在這個信息爆炸的時代,我們不得不對信息的安全提高警惕。加密作為保障數據信息安全的一種方式,越來越受到人們的關注。
下面,我將把自己對Microsoft CryptoAPI的一些膚淺的理解與大家共享,有什麼不妥之處望不吝賜教。
一、 加密方法:
當初,計算機的研究就是為了破解德國人的密碼,人們並沒有想到計算機給今天帶來的信息革命。隨著計算機的發展,運算能力的增強,密碼學已經取得了巨大的進展。大體來說有以下幾種形式。
1、 公用密鑰加密技術
加密和解密使用不同的密鑰,分別叫做“公鑰”和“私鑰”。顧名思義,“私鑰”就是不能讓別人知道的,而“公鑰”就是可以公開的。這兩個必須配對使用,用公鑰加密的數據必須用與其對應的私鑰才能解開。這種技術安全性高,得到廣泛運用,但是效率太低。
2、 對稱密鑰加密技術
要求加密和解密過程使用相同的密鑰,這樣,密鑰必須只能被加解密雙方知道,否則就不安全。這種技術安全性不高,但是效率高。
3、 結合公用和對稱密鑰加密技術
公鑰加密技術以速度為代價換取了高安全性,而對稱加密以低安全換取高性能,所以另一種常見的加密方法就是結合以上兩種技術。
用對稱加密算法對數據進行加密,然後使用更安全的但效率更低的公鑰加密算法對對稱密鑰進行加密。
4、 數字簽名和鑒別
就是對已經加密的數據“簽名”,這樣接收者可以知道加密的數據的來源,以及是否被更改。
二、 CryptoAPI
微軟的CryptoAPI是PKI推薦使用的加密 API。其功能是為應用程序開發者提供在Win32環境下使用加密、驗證等安全服務時的標准加密接口。CryptoAPI處於應用程序和CSP(cryptographic service provider)之間(見圖一)。
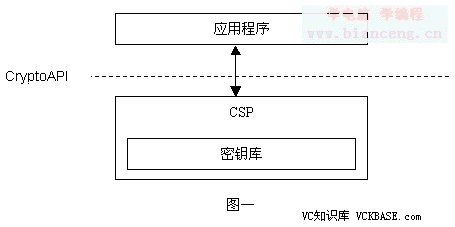
CryptoAPI的編程模型同Windows系統的圖形設備接口 GDI比較類似,其中加密服務提供者CSP等同於圖形設備驅動程序 ,加密硬件(可選)等同於圖形硬件,其上層的應用程序也類似,都不需要同設備驅動程序和硬件直接打交道。
CryptoAPI共有五部分組成:簡單消息函數(Simplified Message Functions)、低層消息函數(Low-level Message Functions)、基本加密函數(Base Cryptographic Functions)、證書編解碼函數(Certificate Encode/Decode Functions)和證書庫管理函數(Certificate Store Functions)。其中前三者可用於對敏感信息進行加密或簽名處理,可保證網絡傳輸信心的私有性;後兩者通過對證書的使用,可保證網絡信息交流中的認證性。
三、 CSP
看到這裡,大家也許對CSP還比較迷惑。其實CSP是真正實行加密的獨立模塊,他既可以由軟件實現也可以由硬件實現。但是他必須符合CryptoAPI接口的規范。
每個CSP都有一個名字和一個類型。每個CSP的名字是唯一的,這樣便於CryptoAPI找到對應的CSP。目前已經有9種CSP類型,並且還在增長。下表列出出它們支持的密鑰交換算法、簽名算法、對稱加密算法和Hash算法。
(表一)
CSP類型 交換算法 簽名算法 對稱加密算法 Hash算法 PROV_RSA_FULL RSA RSA RC2RC4
MD5SHA
PROV_RSA_SIG none RSA none MD5SHA
PROV_RSA_SCHANNEL RSA RSA RC4DES
Triple DES
MD5SHA
PROV_DSS DSS none DSS MD5SHA
PROV_DSS_DH DH DSS CYLINK_MEK MD5SHA
PROV_DH_SCHANNEL DH DSS DESTriple DES
MD5SHA
PROV_FORTEZZA KEA DSS Skipjack SHA PROV_MS_EXCHANGE RSA RSA CAST MD5 PROV_SSL RSA RSA Varies Varies從圖一可以看到,每個CSP有一個密鑰庫,密鑰庫用於存儲密鑰。而每個密鑰庫包括一個或多個密鑰容器(Key Containers)。每個密鑰容器中含屬於一個特定用戶的所有密鑰對。每個密鑰容器被賦予一個唯一的名字。在銷毀密鑰容器前CSP將永久保存每一個密鑰容器,包括保存每個密鑰容器中的公/私鑰對(見圖二)。
四、 創建密鑰容器,得到CSP句柄
說了這麼多只是一些理論性的東西,後面將詳細介紹一下Microsoft CryptoAPI的使用方法。
我們已經提過,每一個CSP都有一個名字和一個類型,並且名字保證唯一。所以可以通過名字和類型得到一個CSP。然而,要想加密肯定需要密鑰,那麼密鑰放哪裡呢?對了,就放在密鑰容器。(有人會問,密碼庫有什麼用?其實密鑰庫是在安裝CSP的時候已經存在了,他與CSP是相對應的。)但是密鑰容器並不是一開始就存在的,需要用戶去創建。下面的代碼實現以上功能(得到CSP即密碼容器)。
if(CryptAcquireContext(
&hCryptProv, // 返回CSP句柄
UserName, // 密碼容器名
NULL, // NULL時使用默認CSP名(微軟RSA Base Provider)
PROV_RSA_FULL, // CSP類型
0)) // Flag values
{
//以UserName為名的密鑰容器存在,那麼我們已經得到了CSP的句柄
printf("A crypto context with the %s key container \n", UserName);
printf("has been acquired.\n\n");
}
else //如果密鑰容器不存在,我們需要創建這個密鑰容器
{
if(CryptAcquireContext(
&hCryptProv,
UserName,
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
CRYPT_NEWKEYSET)) //創建以UserName為名的密鑰容器
{
//創建密鑰容器成功,並得到CSP句柄
printf("A new key container has been created.\n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Could not create a new key container.\n");
