JAVA NIO Socket通道,javaniosocket通道
![]()
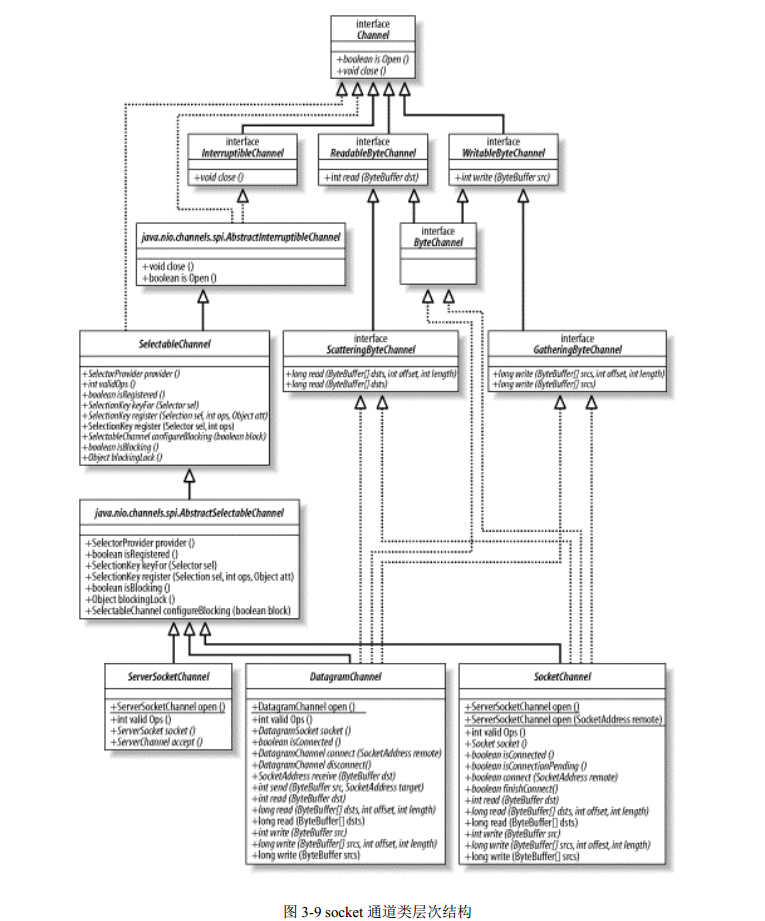
DatagramChannel和SocketChannel都實現定義讀寫功能,ServerSocketChannel不實現,只負責監聽傳入的連接,並建立新的SocketChannel,本身不傳輸數據。
Socket通道被實例化時都會創建一個對等的socket,
通過此方式創建的socket都會有關聯的通道,通過getChannel()獲取。
繼承於 SelectableChannel,所以socket可以在非阻塞模式下運行:
![]()
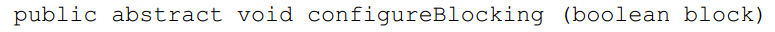
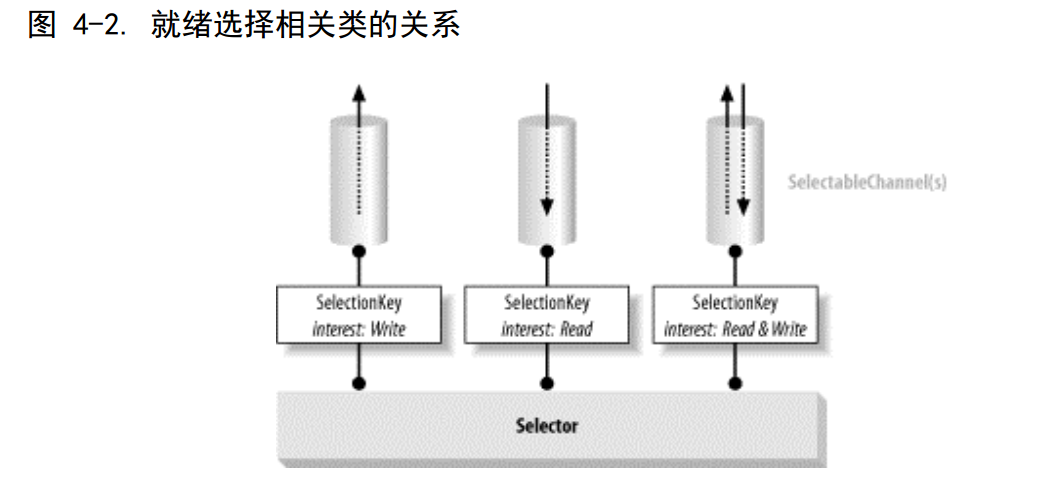
Readiness Selection:就緒選擇,查詢通道的機制,該機制可以判斷通道是否准備好執行下一個目標操作(讀,寫...),其價值在於潛在的大量通道可以同時進行就緒檢查,真正的就緒選擇需要由操作系統來做,處理IO請求,並通知各個線程數據准備情況。
Selector選擇器:提供了這種抽象(抽象接口),是的Java代碼能夠以可移植的方式,請求底層操作系統提供這種服務。
Selector選擇器類:管理著一個被注冊的通道集合的信息和他們的狀態,通道和選擇器是一起被注冊的,並且使用選擇器來更新通道狀態。
一個通道可以被注冊到多個選擇器上,但在每個選擇器上,只能注冊一次。
SelectionKey選擇鍵:封裝了通道和選擇器的注冊關系,選擇鍵被SelectableChannel.register()返回並提供標識這種注冊關系的標記。
通道在被注冊到選擇器之前必須設置為noblocking模式,正常狀態。
chanel.register(selector, keystate):通道注冊選擇器。
selector.select():阻塞操作,直到某一個channel的keystate發生。
selectionKey.cancel(),取消注冊關系。
通道關閉,相關的注冊鍵會自動取消,選擇器關閉,則所有注冊到該選擇器的通道都將被注銷,並且相關的鍵會立刻失效。
selectionkey包含兩個以整數型式進行編碼的比特掩碼,一個用於指示那些通道和選擇器組合所關心的操作,另一個表示通道准備好要執行的操作。當前的interest集合可以通過調用見對象的interestOps()方法來獲取,且永遠不會被選擇器改變,但可以調用interestOps()方法,傳入一個新的比特碼來改變。
readyOpts()獲取相關通道的已就緒的操作,ready集合是interest集合的子集,表示從上次調用select()之後已經就緒的操作。如下:
if((key.readOps() & SelctionKey.OP_READ) != 0){
buffer.clear();
key.channel().read(buffer);
do()....
}
附加參數:attach()
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX, paramObj);
等價:
