1、概述
虛基類是用關鍵字virtual聲明繼承的父類,即便該基類在多條鏈路上被一個子類繼承,但是該子類中只包含一個該虛基類的備份,這也是虛基類的作用所在。
正是由於虛基類的這個作用,所以在每個子類的構造函數中必須顯示的調用該虛基類的構造函數,不管該虛基類是不是直接的父類。
其次,虛基類的構造函數的調用早於其他非虛基類的構造函數的調用。
上面兩點就是虛基類的特性。
2、代碼示例
我們來看一段簡單的代碼,體現虛基類的這兩個特性。
[cpp]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public :
int base;
Base(int a = 0)
{
this->base = a;
cout<<"Base Constructer "<<a<<endl;
}
};
class A : public virtual Base
{
public :
int a;
A(int a, int b):a(a), Base(b)
{
cout<<"A Constructer"<<endl;
}
};
class B : public virtual Base
{
public :
int b;
B(int a, int b) : b(a), Base(b)
{
cout<<"B Constructer"<<endl;
}
};
class C : public B, public A, public virtual Base
{
public :
int c;
C(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e) : A(a, b), B(c, d), Base(e)
{
cout<<"C Constructer"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
C c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
return 0;
}
程序運行結果:
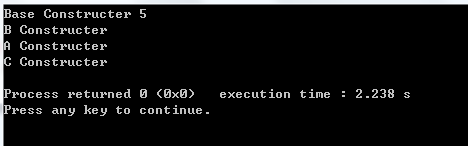 我們看到最後一個子類C顯式的調用了虛基類的構造函數,這個是必須的。
然後就是雖然虛基類在最後一個聲明,但是Base的構造函數最先被調用,而且只被調用了一次,說明子類中只包含了一個該基類的復本。
虛基類的特性就從這段代碼的運行結果中一目了然了。
我們看到最後一個子類C顯式的調用了虛基類的構造函數,這個是必須的。
然後就是雖然虛基類在最後一個聲明,但是Base的構造函數最先被調用,而且只被調用了一次,說明子類中只包含了一個該基類的復本。
虛基類的特性就從這段代碼的運行結果中一目了然了。