學習一種知識,我喜歡看看源碼是怎麼進行它們類之間的關系以及方法的調用,是怎麼實現的。這樣我才感覺踏實。
既然現在談到HandlerMapping,我們先知道HandlerMapping的作用:HandlerMapping的作用就是解析請求鏈接,然後根據請求鏈接找到執行這個請求的類(HandlerMapping所說的handler,也就是我們寫的Controller或是Action)。
現在我們來了解HandlerMapping的繼承體系圖:
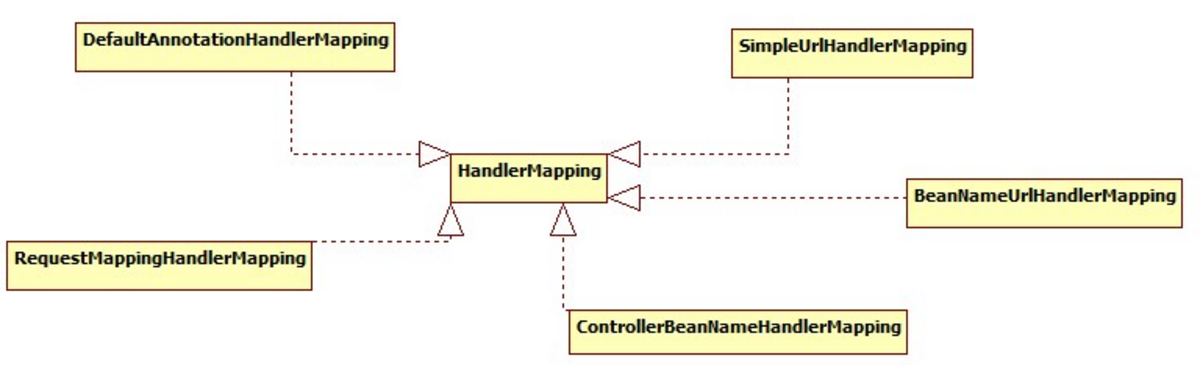
至於我們在配置文件中配置的BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping或者是SimpleUrlHandlerMapping,他們的目的是一樣的,只是通過請求鏈接來找handler的方式不一樣。
我們再來看看更詳細的繼承關系:
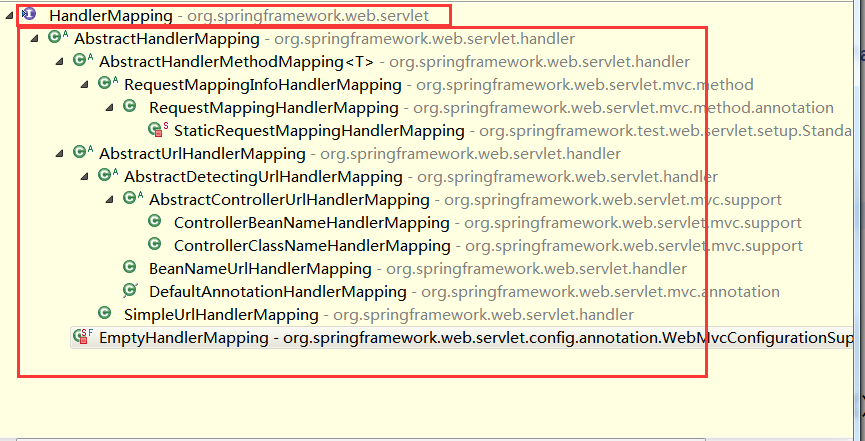
HandlerMapping的使用主要分為兩步:注冊和查找。
注冊是根據配置文件中的配置將一個字符串和一個Controller類以<key,value>的形式存入到Map中,這個key就是對應的url中的某個字段。
查找就是HandlerMapping根據url中的的某個字段,在Map中以這個字段為key值對應的Controller類,並將Controller類封裝成一個HandlerExecutionChain對象,HandlerExecutionChain中除了有Controller對象外,還有一組攔截器。
現在我簡單以SimpleUrlHandlerMapping為例子來分析HandlerMapping是如何根據請求鏈接找到Controller類的。
1.注冊
<!-- SpringMVC中的HandlerMapping配置 配置映射器 -->
<bean id="" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="/*.do">helloword</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!--配置處理器 -->
<bean id="helloword" class="cn.controller.HelloController">
<property name="methodNameResolver" ref="nameResolver">
</property>
</bean>
當我們第一次訪問服務器的時候IOC容器會根據配置文件中的紅色的部分生成一個Map<String, Object>,這個map裡面的值就是{/*.do=/helloworld}。
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的作用就是獲取這個集合,然後根據這個集合裡的value找到對應的bean,這樣就可以把url中的某個字段和我們寫的處理器對應起來。下面是SimpleUrlHandlerMapping中的關鍵源碼
/**
* Calls the {@link #registerHandlers} method in addition to the
* superclass's initialization.