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX);
key.attach(paramObj);
SelectionKey 多線程應用同步問題。
選擇器:
Selector上的
已注冊鍵集合中,會存在失效鍵、null,keys()返回,不可修改。
已選擇鍵集合,selectedKeys()返回,已經准備好的鍵集合,可能為空。
核心:選擇過程,是對select(),poll(),epoll()等本地調用(native call)或者類似的操作系統的本地調用的包裝(抽象),期間,將執行以下過程:
使用內部已取消的鍵的集合來延遲注銷,防止線程在取消鍵時阻塞及與正在進行的選擇操作沖突的優化,
三種形式的select: select(), select(timeout),selectNow()(非阻塞,立刻返回當前狀況)。
調用 Selector 對象的 wakeup( )方法將使得選擇器上的第一個還沒有返回的選擇操作立即回。如果當前沒有在進行中的選擇,那麼下一次對 select( )方法的一種形式的調用將立即返回。後續的選擇操作將正常進行。在選擇操作之間多次調用 wakeup( )方法與調用它一次沒有什麼不同。有時這種延遲的喚醒行為並不是您想要的。您可能只想喚醒一個睡眠中的線程,而使得後續的
選擇繼續正常地進行。您可以通過在調用 wakeup( )方法後調用 selectNow( )方法來繞過這個問題。
通常的做法是在選擇器上調用一次 select 操作(這將更新已選擇的鍵的集合),然後遍歷 selectKeys( )方法返回的鍵的集合。在按順序進行檢查每個鍵的過程中,相關的通道也根據鍵的就緒集合進行處理。然後鍵將從已選擇的鍵的集合中被移除(通過在 Iterator對象上調用 remove( )方法),然後檢查下一個鍵。完成後,通過再次調用 select( )方法重復這個循環。如下:
1 package org.windwant.nio;
2
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
5 import java.net.ServerSocket;
6 import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
7 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
8 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
9 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
10 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
11 import java.util.Iterator;
12 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
13 import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
14
15 /**
16 * Created by windwant on 2016/10/27.
