)
123
>>> str(3.14)
3.14int()用於將字符串轉換為整數。
>>> int("123")
123
>>> int(3.14)
3▍8、條件語句
條件語句是用於根據特定條件更改程序流程的代碼塊。這些語句只有在滿足特定條件時才會執行。
在Python中,我們使用if,if-else,循環(for,while)作為條件語句根據某些條件來改變程序的流程。
if-else語句。
>>> num = 5
>>> if (num > 0):
>>> print("Positive integer")
>>> else:
>>> print("Negative integer")elif語句。
>>> name = 'admin'
>>> if name == 'User1':
>>> print('Only read access')
>>> elif name == 'admin':
>>> print('Having read and write access')
>>> else:
>>> print('Invalid user')
Having read and write access▍9、循環語句
循環是一個條件語句,用於重復某些語句(在其主體中),直到滿足某個條件。
在Python中,我們通常使用for和while循環。
for循環。
>>> # loop through a list
>>> companies = ["apple", "google", "tcs"]
>>> for x in companies:
>>> print(x)
apple
google
tcs
>>> # loop through string
>>> for x in "TCS":
>>> print(x)
T
C
Srange()函數返回一個數字序列,它可以用作for循環控制。
它基本上需要三個參數,其中第二個和第三個是可選的。參數是開始值、停止值和步進數。步進數是每次迭代循環變量的增量值。
>>> # loop with range() function
>>> for x in range(5):
>>> print(x)
0
1
2
3
4
>>> for x in range(2, 5):
>>> print(x)
2
3
4
>>> for x in range(2, 10, 3):
>>> print(x)
2
5
8我們還可以使用else關鍵字在循環結束時執行一些語句。
在循環結束時提供else語句以及循環結束時需要執行的語句。
>>> for x in range(5):
>>> print(x)
>>> else:
>>> print("finished")
0
1
2
3
4
finishedwhile循環。
>>> count = 0
>>> while (count < 5):
>>> print(count)
>>> count = count + 1
0
1
2
3
4我們可以在while循環的末尾使用else,類似於for循環,當條件為假時執行一些語句。
>>> count = 0
>>> while (count < 5):
>>> print(count)
>>> count = count + 1
>>> else:
>>> print("Count is greater than 4")
0
1
2
3
4
Count is greater than 4▍10、函數
函數是用於執行任務的可重用代碼塊。在代碼中實現模塊化並使代碼可重用,這是非常有用的。
>>> # This prints a passed string into this function
>>> def display(str):
>>> print(str)
>>> return
>>> display("Hello World")
Hello World▍11、異常處理
即使語句在語法上是正確的,它也可能在執行時發生錯誤。這些類型的錯誤稱為異常。我們可以使用異常處理機制來避免此類問題。
在Python中,我們使用try,except和finally關鍵字在代碼中實現異常處理。
>>> def divider(num1, num2):
>>> try:
>>> return num1 / num2
>>> except ZeroDivisionError as e:
>>> print('Error: Invalid argument: {}'.format(e))
>>> finally:
>>> print("finished")
>>>
>>> print(divider(2,1))
>>> print(divider(2,0))
finished
2.0
Error: Invalid argument: division by zero
finished
None▍12、字符串操作
字符串是用單引號或雙引號(',")括起來的字符集合。
我們可以使用內置方法對字符串執行各種操作,如連接、切片、修剪、反轉、大小寫更改和格式化,如split()、lower()、upper()、endswith()、join()和ljust()、rjust()、format()。
>>> msg = 'Hello World'
>>> print(msg)
Hello World
>>> print(msg[1])
e
>>> print(msg[-1])
d
>>> print(msg[:1])
H
>>> print(msg[1:])
ello World
>>> print(msg[:-1])
Hello Worl
>>> print(msg[::-1])
dlroW olleH
>>> print(msg[1:5])
ello
>>> print(msg.upper())
HELLO WORLD
>>> print(msg.lower())
hello world
>>> print(msg.startswith('Hello'))
True
>>> print(msg.endswith('World'))
True
>>> print(', '.join(['Hello', 'World', '2022']))
Hello, World, 2022
>>> print(' '.join(['Hello', 'World', '2022']))
Hello World 2022
>>> print("Hello World 2022".split())
['Hello', 'World', '2022']
>>> print("Hello World 2022".rjust(25, '-'))
---------Hello World 2022
>>> print("Hello World 2022".ljust(25, '*'))
Hello World 2022*********
>>> print("Hello World 2022".center(25, '#'))
#####Hello World 2022####
>>> name = "Codemaker"
>>> print("Hello %s" % name)
Hello Codemaker
>>> print("Hello {}".format(name))
Hello Codemaker
>>> print("Hello {0}{1}".format(name, "2022"))
Hello Codemaker2022▍13、正則表達式
導入regex模塊,import re。
re.compile()使用該函數創建一個Regex對象。
將搜索字符串傳遞給search()方法。
調用group()方法返回匹配的文本。
>>> import re
>>> phone_num_regex = re.compile(r'\d\d\d-\d\d\d-\d\d\d\d')
>>> mob = phone_num_regex.search('My number is 996-190-7453.')
>>> print('Phone number found: {}'.format(mob.group()))
Phone number found: 996-190-7453
>>> phone_num_regex = re.compile(r'^\d+$')
>>> is_valid = phone_num_regex.search('+919961907453.') is None
>>> print(is_valid)
True
>>> at_regex = re.compile(r'.at')
>>> strs = at_regex.findall('The cat in the hat sat on the mat.')
>>> print(strs)
['cat', 'hat', 'sat', 'mat']好了,本期的分享就到此結束了,有興趣的小伙伴可以自行去實踐學習。
萬水千山總是情,點個 行不行。
推薦閱讀



··· END ···

 According to the longitude and latitude coordinates, the name of the administrative division city of the province, city and county is obtained, and the self built database Java Python PHP C # Net
According to the longitude and latitude coordinates, the name of the administrative division city of the province, city and county is obtained, and the self built database Java Python PHP C # Net
stay LBS Application , It is a