}
} // End of else
好了,我們已經創建了密鑰容器,並得到了CSP的句柄。也可以這樣理解,我們得到了一個CSP的句柄,並且它被綁定到以UserName為名的密鑰容器上。嘿嘿……
那麼,以後的加解密等操作,都將在這個CSP上進行。
可以如下刪除密鑰容器。
CryptAcquireContext(&hCryptProv, userName, NULL, PROV_RSA_FULL, CRYPT_DELETEKEYSET);
五、 一個文件加密的例子
看到這裡肯定有人開始說了,“這麼多廢話,還不快講怎麼加密怎麼解密!”您先別急,有些原理性的東西還是先了解了比較好,對以後的使用會有很大幫助。
言歸正傳,我們來看一段文件加密的代碼。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <wincrypt.h>
#define MY_ENCODING_TYPE (PKCS_7_ASN_ENCODING | X509_ASN_ENCODING)
#define KEYLENGTH 0x00800000
void HandleError(char *s);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// These additional #define statements are required.
#define ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM CALG_RC4
#define ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE 8
// Declare the function EncryptFile. The function definition
// follows main.
BOOL EncryptFile(
PCHAR szSource,
PCHAR szDestination,
PCHAR szPassword);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Begin main.
void main(void)
{
CHAR szSource[100];
CHAR szDestination[100];
CHAR szPassword[100];
printf("Encrypt a file. \n\n");
printf("Enter the name of the file to be encrypted: ");
scanf("%s",szSource);
printf("Enter the name of the output file: ");
scanf("%s",szDestination);
printf("Enter the password:");
scanf("%s",szPassword);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Call EncryptFile to do the actual encryption.
if(EncryptFile(szSource, szDestination, szPassword))
{
printf("Encryption of the file %s was a success. \n", szSource);
printf("The encrypted data is in file %s.\n",szDestination);
}
else
{
HandleError("Error encrypting file!");
}
} // End of main
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Code for the function EncryptFile called by main.
static BOOL EncryptFile(
PCHAR szSource,
PCHAR szDestination,
PCHAR szPassword)
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Parameters passed are:
// szSource, the name of the input, a plaintext file.
// szDestination, the name of the output, an encrypted file to be
// created.
// szPassword, the password.
{
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Declare and initialize local variables.
FILE *hSource;
FILE *hDestination;
HCRYPTPROV hCryptProv;
HCRYPTKEY hKey;
HCRYPTHASH hHash;
PBYTE pbBuffer;
DWORD dwBlockLen;
DWORD dwBufferLen;
DWORD dwCount;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Open source file.
if(hSource = fopen(szSource,"rb"))
{
printf("The source plaintext file, %s, is open. \n", szSource);
}
else
{
HandleError("Error opening source plaintext file!");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Open destination file.