17 */
18 public class SocketChannelOpt {
19
20 private static final String HOST = "localhost";
21 private static final int PORT = 8888;
22
23 private static ExecutorService read = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
24 private static ExecutorService write = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
25
26 public static void main(String[] args){
27 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
28 ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
29 Selector selector = null;
30 try {
31 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();//工廠方法創建ServerSocketChannel
32 serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket(); //獲取channel對應的ServerSocket
33 serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT)); //綁定地址
34 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //設置ServerSocketChannel非阻塞模式
35 selector = Selector.open();//工廠方法創建Selector
36 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//通道注冊選擇器,接受連接就緒狀態。
37 while (true){//循環檢查
38 if(selector.select() == 0){//阻塞檢查,當有就緒狀態發生,返回鍵集合
39 continue;
40 }
41
42 Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); //獲取就緒鍵遍歷對象。
43 while (it.hasNext()){
44 SelectionKey selectionKey = it.next();
45 //處理就緒狀態
46 if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
47 ServerSocketChannel schannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();//只負責監聽,阻塞,管理,不發送、接收數據
48 SocketChannel socketChannel = schannel.accept();//就緒後的操作,剛到達的socket句柄
49 if(null == socketChannel){
50 continue;
51 }
52 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
53 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //告知選擇器關心的通道,准備好讀數據
54 }else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
55 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
56 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4*1024);
57
58 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
59 while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0){//確保讀完
60 byteBuffer.flip();
61 result.append(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
62 byteBuffer.clear();//每次清空 對應上面flip()
63 }
64
65 System.out.println("server receive: " + result.toString());
66 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
67
68 }else if(selectionKey.isWritable()){
69 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
70 String sendStr = "server send data: " + Math.random();
71 ByteBuffer send = ByteBuffer.wrap(sendStr.getBytes());
72 while (send.hasRemaining()){
73 socketChannel.write(send);
74 }
75 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
76 System.out.println(sendStr);
77 }
78 it.remove();
79 }
80 }
81
82 } catch (IOException e) {
83 e.printStackTrace();
84 }
85 }
86 }
Selector多線程執行,同步需求。
一個線程監控通道的就緒狀態,一個線程池處理業務需求。
線程池也可以擴展為不同的業務處理線程池,如日志、業務、心跳。
1 package org.windwant.nio;
2
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
5 import java.net.ServerSocket;
6 import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
7 import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
8 import java.nio.channels.Selector;
9 import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
10 import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
11 import java.util.Iterator;
12 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
13 import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
14
15 /**
16 * 線程處理讀取,寫出
17 * Created by windwant on 2016/10/27.
