環境
開發包:appserv-win32-2.5.10
服務器:Apache2.2
數據庫:phpMyAdmin
語言:php5,java
平台:windows 10
java驅動:mysql-connector-java-5.1.37
需求
編寫一個PHP腳本語言,連接到phpMyAdmin數據庫的test庫
編寫一個java web服務端,連接到phpMyAdmin數據庫的test庫
代碼
php連接方式
mysql.php
<?php
/*****************************
*數據庫連接
*****************************/
$conn = @mysql_connect("localhost","root","123");
if (!$conn){
die("連接數據庫失敗:" . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("test", $conn);
//字符轉換,讀庫
mysql_query("set character set utf8");
mysql_query("set names utf8");
?>
test.php測試
<?php
error_reporting(0); //防止報錯
include('mysql.php');
$result=mysql_query("select * from user"); //根據前面的計算出開始的記錄和記錄數
// 循環取出記錄
$six;
while($row=mysql_fetch_row($result))
{
echo $row[0];
echo $row[1];
}
?>
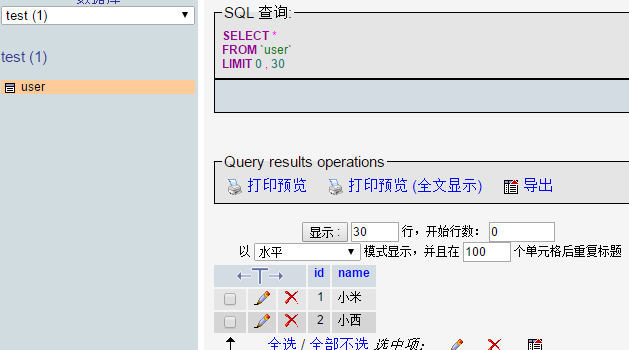
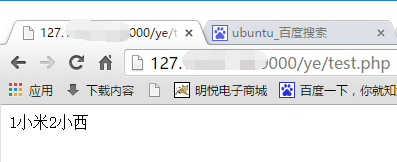
運行截圖 :
java 連接方式
1.新建一個java project為mysqlTest
2.加載JDBC驅動,mysql-connector-java-5.1.37
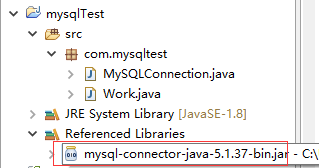
MySQLConnection.java
package com.mysqltest;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
* **Mysql連接**
*
* 參數:
* conn 連接
* url mysql數據庫連接地址
* user 數據庫登陸賬號
* password 數據庫登陸密碼
* 方法:
* conn 獲取連接
*/
public class MySQLConnection {
public static Connection conn = null;
public static String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/post";
public static String user = "root";
public static String password = "123";
/*
* 創建Mysql數據連接 第一步:加載驅動 Class.forName(Driver) 第二步:創建連接
* DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
*/
public Connection conn() {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("驅動加載錯誤");
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("數據庫鏈接錯誤");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
}
Work.java
package com.mysqltest;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
* mysql增刪改查
*/
public class Work {
/*
* insert 增加
*/
public static int insert() {
MySQLConnection connection = new MySQLConnection();
Connection conns; // 獲取連接
PreparedStatement pst; // 執行Sql語句
int i = 0;
String sql = "insert into user (username,password) values(?,?)";
try {
conns = connection.conn();
pst = conns.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1, "lizi");
pst.setString(2, "123");
i = pst.executeUpdate();
pst.close();
conns.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("數據寫入失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/*
* select 寫入
*/
public static void select() {
MySQLConnection connection = new MySQLConnection();
Connection conns; // 獲取連接
PreparedStatement pst; // 執行Sql語句(Statement)
ResultSet rs; // 獲取返回結果
String sql = "select * from user";
try {
conns = connection.conn();
pst = conns.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pst.executeQuery(sql);// 執行sql語句
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
System.out.println("名字 | 密碼");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("username") + " | " + rs.getString("password"));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
conns.close();
pst.close();
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("數據查詢失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* update 修改
*/
public static int update() {
MySQLConnection connection = new MySQLConnection();
Connection conns; // 獲取連接
PreparedStatement pst; // 執行Sql語句(Statement)
int i = 0;
String sql = "update user set password = ? where username = ?";
try {
conns = connection.conn();
pst = conns.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1, "123");
pst.setString(2, "lizi");
i = pst.executeUpdate();
pst.close();
conns.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("數據修改失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/*
* delete 刪除
*/
public static int delete() {
MySQLConnection connection = new MySQLConnection();
Connection conns; // 獲取連接
PreparedStatement pst; // 執行Sql語句(Statement)
int i = 0;
String sql = "delete from user where username = ?";
try {
conns = connection.conn();
pst = conns.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1, "lizi");
i = pst.executeUpdate();
pst.close();
conns.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("數據刪除失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return i;
}
/*
* test
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.out.println(insert());
select();
// System.out.println(update());
// System.out.println(delete());
}
}
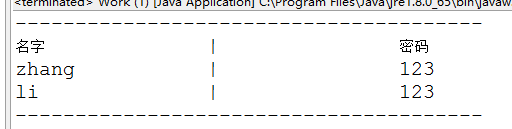
test截圖
ps:php操作MySQL數據庫中語句
我們常常用conn.php文件來建立與數據庫的鏈接,然後在所需的文件中利用include 進行調用。這樣有效防止對數據庫屬性的改動 而引起其他有關文件對數據調用的錯誤。
現在來看一個conn.php文件,代碼如下:
<?php
$conn=@mysql_connect("localhost","root","")or die("數據庫連接錯誤");//鏈接數據庫服務器
mysql_select_db("messageboard",$conn);//選擇數據庫名為messageboard
mysql_query("set names 'utf'");//使用utf編碼,這裡不能寫成utf-否則將顯示亂碼,但UTF不區分大小寫
?>
學習積累,收集了PHP操作MYSQL的幾個基礎函數:
.使用mysql_connect()函數連接MySQL服務器:mysql_connect("hostname", "username","password");
如,$link = mysql_connect("localhost", "root", "") or die("不能連接到數據庫服務器!可能是數據庫服務器沒有啟動,或者用戶名密碼有誤!".mysql_error());
.使用mysql_select_db()函數選擇數據庫文件:mysql_query("use 數據庫名",$link);
如,$db_selected=mysql_query("use example",$link);
.使用mysql_query()函數執行SQL語句:mysql_query(string query(SQL語句),$link);
如:
添加會員:$result=mysql_query("insert into tb_member values('a','')",$link);
修改會員:$result=mysql_query("update tb_member setuser='b',pwd=''where user='a'",$link);
刪除會員:$result=mysql_query("delecte from tb_member where user='b'",$link);
查詢會員:$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book");
模糊查詢:$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book where bookname like '%".trim($txt_book)."%'");
//通用符%表示零個或任意多個字符。
顯示表結構:$result=mysql_query("DESC tb_member");
.使用mysql_fetch_array()函數從數組結果集中獲得信息:
語法結構:array mysql_fetch_array(resource result[,int result_type])
參數result資源類型的參數,整形型參數,要傳入的是由mysql_fetch_array()函數返回的數據指針;
參數result_type:可選項,php操作MySQL數據庫語句基礎整數型參數,要傳入的是MYSQL_ASSOC(關聯索引)、MYSQL_NUM(數字索引) MYSQL_BOTH(包括前兩者,默認值)
如:
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book");
$info=mysql_fetch_object($sql);
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book where bookname like '%".trim($txt_book)."%'");
$info=mysql_fetch_object($sql);
.使用mysql_fetch_object()函數從結果集中獲取一行作為對象:
語法結構:object mysql_fetch_object(resource result);
如:
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book");
$info=mysql_fetch_object($sql);
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book where bookname like '%".trim($txt_book)."%'");
$info=mysql_fetch_object($sql);
mysql_fetch_object()函數與mysql_fetch_array()函數類似,只有一點區別,即返回一個對象而不是數組,該函數只能通過字段名來訪問數組。訪問結果集中行的元素的語法結構:$row->col_name(列名)
.使用mysql_fetch_row()函數逐行獲得結果集中的每條記錄:
語法結構:array mysql_fetch_row(resource result)
如:
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book");
$row=mysql_fetch_row($sql);
<>$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book where bookname like '%".trim($txt_book)."%'");
$row=mysql_fetch_row($sql);
.使用mysql_num_rows()函數獲取結果集中地記錄數:
語法結構:int mysql_num_rows(resource result)
如:
$sql=mysql_query("select * from tb_book");
......
<?php $nums=mysql_num_rows($sql);echo $nums;?>
注:若要獲得insert、update、delete語句的所影響到的數據,則必須使用mysql_affected_rows()函數來實現。
.mysql_query("set names gb");//設置MySQL的編碼格式為 gb類型,以屏蔽亂碼。
.關閉記錄集:mysql_free_result($sql);
.關閉MySQL數據庫服務器:mysql_close($conn);