容器 就是存放數據的一個集合
(java提供了一個接口專門去約束我們容器的實現類)
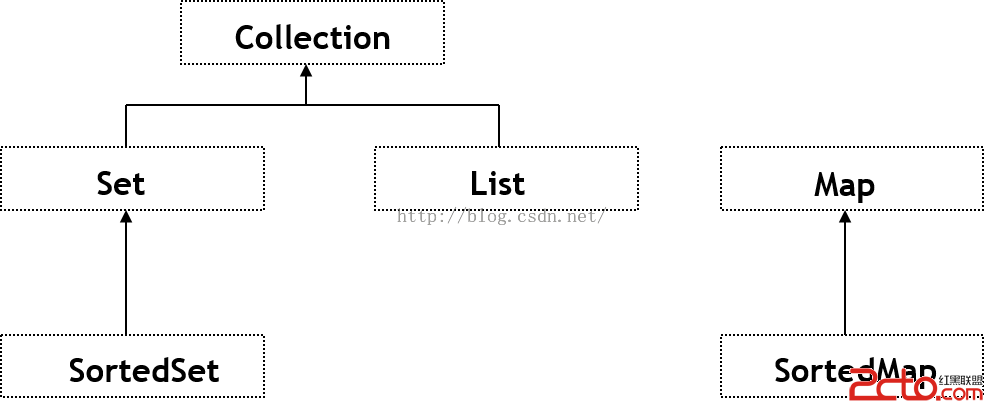
Set: does not allow duplicate objects toenter the collection of elements
SortedSet: similar to set except that theelements in the set are stored in ascending order
List: is ordered, maintain an order asobjects are added and removed from the collection,can also contain duplicateentries of objects
Map: stores objects that are identifiedby unique keys, and may not store duplicate keys
SortedMap: similar to Map, except the objectsare stored in ascending order according to their keys
即:
?Collection 接口:定義了存取一組對象的方法,其子接口Set和List分別定義了存儲方式。
– Set 中的數據對象沒有順序且不可以重復。
– List 中的數據對象有順序且可以重復。
– Map 接口定義了存儲“鍵(key)- 值(value)映射對”的方法。
? Collection 表示一組對象,它是集中,收集的意思,就是把一些數據收集起來。
? Collection函數庫是在java.util 包下的一些接口和類,類是用來產生對象存放數據用的,而接口是訪問數據的方式。
? Collection函數庫與數組的兩點不同:
1.數組的容量是有限制的,而Collection庫沒有這樣的限制,它容量可以自動的調節 。
2.Collection函數庫只能用來存放對象,而數組沒有這樣的限制。
? Collection接口是Collection層次結構 中的根接口,它定義了一些最基本的訪問方法,讓我們能用統一的方式通過它或它的子接口來訪問數據。
? 區別:Collection代表一組對象, Collection函數庫就是java中的集合框架,Collection接口,是這個集合框架中的根接口。
? 存放在Collection 庫中的數據,被稱為元素(element) 。
Demo
public class Person {
private intid;
private Stringname;
public Person(int id, String name) {
this. id= id; this. name = name;
}
public intgetId() { return id; }
public StringgetName() { return name; }
public voidsetId (int id) {
this. id= id;
}
public voidsetName (String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public StringtoString() {
return “id: ” + id + “|name: ” + name;
}
}
========================================================================
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionTest1 {
public staticvoid main (String[] args) {
Collectionc = new HashSet();
c. add(new Person(1, “c++"));
c. add(new Person(2, “java"));
System.out.println(c. size() + ": " + c);
System.out.println("contains: " + c. contains (new Person(2, "java")));
System.out.println(c. remove (new Person(2, " java")));
System.out.println(c. size() + ": " + c);
}
}
輸出結果:

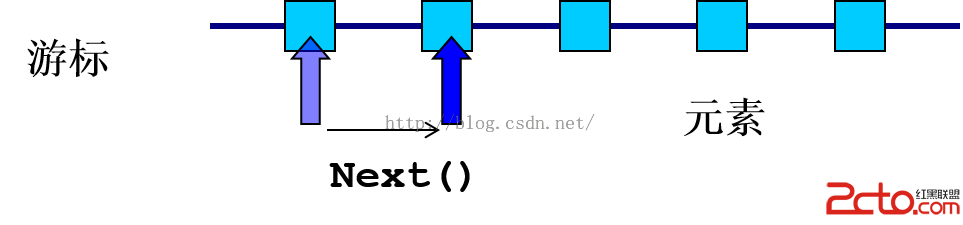
? 所有實現了Collection接口的容器類都有一個iterator方法用以返回一個實現了Iterator接口的對象。
? Iterator對象稱作迭代器,用以方便的實現對容器內元素的遍歷操作。
? Iterator接口定義了如下方法:

 Demo
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class IteratorTest1 {
public staticvoid main(String[] args) {
Collectionc = new ArrayList();
c.add("good"); c.add("morning");
c.add("key"); c.add("happy");
for(Iterator it = c.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
Stringtem = (String) it.next();
if(tem.trim().length() <= 3) {
it.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(c);
}
}

? Set 接口是Collection接口的子接口,Set接口沒有提供額外的方法,Set接口的特性是容器類中的元素是沒有順序的,而且不可以重復。
? Set 容器可以與數學中“集合”的概念相對應。
? J2SDK API中所提供的 Set 容器類有 HashSet,TreeSet 等。
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class SetTest {
public staticvoid main (String[] args) {
Set s =new HashSet();
s.add("hello");
s.add("world");
s.add(new Integer(4));
s.add(new Double(1.2));
s.add("hello"); // 相同的元素不會被加入
System.out.println(s);
}
}