18 */
19 public class TSocketChannelOpt {
20
21 private static final String HOST = "localhost";
22 private static final int PORT = 8888;
23
24 private static ExecutorService read = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
25 private static ExecutorService write = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
26
27 public static void main(String[] args){
28 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
29 ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
30 Selector selector = null;
31 try {
32 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();//工廠方法創建ServerSocketChannel
33 serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket(); //獲取channel對應的ServerSocket
34 serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT)); //綁定地址
35 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //設置ServerSocketChannel非阻塞模式
36 selector = Selector.open();//工廠方法創建Selector
37 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//通道注冊選擇器,接受連接就緒狀態。
38 while (true){//循環檢查
39 if(selector.select() == 0){//阻塞檢查,當有就緒狀態發生,返回鍵集合
40 continue;
41 }
42
43 Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); //獲取就緒鍵遍歷對象。
44 while (it.hasNext()){
45 SelectionKey selectionKey = it.next();
46 it.remove();
47 //處理就緒狀態
48 if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
49 ServerSocketChannel schannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();//只負責監聽,阻塞,管理,不發送、接收數據
50 SocketChannel socketChannel = schannel.accept();//就緒後的操作,剛到達的socket句柄
51 if(null == socketChannel){
52 continue;
53 }
54 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
55 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //告知選擇器關心的通道,准備好讀數據
56 }else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
57 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
58 read.execute(new MyReadRunnable(socketChannel));
59
60 // SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
61 // ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4*1024);
62 //
63 // StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
64 // while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0){//確保讀完
65 // byteBuffer.flip();
66 // result.append(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
67 // byteBuffer.clear();//每次清空 對應上面flip()
68 // }
69 //
70 // System.out.println("server receive: " + result.toString());
71 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
72
73 }else if(selectionKey.isWritable()){
74 SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
75 write.execute(new MyWriteRunnable(socketChannel));
76 // String sendStr = "server send data: " + Math.random();
77 // ByteBuffer send = ByteBuffer.wrap(sendStr.getBytes());
78 // while (send.hasRemaining()){
79 // socketChannel.write(send);
80 // }
81 // System.out.println(sendStr);
82 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
83 }
84 }
85 }
86
87 } catch (IOException e) {
88 e.printStackTrace();
89 }
90 }
91
92 static class MyReadRunnable implements Runnable {