*/
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
super.initApplicationContext();
registerHandlers(this.urlMap);
}
我們來看看HandlerMapping的父類
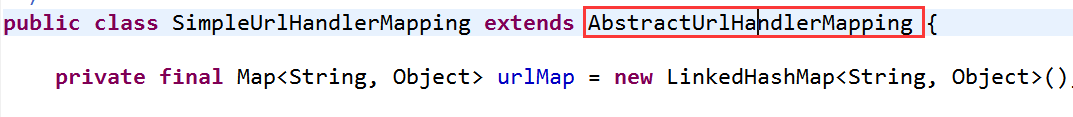
但是在這個類中沒有initApplicationContext()方法,我們就再來看看AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的父類

的確,在這個類中有了我們想要的initApplicationContext()方法。
/**
* Initializes the interceptors.
* @see #extendInterceptors(java.util.List)
* @see #initInterceptors()
*/
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
這個方法就是初始化SpringMVC容器,並對handler進行注冊,urlMap中的值根據上面的配置文件就是{/*.do=/helloWorld}的
現在我們一起來看registerHandlers方法,
/**
* Register all handlers specified in the URL map for the corresponding paths.
* @param urlMap Map with URL paths as keys and handler beans or bean names as values
* @throws BeansException if a handler couldn't be registered
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is a conflicting handler registered
*/
protected void registerHandlers(Map<String, Object> urlMap) throws BeansException {
if (urlMap.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("Neither 'urlMap' nor 'mappings' set on SimpleUrlHandlerMapping");
}
else {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : urlMap.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
Object handler = entry.getValue();
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!url.startsWith("/")) {
url = "/" + url;
}
// Remove whitespace from handler bean name.
if (handler instanceof String) {
handler = ((String) handler).trim();
}
registerHandler(url, handler);
}
}
}
主要是對urlMap中的key值進行了一些處理,要是沒有“/”的就加上"/",去掉空格等處理。這個方法中的重點是調用了registerHandler(url, handler)這個方法,在這個方法是它的父類AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的方法。
我們來看看AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的registerHandler(url, handler)的方法
/**
* Register the specified handler for the given URL path.
* @param urlPath the URL the bean should be mapped to
* @param handler the handler instance or handler bean name String
* (a bean name will automatically be resolved into the corresponding handler bean)
* @throws BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is a conflicting handler registered
*/
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
// Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name.
if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
if (getApplicationContext().isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (mappedHandler != null) {
if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath +
"]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
}
else {
if (urlPath.equals("/")) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
}
else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
看registerHandler方法紅色的部分大家,可以看出是根據SimpleUrlHandlerMapping中的urlMap中的value值在ioc容器中找到對應的bean,並將url的某個字段作為key值,bean作為value存入到AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的urlMap屬性中去,這樣就達到url的某個字段對應到具體的controller了的目的,當遇到有請求訪問服務器的時候,就可以根據url找到具體的controller去執行這個請求了。
2.查找
在Dispatcher類中,根據配置文件對handlerMapping進行注冊,即對handlerMapping的初始化。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
<span >initHandlerMappings(context);</span>
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
<span >Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);</span>
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
<span >this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());</span>
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
於在配置文件中有兩種不同類型的handlerMapping,所以從ioc容器中讀取出來的handlerMapping有兩個,然後將這兩個handlerMapping的實例放入Dodispatcher中的handlerMappings屬性中。
下面一步就是真正的根據url中的某個字段到已經注冊好了的Map<urlString,Controller>中找出執行這個url請求的Controller,用戶的請求在被Dispatcher攔截後,會交給Dispatcher的doDispatch執行。在doDispatch方法中主要看紅色標記的getHandler方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
int interceptorIndex = -1;
try {
ModelAndView mv;
boolean errorView = false;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
<span >mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);</span>
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + requestUri + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// Apply preHandle methods of registered interceptors.
