最近為了提升python水平,在網上找到了python習題,然後根據自己對於python的掌握,整理出來了答案,如果小伙伴們有更好的實現方式,可以下面留言大家一起討論哦~
已知一個字符串為 “hello_world_yoyo”, 如何得到一個隊列 [“hello”,”world”,”yoyo”]
test = ‘hello_world_yoyo’
print(test.split(“_”))
結果:
[‘hello’, ‘world’, ‘yoyo’]
Process finished with exit code 0
有個列表 [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”]如何把把列表裡面的字符串聯起來,得到字符串 “hello_world_yoyo”
test = [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”]
print(“_”.join(test))
結果:
hello_world_yoyo
Process finished with exit code 0
這邊如果不依賴python提供的join方法,我們還可以通過for循環,然後將字符串拼接,但是在用"+"連接字符串時,結果會生成新的對象,
用join時結果只是將原列表中的元素拼接起來,所以join效率比較高
test = ["hello", "world", "yoyo"]
# 定義一個空字符串
j = ''
# 通過 for 循環 打印出列表中的數據
for i in test:
j = j + "_" + i
# 因為通過上面的字符串拼接,得到的數據是“_hello_world_yoyo”,前面會多一個下劃線,所以我們下面把這個下劃線去掉
print(j.lstrip("_"))
把字符串 s 中的每個空格替換成”%20”
輸入:s = “We are happy.”
輸出:”We%20are%20happy.”
s = ‘We are happy.’
print(s.replace(’ ', ‘%20’))
結果:
We%20are%20happy.
Process finished with exit code 0
打印99乘法表
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, i+1):
print(‘{}x{}={} ‘.format(j, i, i*j), end=’’)
print()
結果:
1x1=1
1x2=2 2x2=4
1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9
1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16
1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25
1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36
1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49
1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64
1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81
Process finished with exit code 0
下面是使用while循環實現
i = 1
while i <= 9:
j = 1
while j <= i:
print("%d*%d=%-2d"%(i,j,i*j),end = ' ') # %d: 整數的占位符,'-2'代表靠左對齊,兩個占位符
j += 1
print()
i += 1
找出單詞 “welcome” 在 字符串”Hello, welcome to my world.” 中出現的位置,找不到返回-1
從下標0開始索引
def test():
message = ‘Hello, welcome to my world.’
world = ‘welcome’
if world in message:
return message.find(world)
else:
return -1
print(test())
結果:
7
Process finished with exit code 0
統計字符串“Hello, welcome to my world.” 中字母w出現的次數
統計單詞 my 出現的次數
def test():
message = ‘Hello, welcome to my world.’
# 計數
num = 0
# for 循環message
for i in message:
# 判斷如果 ‘w’ 字符串在 message中,則num +1
if ‘w’ in i:
num += 1
return num
print(test())
題目:輸入一個字符串str, 輸出第m個只出現過n次的字符,如在字符串 gbgkkdehh 中,
找出第2個只出現1 次的字符,輸出結果:d
def test(str_test, num, counts):
“”"
:param str_test: 字符串
:param num: 字符串出現的次數
:param count: 字符串第幾次出現的次數
:return:
“”"
# 定義一個空數組,存放邏輯處理後的數據
list = []
# for循環字符串的數據
for i in str_test:
# 使用 count 函數,統計出所有字符串出現的次數
count = str_test.count(i, 0, len(str_test))
# 判斷字符串出現的次數與設置的counts的次數相同,則將數據存放在list數組中
if count == num:
list.append(i)
# 返回第n次出現的字符串
return list[counts-1]
print(test(‘gbgkkdehh’, 1, 2))
結果:
d
Process finished with exit code 0
判斷字符串a=”welcome to my world” 是否包含單詞b=”world”
包含返回True,不包含返回 False
def test():
message = ‘welcome to my world’
world = ‘world’
if world in message:
return True
return False
print(test())
結果:
True
Process finished with exit code 0
輸出指定字符串A在字符串B中第一次出現的位置,如果B中不包含A,則輸出-1
從 0 開始計數
A = “hello”
B = “hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo !”
def test():
message = ‘hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo !’
world = ‘hello’
return message.find(world)
print(test())
結果:
15
Process finished with exit code 0
輸出指定字符串A在字符串B中最後出現的位置,如果B中不包含A, 出-1從 0 開始計數
A = “hello”
B = “hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo !”