93
94 private SocketChannel channel;
95
96 public MyReadRunnable(SocketChannel channel){
97 this.channel = channel;
98 }
99
100 @Override
101 public synchronized void run() {
102 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4*1024);
103
104 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
105 try {
106 while (channel.read(byteBuffer) > 0){//確保讀完
107 byteBuffer.flip();
108 result.append(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
109 byteBuffer.clear();//每次清空 對應上面flip()
110 }
111 System.out.println("server receive: " + result.toString());
112 } catch (IOException e) {
113 e.printStackTrace();
114 }
115
116
117 }
118 }
119
120 static class MyWriteRunnable implements Runnable {
121
122 private SocketChannel channel;
123
124 public MyWriteRunnable(SocketChannel channel){
125 this.channel = channel;
126 }
127
128 @Override
129 public void run() {
130 String sendStr = "server send data: " + Math.random();
131 ByteBuffer send = ByteBuffer.wrap(sendStr.getBytes());
132 try {
133 while (send.hasRemaining()) {
134 channel.write(send);
135 }
136 System.out.println(sendStr);
137 }catch (Exception e){
138 e.printStackTrace();
139 }
140
141 }
142 }
143 }
 DatagramChannel和SocketChannel都實現定義讀寫功能,ServerSocketChannel不實現,只負責監聽傳入的連接,並建立新的SocketChannel,本身不傳輸數據。
Socket通道被實例化時都會創建一個對等的socket,通過此方式創建的socket都會有關聯的通道,通過getChannel()獲取。
繼承於 SelectableChannel,所以socket可以在非阻塞模式下運行:
DatagramChannel和SocketChannel都實現定義讀寫功能,ServerSocketChannel不實現,只負責監聽傳入的連接,並建立新的SocketChannel,本身不傳輸數據。
Socket通道被實例化時都會創建一個對等的socket,通過此方式創建的socket都會有關聯的通道,通過getChannel()獲取。
繼承於 SelectableChannel,所以socket可以在非阻塞模式下運行:
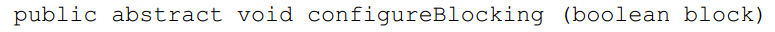 Readiness Selection:就緒選擇,查詢通道的機制,該機制可以判斷通道是否准備好執行下一個目標操作(讀,寫...),其價值在於潛在的大量通道可以同時進行就緒檢查,真正的就緒選擇需要由操作系統來做,處理IO請求,並通知各個線程數據准備情況。
Selector選擇器:提供了這種抽象(抽象接口),是的Java代碼能夠以可移植的方式,請求底層操作系統提供這種服務。
Selector選擇器類:管理著一個被注冊的通道集合的信息和他們的狀態,通道和選擇器是一起被注冊的,並且使用選擇器來更新通道狀態。
一個通道可以被注冊到多個選擇器上,但在每個選擇器上,只能注冊一次。
SelectionKey選擇鍵:封裝了通道和選擇器的注冊關系,選擇鍵被SelectableChannel.register()返回並提供標識這種注冊關系的標記。
通道在被注冊到選擇器之前必須設置為noblocking模式,正常狀態。
Readiness Selection:就緒選擇,查詢通道的機制,該機制可以判斷通道是否准備好執行下一個目標操作(讀,寫...),其價值在於潛在的大量通道可以同時進行就緒檢查,真正的就緒選擇需要由操作系統來做,處理IO請求,並通知各個線程數據准備情況。
Selector選擇器:提供了這種抽象(抽象接口),是的Java代碼能夠以可移植的方式,請求底層操作系統提供這種服務。
Selector選擇器類:管理著一個被注冊的通道集合的信息和他們的狀態,通道和選擇器是一起被注冊的,並且使用選擇器來更新通道狀態。
一個通道可以被注冊到多個選擇器上,但在每個選擇器上,只能注冊一次。
SelectionKey選擇鍵:封裝了通道和選擇器的注冊關系,選擇鍵被SelectableChannel.register()返回並提供標識這種注冊關系的標記。
通道在被注冊到選擇器之前必須設置為noblocking模式,正常狀態。
 chanel.register(selector, keystate):通道注冊選擇器。
selector.select():阻塞操作,直到某一個channel的keystate發生。
selectionKey.cancel(),取消注冊關系。
通道關閉,相關的注冊鍵會自動取消,選擇器關閉,則所有注冊到該選擇器的通道都將被注銷,並且相關的鍵會立刻失效。
selectionkey包含兩個以整數型式進行編碼的比特掩碼,一個用於指示那些通道和選擇器組合所關心的操作,另一個表示通道准備好要執行的操作。當前的interest集合可以通過調用見對象的interestOps()方法來獲取,且永遠不會被選擇器改變,但可以調用interestOps()方法,傳入一個新的比特碼來改變。
readyOpts()獲取相關通道的已就緒的操作,ready集合是interest集合的子集,表示從上次調用select()之後已經就緒的操作。如下:
if((key.readOps() & SelctionKey.OP_READ) != 0){
buffer.clear();
key.channel().read(buffer);
do()....
