動手動腦,第六次Tutorial——數組
這次的Tutorial講解了Java中如何進行數組操作,包括數組聲明創建使用和賦值運算,寫這篇文章的目的就是通過實際運用已達到對數組使用的更加熟練,下面是實踐代碼之後的感悟與總結:
動手動腦1:PassArray.java
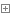
1 // PassArray.java
2 // Passing arrays and individual array elements to methods
3
4 public class PassArray {
5
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
8 String output = "The values of the original array are:\n";
9
10 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
11 output += " " + a[i];
12
13 output += "\n\nEffects of passing array " + "element call-by-value:\n"
14 + "a[3] before modifyElement: " + a[3];
15
16 modifyElement(a[3]);
17
18 output += "\na[3] after modifyElement: " + a[3];
19
20 output += "\n Effects of passing entire array by reference";
21
22 modifyArray(a); // array a passed call-by-reference
23
24 output += "\n\nThe values of the modified array are:\n";
25
26 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
27 output += " " + a[i];
28
29 System.out.println(output);
30 }
31
32 public static void modifyArray(int b[]) {
33 for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++)
34 b[j] *= 2;
35 }
36
37 public static void modifyElement(int e) {
38 e *= 2;
39 }
40
41 }
PassArray.java
觀察並分析程序的輸出結果:
可以得出如下結論:
動手動腦2:QiPan.java

1 import java.io.*;
2
3 public class QiPan
4 {
5 //定義一個二維數組來充當棋盤
6 private String[][] board;
7 //定義棋盤的大小
8 private static int BOARD_SIZE = 15;
9 public void initBoard()
10 {
11 //初始化棋盤數組
12 board = new String[BOARD_SIZE][BOARD_SIZE];
13 //把每個元素賦為"╋",用於在控制台畫出棋盤
14 for (int i = 0 ; i < BOARD_SIZE ; i++)
15 {
16 for ( int j = 0 ; j < BOARD_SIZE ; j++)
17 {
18 board[i][j] = "╋";
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 //在控制台輸出棋盤的方法
23 public void printBoard()
24 {
25 //打印每個數組元素
26 for (int i = 0 ; i < BOARD_SIZE ; i++)
27 {
28 for ( int j = 0 ; j < BOARD_SIZE ; j++)
29 {
30 //打印數組元素後不換行
31 System.out.print(board[i][j]);
32 }
33 //每打印完一行數組元素後輸出一個換行符
34 System.out.print("\n");
35 }
36 }
37 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
38 {
39 QiPan gb = new QiPan();
40 gb.initBoard();
41 gb.printBoard();
42 //這是用於獲取鍵盤輸入的方法
43 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
44 String inputStr = null;
45 System.out.println("請輸入您下棋的座標,應以x,y的格式:");
46 //br.readLine():每當在鍵盤上輸入一行內容按回車,剛輸入的內容將被br讀取到。
47 while ((inputStr = br.readLine()) != null)
48 {
49 //將用戶輸入的字符串以逗號(,)作為分隔符,分隔成2個字符串
50 String[] posStrArr = inputStr.split(",");
51 //將2個字符串轉換成用戶下棋的座標
52 int xPos = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[0]);
53 int yPos = Integer.parseInt(posStrArr[1]);
54 //把對應的數組元素賦為"●"。
55 gb.board[xPos - 1][yPos - 1] = "●";
56 /*
57 電腦隨機生成2個整數,作為電腦下棋的座標,賦給board數組。
58 還涉及
59 1.座標的有效性,只能是數字,不能超出棋盤范圍
60 2.如果下的棋的點,不能重復下棋。
61 3.每次下棋後,需要掃描誰贏了
62 */
63 gb.printBoard();
64 System.out.println("請輸入您下棋的座標,應以x,y的格式:");
65 }
66 }
67 }
QiPan.java
程序運行輸出結果:
棋盤是如何表示的?
整個棋盤是用一個個“+”組成的,共15行15列,所以可以使用一個15X15的二維數組表示,用戶下棋的位置用行列位置表示,這樣用戶下棋的位置所對應的數組元素將由“+”變為“·”。棋盤類結構如下:
1. 私有靜態變量BOARD_SIZE,初始值為15;
2. 私有變量二維字符串數組board[][];
3. 共有方法InitBoard(),初始化棋盤;
4. 共有方法PrintBoard(),打印棋盤;
動手動腦3:IntToChinese.java
問題描述:
請編寫一個程序將一個整數轉換為漢字讀法字符串。比如“1123”轉換為“一千一百二十三”。
設計思想:
假如說這個整數最高位數不超過5位,那麼問題其實並不是很復雜。實現這個功能的方法可以這麼定義:
源代碼:

1 import java.util.Scanner;
2 public class IntToChinese {
3
4 public static void main(String[] args) {
5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
6 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
7 System.out.print("請輸入一個99999以內的一個整數:");
8 int number = in.nextInt();
9 System.out.println("轉換中。。。。");
10 System.out.println( ToChinese(number) );
11 }
12
13 public static String ToChinese(int num) {
14 // 將阿拉伯數字用漢字表示
15 String chineseNumber[] = {"零","一","二","三","四","五","六","七","八","九"};
16 String chinesePost[] = {"","十","百","千","萬"};
17 String result = ""; // 存放結果
18 String n = Integer.toString(num); // 將數字轉化為字符串
19 char c[] = n.toCharArray();
20 for (int i = 0; i < n.length(); i++) {
21 result += chineseNumber[c[i]-'0']+chinesePost[n.length()-i-1];
22 }
23 return result;
24 }
25 }
IntToChinese.java
運行結果:
動手動腦4:BigNumber.java
問題描述:
利用數組實現大數相加減。
設計思想:
一個數組元素存取一位數字,無論加法還是減法,都是從低位開始運算,即數組的最後一個元素開始運算,加法滿10進1,每個數組元素的最高值為9,相加的和a超過9就讓前一個數組+a/10,新的元素值就是a%10,如:
源代碼:
【添加代碼】
運行結果:
【結果截圖】