def test(string, str):
# 定義 last_position 初始值為 -1
last_position = -1
while True:
position = string.find(str, last_position+1)
if position == -1:
return last_position
last_position = position
print(test(‘hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo !’, ‘hello’))
結果:
28
Process finished with exit code 0
給定一個數a,判斷一個數字是否為奇數或偶數
a1 = 13
a2 = 10
while True:
try:
# 判斷輸入是否為整數
num = int(input(‘輸入一個整數:’))
# 不是純數字需要重新輸入
except ValueError:
print(“輸入的不是整數!”)
continue
if num % 2 == 0:
print(‘偶數’)
else:
print(‘奇數’)
break
結果:
輸入一個整數:100
偶數
Process finished with exit code 0
輸入一個姓名,判斷是否姓王
a = “王五”
b = “老王”
def test():
user_input = input(“請輸入您的姓名:”)
if user_input[0] == '王':
return "用戶姓王"
return "用戶不姓王"
print(test())
結果:
請輸入您的姓名:王總
用戶姓王
Process finished with exit code 0
如何判斷一個字符串是不是純數字組成
a = “123456”
b = “yoyo123”
這個答案,其實有些取巧,利用python提供的類型轉行,將用戶輸入的數據轉換成浮點數類型,如果轉換拋異常,則判斷數字不是純數字組成
def test(num):
try:
return float(num)
except ValueError:
return "請輸入數字"
print(test('133w3'))
將字符串 a = “This is string example….wow!” 全部轉成大寫
字符串 b = “Welcome To My World” 全部轉成小寫
a = ‘This is string example….wow!’
b = ‘Welcome To My World’
print(a.upper())
print(b.lower())
將字符串 a = “ welcome to my world “首尾空格去掉
python提供了strip()方法,可以去除首尾空格
rstrip()去掉尾部空格
lstrip()去掉首部空格
replace(" ", “”) 去掉全部空格
a = ' welcome to my world '
print(a.strip())
還可以通過遞歸的方式實現
def trim(s):
flag = 0
if s[:1]==' ':
s = s[1:]
flag = 1
if s[-1:] == ' ':
s = s[:-1]
flag = 1
if flag==1:
return trim(s)
else:
return s
print(trim(' Hello world! '))
通過while循環實現
def trim(s):
while(True):
flag = 0
if s[:1]==' ':
s = s[1:]
flag = 1
if s[-1:] == ' ':
s = s[:-1]
flag = 1
if flag==0:
break
return s
print(trim(' Hello world! '))
s = “ajldjlajfdljfddd”,去重並從小到大排序輸出”adfjl”
def test():
s = ‘ajldjlajfdljfddd’
# 定義一個數組存放數據
str_list = []
# for循環s字符串中的數據,然後將數據加入數組中
for i in s:
# 判斷如果數組中已經存在這個字符串,則將字符串移除,加入新的字符串
if i in str_list:
str_list.remove(i)
str_list.append(i)
# 使用 sorted 方法,對字母進行排序
a = sorted(str_list)
# sorted方法返回的是一個列表,這邊將列表數據轉換成字符串
return "".join(a)
print(test())
結果:
adfjl
Process finished with exit code 0
題目 打印出如下圖案(菱形):

def test():
n = 8
for i in range(-int(n/2), int(n/2) + 1):
print(" "*abs(i), "*"*abs(n-abs(i)*2))
print(test())
結果:
**
****
******
********
******
****
**
Process finished with exit code 0
題目 給一個不多於5位的正整數,要求:
一、求它是幾位數,
二、逆序打印出各位數字。
a = 12345
class Test:
# 計算數字的位數
def test_num(self, num):
try:
# 定義一個 length 的變量,來計算數字的長度
length = 0
while num != 0:
# 判斷當 num 不為 0 的時候,則每次都除以10取整
length += 1
num = int(num) // 10
if length > 5:
return "請輸入正確的數字"
return length
except ValueError:
return "請輸入正確的數字"
# 逆序打印出個位數
def test_sorted(self, num):
if self.test_num(num) != "請輸入正確的數字":
# 逆序打印出數字
sorted_num = num[::-1]
# 返回逆序的個位數
return sorted_num[-1]
print(Test().test_sorted(‘12346’))
結果:
1
Process finished with exit code 0
如果一個 3 位數等於其各位數字的立方和,則稱這個數為水仙花數。
例如:153 = 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3,因此 153 就是一個水仙花數
那麼問題來了,求1000以內的水仙花數(3位數)
def test():
for num in range(100, 1000):
i = num // 100
j = num // 10 % 10
k = num % 10
if i ** 3 + j ** 3 + k ** 3 == num:
print(str(num) + "是水仙花數")
test()
求1+2+3…+100和
i = 1
for j in range(101):
i = j + i
print(i)
結果:
5051
Process finished with exit code 0
計算求1-2+3-4+5-…-100的值
def test(sum_to):
# 定義一個初始值
sum_all = 0
# 循環想要計算的數據
for i in range(1, sum_to + 1):
sum_all += i * (-1) ** (1 + i)
return sum_all
if name == ‘main’:
result = test(sum_to=100)
print(result)
-50
Process finished with exit code 0
計算公式 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + …….+ n3
實現要求:
輸入 : n = 5
輸出 : 225
對應的公式 : 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + 53 = 225
def test(n):
sum = 0
for i in range(1, n+1):
sum += i*i*i
return sum
print(test(5))
結果:
225
Process finished with exit code 0
已知 a的值為”hello”,b的值為”world”,如何交換a和b的值?
得到a的值為”world”,b的值為”hello”
a = ‘hello’
b = ‘world’
c = a
a = b
b = c
print(a, b)
如何判斷一個數組是對稱數組:
要求:判斷數組元素是否對稱。例如[1,2,0,2,1],[1,2,3,3,2,1]這樣的都是對稱數組
用Python代碼判斷,是對稱數組打印True,不是打印False,如:
x = [1, “a”, 0, “2”, 0, “a”, 1]
def test():
x = [1, 'a', 0, '2', 0, 'a', 1]
# 通過下標的形式,將字符串逆序進行比對
if x == x[::-1]:
return True
return False
print(test())
結果:
True
Process finished with exit code 0
如果有一個列表a=[1,3,5,7,11]
問題:1如何讓它反轉成[11,7,5,3,1]
2.取到奇數位值的數字,如[1,5,11]
def test():
a = [1, 3, 5, 7, 11]
# 逆序打印數組中的數據
print(a[::-1])
# 定義一個計數的變量
count = 0
for i in a:
# 判斷每循環列表中的一個數據,則計數器中會 +1
count += 1
# 如果計數器為奇數,則打印出來
if count % 2 != 0:
print(i)
test()
結果:
[11, 7, 5, 3, 1]
1
5
11
Process finished with exit code 0
問題:對列表a 中的數字從小到大排序
a = [1, 6, 8, 11, 9, 1, 8, 6, 8, 7, 8]
a = [1, 6, 8, 11, 9, 1, 8, 6, 8, 7, 8]
print(sorted(a))
結果:
[1, 1, 6, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 11]
Process finished with exit code 0
L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
找出列表中最大值和最小值
L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
print(max(L1))
print(min(L1))
結果:
88
1
Process finished with exit code 0
上面是通過python自帶的函數,下面有可以自己寫一個計算程序,貼代碼:
class Test(object):
def __init__(self):
# 測試的列表數據
self.L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
# 從列表中取第一個值,對於數據大小比對
self.num = self.L1[0]
def test_small_num(self, count):
"""
:param count: count為 1,則表示計算最大值,為 2 時,表示最小值
:return:
"""
# for 循環查詢列表中的數據
for i in self.L1:
if count == 1:
# 循環判斷當數組中的數據比初始值小,則將初始值替換
if i > self.num:
self.num = i
elif count == 2:
if i < self.num:
self.num = i
elif count != 1 or count != 2:
return "請輸入正確的數據"
return self.num
print(Test().test_small_num(1))
print(Test().test_small_num(2))
結果:
88
1
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”, “congratulations”]
找出列表中單詞最長的一個
def test():
a = [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”, “congratulations”]
# 統計數組中第一個值的長度
length = len(a[0])
for i in a:
# 循環數組中的數據,當數組中的數據比初始值length中的值長,則替換掉length的默認值
if len(i) > length:
length = i
return length
print(test())
結果:
congratulations
Process finished with exit code 0
取出列表中最大的三個值
L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
def test():
L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
return sorted(L1)[:3]
print(test())
結果:
[1, 2, 2]
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [1, -6, 2, -5, 9, 4, 20, -3] 按列表中的數字絕對值從小到大排序
def test():
a = [1, -6, 2, -5, 9, 4, 20, -3]
# 定義一個數組,存放處理後的絕對值數據
lists = []
for i in a:
# 使用 abs() 方法處理絕對值
lists.append(abs(i))
return lists
print(test())
結果:
[1, 6, 2, 5, 9, 4, 20, 3]
Process finished with exit code 0
b = [“hello”, “helloworld”, “he”, “hao”, “good”]