}
附加參數:attach()
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX, paramObj);
等價:
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX);
key.attach(paramObj);
SelectionKey 多線程應用同步問題。
選擇器:
Selector上的已注冊鍵集合中,會存在失效鍵、null,keys()返回,不可修改。
已選擇鍵集合,selectedKeys()返回,已經准備好的鍵集合,可能為空。
核心:選擇過程,是對select(),poll(),epoll()等本地調用(native call)或者類似的操作系統的本地調用的包裝(抽象),期間,將執行以下過程:
使用內部已取消的鍵的集合來延遲注銷,防止線程在取消鍵時阻塞及與正在進行的選擇操作沖突的優化,
三種形式的select: select(), select(timeout),selectNow()(非阻塞,立刻返回當前狀況)。
調用 Selector 對象的 wakeup( )方法將使得選擇器上的第一個還沒有返回的選擇操作立即回。如果當前沒有在進行中的選擇,那麼下一次對 select( )方法的一種形式的調用將立即返回。後續的選擇操作將正常進行。在選擇操作之間多次調用 wakeup( )方法與調用它一次沒有什麼不同。有時這種延遲的喚醒行為並不是您想要的。您可能只想喚醒一個睡眠中的線程,而使得後續的
選擇繼續正常地進行。您可以通過在調用 wakeup( )方法後調用 selectNow( )方法來繞過這個問題。
通常的做法是在選擇器上調用一次 select 操作(這將更新已選擇的鍵的集合),然後遍歷 selectKeys( )方法返回的鍵的集合。在按順序進行檢查每個鍵的過程中,相關的通道也根據鍵的就緒集合進行處理。然後鍵將從已選擇的鍵的集合中被移除(通過在 Iterator對象上調用 remove( )方法),然後檢查下一個鍵。完成後,通過再次調用 select( )方法重復這個循環。如下:
chanel.register(selector, keystate):通道注冊選擇器。
selector.select():阻塞操作,直到某一個channel的keystate發生。
selectionKey.cancel(),取消注冊關系。
通道關閉,相關的注冊鍵會自動取消,選擇器關閉,則所有注冊到該選擇器的通道都將被注銷,並且相關的鍵會立刻失效。
selectionkey包含兩個以整數型式進行編碼的比特掩碼,一個用於指示那些通道和選擇器組合所關心的操作,另一個表示通道准備好要執行的操作。當前的interest集合可以通過調用見對象的interestOps()方法來獲取,且永遠不會被選擇器改變,但可以調用interestOps()方法,傳入一個新的比特碼來改變。
readyOpts()獲取相關通道的已就緒的操作,ready集合是interest集合的子集,表示從上次調用select()之後已經就緒的操作。如下:
if((key.readOps() & SelctionKey.OP_READ) != 0){
buffer.clear();
key.channel().read(buffer);
do()....
}
附加參數:attach()
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX, paramObj);
等價:
SelectionKey key = SelectableChannel.register(Selector, SelectionKey.OP_XXX);
key.attach(paramObj);
SelectionKey 多線程應用同步問題。
選擇器:
Selector上的已注冊鍵集合中,會存在失效鍵、null,keys()返回,不可修改。
已選擇鍵集合,selectedKeys()返回,已經准備好的鍵集合,可能為空。
核心:選擇過程,是對select(),poll(),epoll()等本地調用(native call)或者類似的操作系統的本地調用的包裝(抽象),期間,將執行以下過程:
使用內部已取消的鍵的集合來延遲注銷,防止線程在取消鍵時阻塞及與正在進行的選擇操作沖突的優化,
三種形式的select: select(), select(timeout),selectNow()(非阻塞,立刻返回當前狀況)。
調用 Selector 對象的 wakeup( )方法將使得選擇器上的第一個還沒有返回的選擇操作立即回。如果當前沒有在進行中的選擇,那麼下一次對 select( )方法的一種形式的調用將立即返回。後續的選擇操作將正常進行。在選擇操作之間多次調用 wakeup( )方法與調用它一次沒有什麼不同。有時這種延遲的喚醒行為並不是您想要的。您可能只想喚醒一個睡眠中的線程,而使得後續的
選擇繼續正常地進行。您可以通過在調用 wakeup( )方法後調用 selectNow( )方法來繞過這個問題。
通常的做法是在選擇器上調用一次 select 操作(這將更新已選擇的鍵的集合),然後遍歷 selectKeys( )方法返回的鍵的集合。在按順序進行檢查每個鍵的過程中,相關的通道也根據鍵的就緒集合進行處理。然後鍵將從已選擇的鍵的集合中被移除(通過在 Iterator對象上調用 remove( )方法),然後檢查下一個鍵。完成後,通過再次調用 select( )方法重復這個循環。如下: