POJ 2003 Hire and Fire (多重鏈表 樹結構 好題)
Hire and Fire
Time Limit: 1000MS
Memory Limit: 30000K
Total Submissions: 2316
Accepted: 655
Description
In this problem, you are asked to keep track of the hierarchical structure of an organization's changing staff. As the first event in the life of an organization, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is named. Subsequently, any number of hires and fires can occur. Any member of the organization (including the CEO) can hire any number of direct subordinates, and any member of the organization (including the CEO) can be fired. The organization's hierarchical structure can be represented by a tree. Consider the example shown by Figure 1:
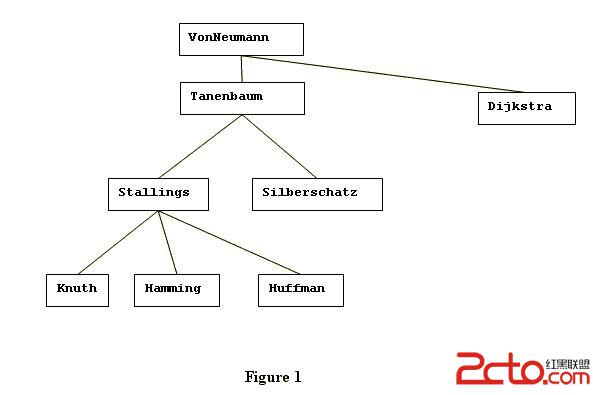
VonNeumann is the CEO of this organization. VonNeumann has two direct subordinates: Tanenbaum and Dijkstra. Members of the organization who are direct subordinates of the same member are ranked by their respective seniority. In the diagram, the seniority of such members decrease from left to right. For example Tanenbaum has higher seniority than Dijkstra.
When a member hires a new direct subordinate, the newly hired subordinate has lower seniority than any other direct subordinates of the same member. For example, if VonNeumann (in Figure 1) hires Shannon, then VonNeumann's direct subordinates are Tanenbaum, Dijkstra, and Shannon in order of decreasing seniority.
When a member of the organization gets fired, there are two possible scenarios. If the victim (the person who gets fired) had no subordinates, then he/she will be simply dropped from the organization's hierarchy. If the victim had any subordinates, then his/her highest ranking (by seniority) direct subordinate will be promoted to fill the resulting vacancy. The promoted person will also inherit the victim's seniority. Now, if the promoted person also had some subordinates then his/her highest ranking direct subordinate will similarly be promoted, and the promotions will cascade down the hierarchy until a person having no subordinates has been promoted. In Figure 1, if Tanenbaum gets fired, then Stallings will be promoted to Tanenbaum's position and seniority, and Knuth will be promoted to Stallings' previous position and seniority.
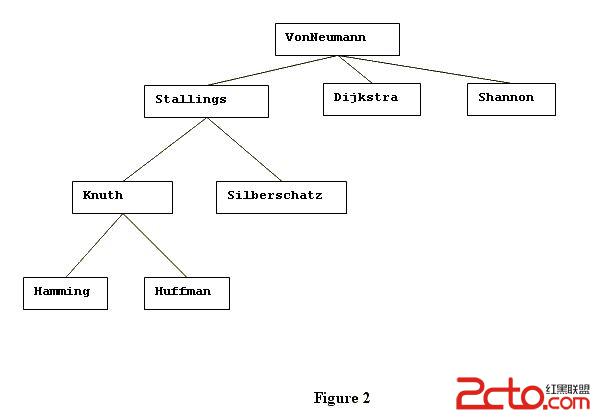
Figure 2 shows the hierarchy resulting from Figure 1 after (1) VonNeumann hires Shannon and (2) Tanenbaum gets fired:
Input
The first line of the input contains only the name of the person who is initially the CEO. All names in the input file consist of 2 to 20 characters, which may be upper or lower case letters, apostrophes, and hyphens. (In particular, no blank spaces.) Each name contains at least one upper case and at least one lower case letter.
The first line will be followed by one or more additional lines. The format of each of these lines will be determined by one of the following three rules of syntax:
[existing member] hires [new member]
fire [existing member]
print
Here [existing member] is the name of any individual who is already a member of the organization, [new member] is the name of an individual who is not a member of the organization as yet. The three types of lines (hires, fire, and print) can appear in any order, any number of times.
You may assume that at any time there is at least one member (who is the CEO) and no more than 1000 members in the organization.
Output
For each print command, print the current hierarchy of the organization, assuming all hires and fires since the beginning of the input have been processed as explained above. Tree diagrams (such as those in Figures 1 and 2) are translated into textual format according to the following rules:
Each line in the textual representation of the tree will contain exactly one name.
The first line will contain the CEO's name, starting in column 1.
The entire tree, or any sub-tree, having the form
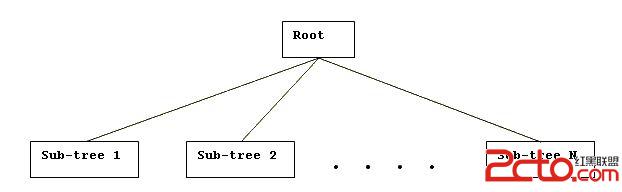
will be represented in textual form as:

The output resulting from each print command in the input will be terminated by one line consisting of exactly 60 hyphens. There will not be any blank lines in the output.
Sample Input
VonNeumann
VonNeumann hires Tanenbaum
VonNeumann hires Dijkstra
Tanenbaum hires Stallings
Tanenbaum hires Silberschatz
Stallings hires Knuth
Stallings hires Hamming
Stallings hires Huffman
print
VonNeumann hires Shannon
fire Tanenbaum
print
fire Silberschatz
fire VonNeumann
print
Sample Output
VonNeumann
+Tanenbaum
++Stallings
+++Knuth
+++Hamming
+++Huffman
++Silberschatz
+Dijkstra
------------------------------------------------------------
VonNeumann
+Stallings
++Knuth
+++Hamming
+++Huffman
++Silberschatz
+Dijkstra
+Shannon
------------------------------------------------------------
Stallings
+Knuth
++Hamming
+++Huffman
+Dijkstra
+Shannon
------------------------------------------------------------
Source
Rocky Mountain 2004
題目鏈接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2003
題目大意:看題面和輸入輸出很恐怖的樣子,其實題意很簡答,一棵樹
A hires B 表示把B做為A的兒子
fire A 表示把A結點去掉,去掉以後其第一個兒子結點到它的位置,然後其第一個孫子結點到其第一個兒子結點出,以此類推。。。直到葉子
print 表示按先序遍歷,遍歷整棵樹,+號個數表示當前點所在層的層數
題目分析:想到好的數據結構可以簡化一大部分問題,像這種要對樹上結點增刪查的問題,我們采用多重鏈表來構樹
多重鏈表結構體裡有三個參數,點的名字,父指針,存儲兒子指針的鏈表,還需要一個鍵值對存儲作為子樹根的結點對應的樹指針,顯然用map,具體操作看代碼和注釋吧
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include