按list裡面單詞長度倒敘
def test():
b = ["hello", "helloworld", "he", "hao", "good"]
count = {}
# 循環查看數組匯總每個字符串的長度
for i in b:
# 將數據統計稱字典格式,字符串作為鍵,字符串長度作為值
count[i] = len(i)
# 按照字典的值,將字典數據從大到小排序
message = sorted(count.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
lists = []
for j in message:
# 循環把處理後的數據,加入到新的數組中
lists.append(j[0])
print(lists)
test()
結果:
[‘helloworld’, ‘hello’, ‘good’, ‘hao’, ‘he’]
Process finished with exit code 0
L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]
如何用一行代碼得出[1, 2, 3, 5, 11, 33, 88]
print(sorted(set(L1)))
結果:
[1, 2, 3, 5, 11, 33, 88]
Process finished with exit code 0
將列表中的重復值取出(僅保留第一個),要求保留原始列表順序
如a=[3, 2, 1, 4, 2, 6, 1] 輸出[3, 2, 1, 4, 6]
a = [3, 2, 1, 4, 2, 6, 1]
lists = []
for i in a:
if i not in lists:
lists.append(i)
print(lists)
結果:
[3, 2, 1, 4, 6]
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [1, 3, 5, 7]
b = [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’]
如何得到[1, 3, 5, 7, ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’]
a = [1, 3, 5, 7]
b = [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’]
for i in b:
a.append(i)
print(a)
結果:
[1, 3, 5, 7, ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’]
Process finished with exit code 0
用一行代碼生成一個包含 1-10 之間所有偶數的列表
print([i for i in range(2, 11, 2) if i % 2 == 0])
結果:
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
Process finished with exit code 0
列表a = [1,2,3,4,5], 計算列表成員的平方數,得到[1,4,9,16,25]
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
lists = []
for i in a:
lists.append(i*i)
print(lists)
結果:
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Process finished with exit code 0
使用列表推導式,將列表中a = [1, 3, -3, 4, -2, 8, -7, 6]
找出大於0的數,重新生成一個新的列表
a = [1, 3, -3, 4, -2, 8, -7, 6]
print([i for i in a if i > 0])
結果:
[1, 3, 4, 8, 6]
Process finished with exit code 0
統計在一個隊列中的數字,有多少個正數,多少個負數,如[1, 3, 5, 7, 0, -1, -9, -4, -5, 8]
def test():
lists = [1, 3, 5, 7, 0, -1, -9, -4, -5, 8]
# 定義一個變量,計算正數
positive_num = 0
# 計算負數
negative_num = 0
for i in lists:
# 判斷循環數組中的數據大於0,則正數會+1
if i > 0:
negative_num += 1
# 因為 0 既不是正數也不是負數,所以我們判斷小於0為負數
elif i < 0:
positive_num += 1
return positive_num, negative_num
print(test())
結果:
(4, 5)
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [“張三”,”張四”,”張五”,”王二”] 如何刪除姓張的
def test():
a = [“張三”, “張四”, “張五”, “王二”]
for i in a[:]:
if i[0] == '張':
a.remove(i)
return a
print(test())
結果:
[‘王二’]
Process finished with exit code 0
在實現這個需求的時候,踩到了一個坑,就是當我在for循環判斷數組中的姓名第一個等於張的時候,當時的代碼判斷是這樣寫的
for i in a:
if i[0] == '張':
然後打印出來的數據是 [‘張四’, ‘王二’],我當時還有寫疑惑,我的邏輯判斷是對的,為什麼‘張四’這個名稱會被打印出來,於是我打了一個斷點查看了一下。
發現當第一個‘張三’被刪除之後,再次循環時,直接跳過了‘張三’,百度查了才知道,如圖: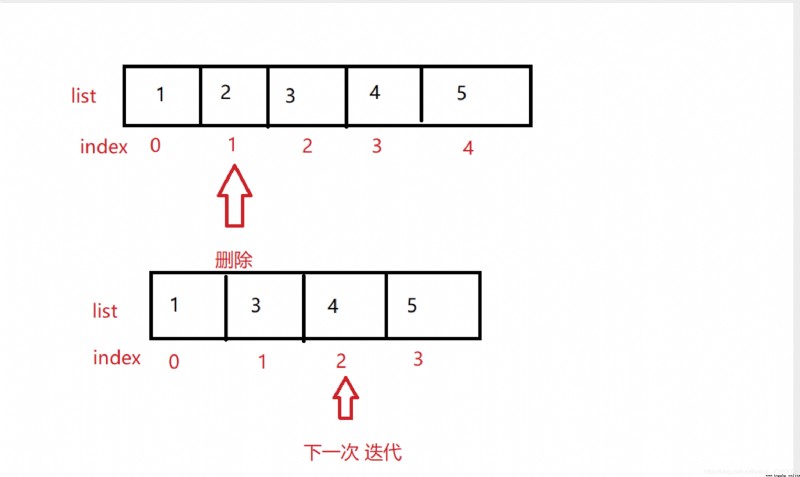