List接口
? List接口是Collection的子接口,實現List接口的容器類中的元素是有順序的,而且可以重復。
? List 容器中的元素都對應一個整數型的序號記載其在容器中的位置,可以根據序號存取容器中的元素。
? J2SDK 所提供的 List 容器類有 ArrayList,LinkedList 等。
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class ListTest {
public staticvoid main(String[] argc) {
List l1= new ArrayList();
for (inti = 0; i <= 5; i++)
l1.add("a"+ i);
System.out.println(l1);
list.add(3,"a100");
System.out.println(l1);
list.set(6,"a200");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.print((String)list.get(2) + " ");
System.out.println(list.indexOf("a3"));
list.remove(1);
System.out.println(list);
}
}

類 java.util.Collections 提供了一些靜態方法實現了基於List容器的一些常用算法。
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionsTest {
publicstatic void main(String[] argc) {
List aList =new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0;i < 5; i++)
aList.add("a"+ i);
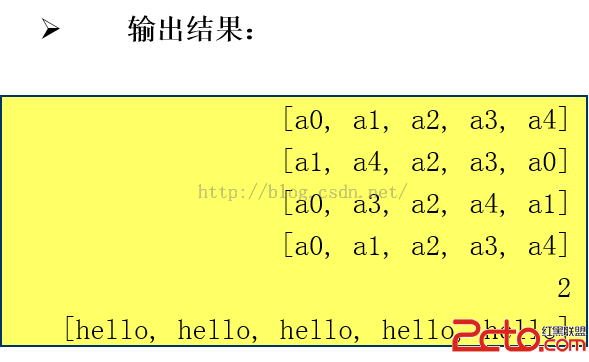
System.out.println(aList);
Collections.shuffle(aList);// 隨機排列
System.out.println(aList);
Collections.reverse(aList);// 逆續
System.out.println(aList);
Collections.sort(aList);// 排序
System.out.println(aList);
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(aList,"a2"));
Collections.fill(aList,"hello");
System.out.println(aList);
}
}
問題:上面的算法根據什麼確定集合中對象的“大小”順序?
?所有可以“排序”的類都實現了java.lang.Comparable 接口,Comparable接口中只有一個方法
public int compareTo(Objectobj);
該方法:
?實現了Comparable 接口的類通過實現 comparaTo 方法從而確定該類對象的排序方式。
Demo
public class Student implements Comparable {
private Stringname;
private Integerscore;
publicStudent(String name, int score) {
this.name =name;
this.score =new Integer(score);
}
public intcompareTo(Object o) {
Student n =(Student) o;
int a =score.compareTo(n.score);
return (a !=0 ? a : name.compareTo(n.name));
}
public StringtoString() {
return"name: " + name + " score: " + score.toString();
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class StudentTest {
public static voidmain(String[] args) {
List l1 = newLinkedList();
l1.add(newStudent(“ttt", 66));
l1.add(newStudent(“bbb", 77));
l1.add(newStudent(“ccc", 99));
l1.add(newStudent(“fff", 88));
l1.add(newStudent(“aaa", 66));
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.sort(l1);
System.out.println(l1);
}
}

? 實現Map接口的類用來存儲鍵(key)-值(value) 對。
? Map 接口的實現類有HashMap和TreeMap等。
? Map類中存儲的鍵-值對通過鍵來標識,所以鍵值不能重復。
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class MapTest {
public staticvoid main(String args[]) {
Map m1 =new HashMap();
Map m2 =new TreeMap();
m1.put("one",new Integer(1));
m1.put("two",new Integer(2));
m1.put("three",new Integer(3));
m2.put("A",new Integer(1));
m2.put("B",new Integer(2));
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one"));
System.out.println(m2.containsValue(newInteger(1)));
if(m1.containsKey("two")) {
inti = ((Integer) m1.get("two")).intValue();
System.out.println(i);
}
Map m3 =new HashMap(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3.size());
}
}
泛型的作用就是為了約束你傳入對象的類型;
通俗來講:傳進去什麼,拿出來什麼。
? 起因:
– JDK1.4以前類型不明確:
?裝入集合的類型都被當作Object對待,從而失去自己的實際類型。
?從集合中取出時往往需要轉型,效率低,容易產生錯誤。
? 解決辦法:
– 在定義集合的時候同時定義集合中對象的類型
?可以在定義Collection的時候指定
?也可以在循環時用Iterator指定
? 好處:
– 增強程序的可讀性和穩定性
Demo
import java.util.*;
public class MapTest1 {
public staticvoid main(String args[]) {
Map m = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
m.put(String.valueOf(i),1);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
m.put(String.valueOf(i),1);
}
System.out.println(m.size()+ " distinct words detected:");
System.out.println(m);
Setset = m.keySet();
Iteratorit = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(m.get(it.next()));
}
}
}
?增強的for循環對於遍歷array 或 Collection的時候相當簡便
?缺陷:
–數組:
?不能方便的訪問下標值
–集合:
?與使用Iterator相比,不能方便的刪除集合中的內容
?總結:
–除了簡單遍歷並讀出其中的內容外,不建議使用增強for
JAVA提供的這個接口專門約束我們容器的實現類,從很大程度上減輕了我們設計人員的負擔,提高效率。
容器類的總結相對來說是比較零散的知識點,很難完整的講述出來,在不斷的使用中,可以得到更好地理解。