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = mappedHandler.getInterceptors();
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler())) {
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
return;
}
interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Do we need view name translation?
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request));
}
// Apply postHandle methods of registered interceptors.
if (interceptors != null) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler(), mv);
}
}
}
catch (ModelAndViewDefiningException ex) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", ex);
mv = ex.getModelAndView();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(processedRequest, response, handler, ex);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, processedRequest, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
// Trigger after-completion for successful outcome.
triggerAfterCompletion(mappedHandler, interceptorIndex, processedRequest, response, null);
}
getHandler方法主要會調用已經注冊好了的handlerMapping中的getHandler方法
DispatcherServlet中的getHandler方法
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
現在再來看看HandlerMapping的getHandler方法,可以看到HandlerMapping接口中只有一個getHandler方法
public interface HandlerMapping {
/**
* Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the path
* within the handler mapping, in case of a pattern match, or the full
* relevant URI (typically within the DispatcherServlet's mapping) else.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will
* typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect
* this request attribute to be present in all scenarios.
*/
String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping";
/**
* Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the
* best matching pattern within the handler mapping.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will
* typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect
* this request attribute to be present in all scenarios.
*/
String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern";
/**
* Name of the boolean {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that indicates
* whether type-level mappings should be inspected.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations.
*/
String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping";
/**
* Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the URI
* templates map, mapping variable names to values.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations. URL-based HandlerMappings will
* typically support it, but handlers should not necessarily expect
* this request attribute to be present in all scenarios.
*/
String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
/**
* Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains a map with
* URI matrix variables.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations and may also not be present depending on
* whether the HandlerMapping is configured to keep matrix variable content
* in the request URI.
*/
String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables";
/**
* Name of the {@link HttpServletRequest} attribute that contains the set of
* producible MediaTypes applicable to the mapped handler.
* <p>Note: This attribute is not required to be supported by all
* HandlerMapping implementations. Handlers should not necessarily expect
* this request attribute to be present in all scenarios.
*/
String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes";
/**
* Return a handler and any interceptors for this request. The choice may be made
* on request URL, session state, or any factor the implementing class chooses.
* <p>The returned HandlerExecutionChain contains a handler Object, rather than
* even a tag interface, so that handlers are not constrained in any way.
* For example, a HandlerAdapter could be written to allow another framework's
* handler objects to be used.
* <p>Returns {@code null} if no match was found. This is not an error.
* The DispatcherServlet will query all registered HandlerMapping beans to find
* a match, and only decide there is an error if none can find a handler.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return a HandlerExecutionChain instance containing handler object and
* any interceptors, or {@code null} if no mapping found
* @throws Exception if there is an internal error
*/
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
再看看實現了HandlerMapping的AbstractHandlerMapping抽象類,AbstractHandlerMapping中的getHandler方法,這個方法的主要作用是根據url找到controller後,並將controller封裝成一個HandlerExecutionChain對象
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal方法是個抽象方法,由AbstractHandlerMapping的子類AbstractUrlHandlerMapping實現
/**
* Look up a handler for the given request, returning {@code null} if no
* specific one is found. This method is called by {@link #getHandler};
* a {@code null} return value will lead to the default handler, if one is set.
* <p>On CORS pre-flight requests this method should return a match not for
* the pre-flight request but for the expected actual request based on the URL
* path, the HTTP methods from the "Access-Control-Request-Method" header, and
* the headers from the "Access-Control-Request-Headers" header thus allowing
* the CORS configuration to be obtained via {@link #getCorsConfigurations},
* <p>Note: This method may also return a pre-built {@link HandlerExecutionChain},
* combining a handler object with dynamically determined interceptors.
