(一),什麼是文件管理系統
答:數據在PC上是以文件的形式儲存在磁盤中的,這些數據的形式一般為ASCII碼或二進制形式。簡單點說就是:管理磁盤上的文件的方法的代碼!
如:我們寫到SD卡上面的數據管理一下,更科學的方法來管理
http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html,官網介紹 Resources下面是源碼
(二),我們在移植時主要是那些函數?
答:Device Control Interface(硬件接口函數)
(三),例程:
1,我們用的是0.09版本的
2,CC936.c中文字體庫
①新建工作區間
/* Register work area for each volume (Always succeeds regardless of disk status) */ f_mount(0,&fs); //(文件管理系統)注冊一個工作區間,工作空間命名為0。
那麼工作區間的命名范圍是什麼呢?
答:
FRESULT f_mount (
BYTE vol, /* Logical drive number to be mounted/unmounted */
FATFS *fs /* Pointer to new file system object (NULL for unmount)*/
)
{
FATFS *rfs;
if (vol >= _VOLUMES) /* Check if the drive number is valid */
return FR_INVALID_DRIVE;
vol就是f_mount的第一個形參(命名),當他的值大於等於 _VOLUMES,就會返回錯誤
#define _VOLUMES 1 //can define 9 /* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. */
②然後再工作區間裡面新建文件
/* function disk_initialize() has been called in f_open */ /* Create new file on the drive 0 */ res = f_open(&fnew, "0:newfile.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE );
OPEN的屬性:
1.怎麼打開呢?
FA_CREATE_ALWAYS 總是以創建總是新建的形式打開這個文件
FA_WRITE:此文件只能寫
2.看下open函數
FRESULT f_open (
FIL* FileObject, /* Pointer to the blank file object structure */ 文件指針,把打開的文件關聯到這個指針連
const TCHAR* FileName, /* Pointer to the file neme */ 文件名字
BYTE ModeFlags /* Mode flags */ 屬性
);
屬性:
可以第一次打開用:FA_CREATE_NEW,之後打開用:FA_OPEN_EXISTING(已存在)就可以了
或者:總是打開,總是關閉
當用到:FA_CREATE_ALWAYS時,我們要將 #define _FS_READONLY 0 /* 0:Read/Write or 1:Read only */ 打開
3.對於返回值(Return Values):我們只測試:FR_OK(是否成功)
③往該文件內寫數據
if ( res == FR_OK )
{
res = f_write(&fnew, textFileBuffer, sizeof(textFileBuffer), &bw);
f_close(&fnew); 寫完之後,把該文件關掉
}
④關掉之後再打開它
res = f_open(&fnew, "0:newfile.txt", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ); // FA_READ:此時打開定義可讀
⑤讀取數據
res = f_read(&fnew, buffer, sizeof(buffer), &br);
⑥打印之後關閉
printf("\r\n %s ", buffer);
/* Close open files */
f_close(&fnew);
⑦在文件系統中注冊掉剛才開辟的“0”工作區間
/* Unregister work area prior to discard it */ f_mount(0, NULL);
(四)文件管理系統與SD卡的關聯!
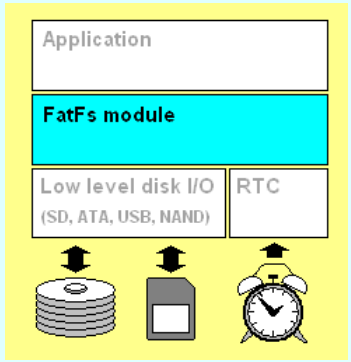
1,Application:就是我們主函數中使用的那些上層函數
2,中間是文件系統模塊,文件系統要操縱底層SD卡的時候呢還需要 Low level disk I/O,這一部分驅動,這一部分驅動需要我們自己寫
/*-------------------------- SD Init ----------------------------- */
Status = SD_Init();
if (Status!=SD_OK )
{
return STA_NOINIT;
}
else
{
return RES_OK;
}
}
和
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Return Disk Status */
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE drv /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
)
{
return RES_OK;
}
底層的磁盤的讀/寫
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to read (1..255) */
)
{
if (count > 1) //多個磁盤
{
SD_ReadMultiBlocks(buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE, count);
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitReadOperation(); //循環查詢dma傳輸是否結束
/* Wait until end of DMA transfer */
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK);
}
else //單個磁盤
{
SD_ReadBlock(buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitReadOperation(); //循環查詢dma傳輸是否結束
/* Wait until end of DMA transfer */
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK);
}
return RES_OK;
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */
#if _READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to write (1..255) */
)
{
if (count > 1)
{
SD_WriteMultiBlocks((uint8_t *)buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE, count);
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitWriteOperation(); //等待dma傳輸結束
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK); //等待sdio到sd卡傳輸結束
}
else
{
SD_WriteBlock((uint8_t *)buff,sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
/* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitWriteOperation(); //等待dma傳輸結束
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK); //等待sdio到sd卡傳輸結束
}
return RES_OK;
}
#endif /* _READONLY */
IO控制為空(直接返回OK)
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE ctrl, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
return RES_OK;
}
嵌入式初學者,看到此文的大神們,有什麼錯誤的地方多多意見啊!
給你個我寫的樣板。。。
char pch[40];
short inum=0,bmpres;
FIL bmpfsrc;
do
{
sprintf((char*)pch,"0:ScreenShort/SS_%d.bmp",inum++);
if(inum>500)return;
bmpres = f_open( &bmpfsrc,(char*)pch, FA_CREATE_NEW | FA_WRITE);
}while(bmpres!=FR_OK);
BmpScreen_short(0,0,400,240,&bmpfsrc);
f_close(&bmpfsrc);
我這個是截圖用的一部分代碼,功能是把當前截圖保存到內存卡上面,內存卡上面已經有一部分截圖了,所以當前截圖的名字需要不和以前的重復,我用了一個while來一直創建,知道創建成功為止。圖片命名裡面有個變量,比如第一張截圖是SS_0.bmp,第二個截圖就是SS_1.bmp。
假設內存卡上面已經有SS_0.bmp和SS_1.bmp,那麼,當前截圖的名字就是SS_2.bmp。你那個比我這個還簡單,希望能夠給你提示。
給你個我寫的樣板。。。
char pch[40];
short inum=0,bmpres;
FIL bmpfsrc;
do
{
sprintf((char*)pch,"0:ScreenShort/SS_%d.bmp",inum++);
if(inum>500)return;
bmpres = f_open( &bmpfsrc,(char*)pch, FA_CREATE_NEW | FA_WRITE);
}while(bmpres!=FR_OK);
BmpScreen_short(0,0,400,240,&bmpfsrc);
f_close(&bmpfsrc);
我這個是截圖用的一部分代碼,功能是把當前截圖保存到內存卡上面,內存卡上面已經有一部分截圖了,所以當前截圖的名字需要不和以前的重復,我用了一個while來一直創建,知道創建成功為止。圖片命名裡面有個變量,比如第一張截圖是SS_0.bmp,第二個截圖就是SS_1.bmp。
假設內存卡上面已經有SS_0.bmp和SS_1.bmp,那麼,當前截圖的名字就是SS_2.bmp。你那個比我這個還簡單,希望能夠給你提示。