if(hDestination = fopen(szDestination,"wb"))
{
printf("Destination file %s is open. \n", szDestination);
}
else
{
HandleError("Error opening destination ciphertext file!");
}
//以下獲得一個CSP句柄
if(CryptAcquireContext(
&hCryptProv,
NULL, //NULL表示使用默認密鑰容器,默認密鑰容器名
//為用戶登陸名
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
0))
{
printf("A cryptographic provider has been acquired. \n");
}
else
{
if(CryptAcquireContext(
&hCryptProv,
NULL,
NULL,
PROV_RSA_FULL,
CRYPT_NEWKEYSET))//創建密鑰容器
{
//創建密鑰容器成功,並得到CSP句柄
printf("A new key container has been created.\n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Could not create a new key container.\n");
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// 創建一個會話密鑰(session key)
// 會話密鑰也叫對稱密鑰,用於對稱加密算法。
// (注: 一個Session是指從調用函數CryptAcquireContext到調用函數
// CryptReleaseContext 期間的階段。會話密鑰只能存在於一個會話過程)
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create a hash object.
if(CryptCreateHash(
hCryptProv,
CALG_MD5,
0,
0,
&hHash))
{
printf("A hash object has been created. \n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Error during CryptCreateHash!\n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// 用輸入的密碼產生一個散列
if(CryptHashData(
hHash,
(BYTE *)szPassword,
strlen(szPassword),
0))
{
printf("The password has been added to the hash. \n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Error during CryptHashData. \n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// 通過散列生成會話密鑰
if(CryptDeriveKey(
hCryptProv,
ENCRYPT_ALGORITHM,
hHash,
KEYLENGTH,
&hKey))
{
printf("An encryption key is derived from the password hash. \n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Error during CryptDeriveKey!\n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Destroy the hash object.
CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
hHash = NULL;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// The session key is now ready.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// 因為加密算法是按ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE 大小的塊加密的,所以被加密的
// 數據長度必須是ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE 的整數倍。下面計算一次加密的
// 數據長度。
dwBlockLen = 1000 - 1000 % ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Determine the block size. If a block cipher is used,
// it must have room for an extra block.
if(ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE > 1)
dwBufferLen = dwBlockLen + ENCRYPT_BLOCK_SIZE;
else
dwBufferLen = dwBlockLen;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Allocate memory.
if(pbBuffer = (BYTE *)malloc(dwBufferLen))
{
printf("Memory has been allocated for the buffer. \n");
}
else
{
HandleError("Out of memory. \n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// In a do loop, encrypt the source file and write to the source file.
do
{
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Read up to dwBlockLen bytes from the source file.
dwCount = fread(pbBuffer, 1, dwBlockLen, hSource);
if(ferror(hSource))
{
HandleError("Error reading plaintext!\n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// 加密數據
if(!CryptEncrypt(
hKey, //密鑰
0, //如果數據同時進行散列和加密,這裡傳入一個
//散列對象
feof(hSource), //如果是最後一個被加密的塊,輸入TRUE.如果不是輸.
//入FALSE這裡通過判斷是否到文件尾來決定是否為
//最後一塊。
0, //保留
pbBuffer, //輸入被加密數據,輸出加密後的數據
&dwCount, //輸入被加密數據實際長度,輸出加密後數據長度
dwBufferLen)) //pbBuffer的大小。
{
HandleError("Error during CryptEncrypt. \n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Write data to the destination file.
fwrite(pbBuffer, 1, dwCount, hDestination);
if(ferror(hDestination))
{
HandleError("Error writing ciphertext.");
}
}
while(!feof(hSource));
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// End the do loop when the last block of the source file has been
// read, encrypted, and written to the destination file.
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Close files.
if(hSource)
fclose(hSource);
if(hDestination)
fclose(hDestination);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Free memory.
if(pbBuffer)
free(pbBuffer);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Destroy session key.
if(hKey)
CryptDestroyKey(hKey);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Destroy hash object.
if(hHash)
CryptDestroyHash(hHash);
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// Release provider handle.
if(hCryptProv)
CryptReleaseContext(hCryptProv, 0);
return(TRUE);
} // End of Encryptfile
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
// This example uses the function HandleError, a simple error
// handling function, to print an error message to the standard error
// (stderr) file and exit the program.
// For most applications, replace this function with one
// that does more extensive error reporting.
void HandleError(char *s)
{
fprintf(stderr,"An error occurred in running the program. \n");
fprintf(stderr,"%s\n",s);
fprintf(stderr, "Error number %x.\n", GetLastError());
fprintf(stderr, "Program terminating. \n");
exit(1);
} // End of HandleError
上面的代碼來自MSDN,並作了修改。注釋已經很詳細了,這裡就不贅述了,
解密與加密大同小異,大家可以自己看代碼。
這次先寫這麼多,也許很多人覺得我寫這些大家都知道,並且也太簡單了。不要急慢慢來,嘿嘿:)接下來會有一些比較深入和實用的技術。
參考:
MSDN相關章節。
(注:如果代碼編譯不過,加入宏定義:_WIN32_WINNT=0x0400)