* Statically specified interceptors will get merged into such an existing chain.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the corresponding handler instance, or {@code null} if none found
* @throws Exception if there is an internal error
*/
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping實現類裡面的getHandlerInternal方法
/**
* Look up a handler for the URL path of the given request.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the handler instance, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Override
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}
getLookupPathForRequest方法主要是截取url中對應controller的那一部分,lookupHandler方法根據截取的url字段找到對應的controller,看到紅色的部分就和我們注冊handlerMapping的那一步相關了,我們早早的就將url的部分字段所對應的controller放到了AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的handlerMap屬性中了,現在就能根據url找到對應的controller了
/**
* Look up a handler instance for the given URL path.
* <p>Supports direct matches, e.g. a registered "/test" matches "/test",
* and various Ant-style pattern matches, e.g. a registered "/t*" matches
* both "/test" and "/team". For details, see the AntPathMatcher class.
* <p>Looks for the most exact pattern, where most exact is defined as
* the longest path pattern.
* @param urlPath URL the bean is mapped to
* @param request current HTTP request (to expose the path within the mapping to)
* @return the associated handler instance, or {@code null} if not found
* @see #exposePathWithinMapping
* @see org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher
*/
protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// Direct match?
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if (handler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null);
}
// Pattern match?
List<String> matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) {
if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern);
}
else if (useTrailingSlashMatch()) {
if (!registeredPattern.endsWith("/") && getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern + "/", urlPath)) {
matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern +"/");
}
}
}
String bestPatternMatch = null;
Comparator<String> patternComparator = getPathMatcher().getPatternComparator(urlPath);
if (!matchingPatterns.isEmpty()) {
Collections.sort(matchingPatterns, patternComparator);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Matching patterns for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + matchingPatterns);
}
bestPatternMatch = matchingPatterns.get(0);
}
if (bestPatternMatch != null) {
handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestPatternMatch);
if (handler == null) {
Assert.isTrue(bestPatternMatch.endsWith("/"));
handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestPatternMatch.substring(0, bestPatternMatch.length() - 1));
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(handler, request);
String pathWithinMapping = getPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestPatternMatch, urlPath);
// There might be multiple 'best patterns', let's make sure we have the correct URI template variables
// for all of them
Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
for (String matchingPattern : matchingPatterns) {
if (patternComparator.compare(bestPatternMatch, matchingPattern) == 0) {
Map<String, String> vars = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(matchingPattern, urlPath);
Map<String, String> decodedVars = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, vars);
uriTemplateVariables.putAll(decodedVars);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("URI Template variables for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + uriTemplateVariables);
}
return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, bestPatternMatch, pathWithinMapping, uriTemplateVariables);
}
// No handler found...
return null;
}
到這裡算是完了。但是大家可能感覺有點蒙,所以還總結了,方便記憶和理解
就對源碼中是如何根據url找到對應的controller進行總結
1.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping根據配置文件中的SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的配置,獲得一個map集合,map中存儲的是{urlString=beanId}。SimpleUrlHandlerMapping調用父類
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler方法。
2.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的registerHandler方法有SimpleUrlHandlerMapping傳入的map中的urlString和beanId,並根據beanId找到對應的bean即controller,將urlString和urlString對應的controller放入AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的handlerMap中。
3.Dispatcher獲取IOC容器中已經初始化好的HandlerMapping,再由HandlerMapping調用自己的getHandler方法根據請求返回HandlerExecutionChain對象。AbstractHandlerMapping方法實現了HandlerMapping接口的getHandler方法。AbstractHandlerMapping中的getHandler方法的主要作用是找到controller,並對controller進行封裝成HandlerExecutionChain對象,HandlerExecutionChain中除了controller對象外,還有攔截器對象的集合。
4.AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法中又 調用了AbstractHandlerMapping子類的AbstractUrlHandlerMapping getHandlerInternal方法。getHandlerInternal方法就是截取url中對應的controller字段,並以這個字段為key值去AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 的handlerMap中找尋對應的value,即controlle。