1 package com.microservice.framework;
2
3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
5
6 @SpringBootApplication
7 public class MySpringAplication {
8
9 public void run(String[] args) {
10 SpringApplication sa = new SpringApplication(MySpringAplication.class);
11 sa.run(args);
12 }
13
14 }
SpringBoot啟動過程:
1、構建SpringApplication對象
2、執行run()
一、構建SpringApplication對象
1 /**
2 * The application context will load beans from the specified sources
3 */
4 public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
5 initialize(sources);
6 }
說明:
private final Set<Object> sources = new LinkedHashSet<Object>();
private boolean webEnvironment;
private Class<?> mainApplicationClass;
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
步驟:
1.1、將傳入的MySpringApplication.class對象放入Set集合
1.2、判斷是否是web環境:
private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private boolean deduceWebEnvironment() {
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
說明:通過在classpath中查看是否存在WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES這個數組中所包含的所有類(實際上就是2個類),如果存在那麼當前程序即是一個Web應用程序,反之則不然。
1.3、創建ApplicationContextInitializer列表
1 private List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers;
2
3 public void setInitializers(
4 Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
5 this.initializers = new ArrayList<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>>();
6 this.initializers.addAll(initializers);
7 }
8
9 private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
10 return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
11 }
12
13 private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
14 Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
15 ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
16
17 // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
18 Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(
19 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
20 List<T> instances = new ArrayList<T>(names.size());
21
22 // Create instances from the names
23 for (String name : names) {
24 try {
25 Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
26 Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
27 Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getConstructor(parameterTypes);
28 T instance = (T) constructor.newInstance(args);
29 instances.add(instance);
30 }
31 catch (Throwable ex) {
32 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
33 "Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
34 }
35 }
36
37 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
38 return instances;
39 }
步驟:
其中,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)如下:
1 /**
2 * The location to look for factories.
3 * <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
4 */
5 public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
6
7 /**
8 * Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
9 * given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
10 * class loader.
11 */
12 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
13 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
14 try {
15 Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
16 ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
17 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
18 while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
19 URL url = urls.nextElement();
20 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
21 String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
22 result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
23 }
24 return result;
25 }
26 catch (IOException ex) {
27 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
28 "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
29 }
30 }
META-INF/spring-factories
1 # Application Context Initializers 2 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ 3 org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ 4 org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ 5 org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ 6 org.springframework.boot.context.web.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
說明:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer)的value(這裡有以上四個ApplicationContextInitializer實現類)
以上四個類的作用:
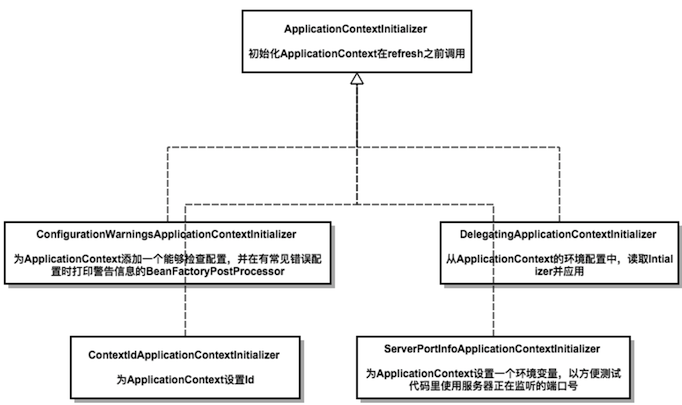
至此,設置ApplicationContextInitialize就完成了。
總結:整個setInitializers實際上就是初始化了SpringApplication的屬性List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers為一個ArrayList列表,該列表中有四個實例:
1.4、初始化ApplicationListener列表
1 private List<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
2
3 /**
4 * Sets the {@link ApplicationListener}s that will be applied to the SpringApplication
5 * and registered with the {@link ApplicationContext}.
6 * @param listeners the listeners to set
7 */
8 public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
9 this.listeners = new ArrayList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
10 this.listeners.addAll(listeners);
11 }
META-INF/spring-factories
1 # Application Listeners 2 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ 3 org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\ 4 org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\ 5 org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\ 6 org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\ 7 org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\ 8 org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener,\ 9 org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\ 10 org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
以上八個listener的作用如下:
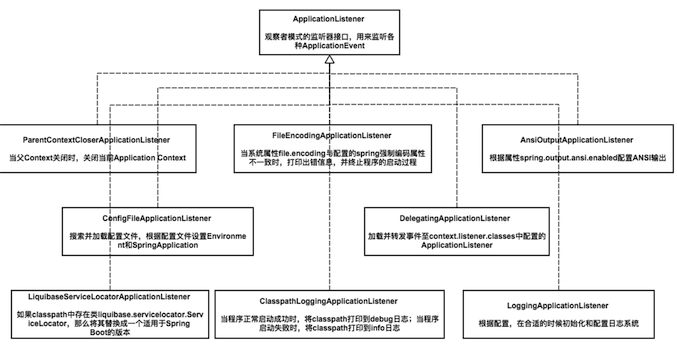
至此,整個setListeners方法結束,初始化了一個包含以上8個ApplicationListener實例的List集合。
1.5、初始化主類mainApplicationClass
1 private Class<?> mainApplicationClass;
2
3 private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
4 try {
5 StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
6 for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
7 if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
8 return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
9 }
10 }
11 }
12 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
13 // Swallow and continue
14 }
15 return null;
16 }
說明:獲取main()方法所在的主類Class對象,並賦值給SpringApplication的mainApplicationClass屬性。
至此,SpringApplication對象初始化完成了。
總結:整個SpringApplication初始化的過程,就是初始化了
注意:
本文基本參照http://zhaox.github.io/java/2016/03/22/spring-boot-start-flow 完成,該文的作者已經解析的很好了,我這裡再抄一遍,只是為了加深記憶!!!