1、背景
最近在搜索Netty和Zookeeper方面的文章時,看到了這篇文章《輕量級分布式 RPC 框架》,作者用Zookeeper、Netty和Spring寫了一個輕量級的分布式RPC框架。花了一些時間看了下他的代碼,寫的干淨簡單,寫的RPC框架可以算是一個簡易版的dubbo。這個RPC框架雖小,但是麻雀雖小,五髒俱全,有興趣的可以學習一下。
項目地址:https://github.com/luxiaoxun/NettyRpc
自己花了點時間整理了下代碼,並修改一些問題,以下是自己學習的一點小結。
2、簡介
RPC,即 Remote Procedure Call(遠程過程調用),調用遠程計算機上的服務,就像調用本地服務一樣。RPC可以很好的解耦系統,如WebService就是一種基於Http協議的RPC。
這個RPC整體框架如下:
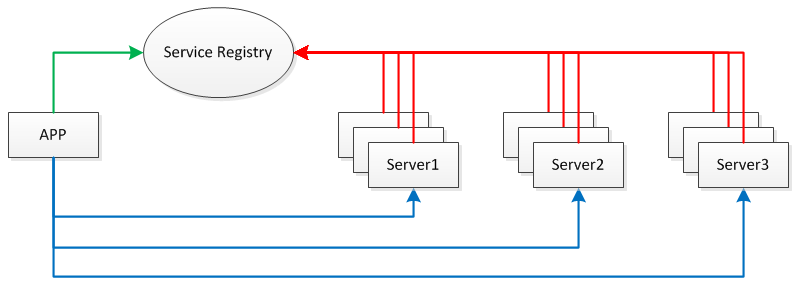
這個RPC框架使用的一些技術所解決的問題:
服務發布與訂閱:服務端使用Zookeeper注冊服務地址,客戶端從Zookeeper獲取可用的服務地址。
通信:使用Netty作為通信框架。
Spring:使用Spring配置服務,加載Bean,掃描注解。
動態代理:客戶端使用代理模式透明化服務調用。
消息編解碼:使用Protostuff序列化和反序列化消息。
3、服務端發布服務
使用注解標注要發布的服務
服務注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface RpcService {
Class<?> value();
}
一個服務接口:
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String name);
String hello(Person person);
}
一個服務實現:使用注解標注
@RpcService(HelloService.class)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "Hello! " + name;
}
@Override
public String hello(Person person) {
return "Hello! " + person.getFirstName() + " " + person.getLastName();
}
}
服務在啟動的時候掃描得到所有的服務接口及其實現:
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) throws BeansException {
Map<String, Object> serviceBeanMap = ctx.getBeansWithAnnotation(RpcService.class);
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBeanMap)) {
for (Object serviceBean : serviceBeanMap.values()) {
String interfaceName = serviceBean.getClass().getAnnotation(RpcService.class).value().getName();
handlerMap.put(interfaceName, serviceBean);
}
}
}
在Zookeeper集群上注冊服務地址:

這裡在原文的基礎上加了AddRootNode()判斷服務父節點是否存在,如果不存在則添加一個PERSISTENT的服務父節點,這樣雖然啟動服務時多了點判斷,但是不需要手動命令添加服務父節點了。
關於Zookeeper的使用原理,可以看這裡《ZooKeeper基本原理》。
4、客戶端調用服務
使用代理模式調用服務:
public class RpcProxy {
private String serverAddress;
private ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery;
public RpcProxy(String serverAddress) {
this.serverAddress = serverAddress;
}
public RpcProxy(ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery) {
this.serviceDiscovery = serviceDiscovery;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(Class<?> interfaceClass) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
if (serviceDiscovery != null) {
serverAddress = serviceDiscovery.discover();
}
if(serverAddress != null){
String[] array = serverAddress.split(":");
String host = array[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
RpcClient client = new RpcClient(host, port);
RpcResponse response = client.send(request);
if (response.isError()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Response error.",new Throwable(response.getError()));
} else {
return response.getResult();
}
}
else{
throw new RuntimeException("No server address found!");
}
}
}
);
}
}
這裡每次使用代理遠程調用服務,從Zookeeper上獲取可用的服務地址,通過RpcClient send一個Request,等待該Request的Response返回。這裡原文有個比較嚴重的bug,在原文給出的簡單的Test中是很難測出來的,原文使用了obj的wait和notifyAll來等待Response返回,會出現“假死等待”的情況:一個Request發送出去後,在obj.wait()調用之前可能Response就返回了,這時候在channelRead0裡已經拿到了Response並且obj.notifyAll()已經在obj.wait()之前調用了,這時候send後再obj.wait()就出現了假死等待,客戶端就一直等待在這裡。使用CountDownLatch可以解決這個問題。
注意:這裡每次調用的send時候才去和服務端建立連接,使用的是短連接,這種短連接在高並發時會有連接數問題,也會影響性能。
從Zookeeper上獲取服務地址:

每次服務地址節點發生變化,都需要再次watchNode,獲取新的服務地址列表。
5、消息編碼
請求消息:

響應消息:

消息序列化和反序列化工具:(基於 Protostuff 實現)

由於處理的是TCP消息,本人加了TCP的粘包處理Handler
channel.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65536,0,4,0,0))
消息編解碼時開始4個字節表示消息的長度,也就是消息編碼的時候,先寫消息的長度,再寫消息。
6、性能改進
Netty本身就是一個高性能的網絡框架,從網絡IO方面來說並沒有太大的問題。
從這個RPC框架本身來說,在原文的基礎上把Server端處理請求的過程改成了多線程異步:
public void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx,final RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
RpcServer.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
LOGGER.debug("Receive request " + request.getRequestId());
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setRequestId(request.getRequestId());
try {
Object result = handle(request);
response.setResult(result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
response.setError(t.toString());
LOGGER.error("RPC Server handle request error",t);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
LOGGER.debug("Send response for request " + request.getRequestId());
}
});
}
});
}
Netty 4中的Handler處理在IO線程中,如果Handler處理中有耗時的操作(如數據庫相關),會讓IO線程等待,影響性能。
個人覺得該RPC的待改進項:
1)客戶端保持和服務進行長連接,不需要每次調用服務的時候進行連接,長連接的管理(通過Zookeeper獲取有效的地址)。
2)客戶端請求異步處理的支持,不需要同步等待:發送一個異步請求,返回Feature,通過Feature的callback機制獲取結果。
3)編碼序列化的多協議支持。
有時間再改改吧。。
項目地址:https://github.com/luxiaoxun/NettyRpc
參考:
輕量級分布式 RPC 框架:http://my.oschina.net/huangyong/blog/361751
你應該知道的RPC原理:http://www.cnblogs.com/LBSer/p/4853234.html