感興趣的小伙伴,可以查看這篇文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouziyuan/p/10137086.html
有個列表a = [1, 3, 5, 7, 0, -1, -9, -4, -5, 8] 使用filter 函數過濾出大於0的數
a = [1, 3, 5, 7, 0, -1, -9, -4, -5, 8]
def test(a):
return a < 0
temlists = filter(test, a)
print(list(temlists))
結果:
[-1, -9, -4, -5]
Process finished with exit code 0
列表b = [“張三”, “張四”, “張五”, “王二”] 過濾掉姓張的姓名
b = [“張三”, “張四”, “張五”, “王二”]
def test(b):
return b[0] != ‘張’
print(list(filter(test, b)))
結果:
[‘王二’]
Process finished with exit code 0
過濾掉列表中不及格的學生
a = [
{“name”: “張三”, “score”: 66},
{“name”: “李四”, “score”: 88},
{“name”: “王五”, “score”: 90},
{“name”: “陳六”, “score”: 56},
]
a = [
{“name”: “張三”, “score”: 66},
{“name”: “李四”, “score”: 88},
{“name”: “王五”, “score”: 90},
{“name”: “陳六”, “score”: 56}
]
print(list(filter(lambda x: x.get(“score”) >= 60, a)))
返回:
[{‘name’: ‘張三’, ‘score’: 66}, {‘name’: ‘李四’, ‘score’: 88}, {‘name’: ‘王五’, ‘score’: 90}]
有個列表 a = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 88, 3, 2, 5, 33]
找出列表中最大的數,出現的位置,下標從0開始
def test():
a = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 88, 3, 2, 5, 33]
# 找到數組中最大的數字
b = max(a)
count = 0
# 定義一個計數器,每次循環一個數字的時候,則計數器+1,用於記錄數字的下標
for i in a:
count += 1
# 判斷當循環到最大的數字時,則退出
if i == b:
break
return count -1
print(test())
結果:
6
Process finished with exit code 0
**a = [
‘my’, ‘skills’, ‘are’, ‘poor’, ‘I’, ‘am’, ‘poor’, ‘I’,
‘need’, ‘skills’, ‘more’, ‘my’, ‘ability’, ‘are’,
‘so’, ‘poor’
]
找出列表中出現次數最多的元素
def test():
a = [
“my”, “skills”, “are”, “poor”, “I”, “am”, “poor”, “I”,
“need”, “skills”, “more”, “my”, “ability”, “are”,
“so”, “poor”
]
dicts = {}
for i in a:
# 統計數組中每個字符串出現的次數,將數據存入到字典中
if i not in dicts.keys():
dicts[i] = a.count(i)
return sorted(dicts.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[0][0]
print(test())
結果:
poor
Process finished with exit code 0
給定一個整數數組A及它的大小n,同時給定要查找的元素val,
請返回它在數組中的位置(從0開始),若不存在該元素,返回-1。
若該元素出現多次請返回第一個找到的位置
如 A1=[1, “aa”, 2, “bb”, “val”, 33]
或 A2 = [1, “aa”, 2, “bb”]
def test(lists, string):
“”"
:param lists: 數組
:param string: 查找的字符串
:return:
“”"
if string not in lists:
return -1
count = 0
for i in lists:
count += 1
if i == string:
return count - 1
print(test([1, “aa”, “val”, 2, “bb”, “val”, 33], ‘val’))
結果:
2
Process finished with exit code 0
給定一個整數數組nums 和一個目標值target ,請你在該數組中找出和為目標值的那兩個整數,並返回他
們的數組下標。
你可以假設每種輸入只會對應一個答案。但是,數組中同一個元素不能使用兩遍。
示例:
給定nums=[2,7,11,15],target=9
因為nums[0] + nums[1] =2+7 = 9
所以返回[0, 1]
def test(target=9):
num = [2, 7, 11, 15]
# 統計數組的長度
length = len(num)
dicts = {}
for i in range(length):
# 添加兩個 for 循環,第二次for循環時,循環的位置會比第一次循環多一次
for j in range(i + 1, length):
# 將循環後的數據放在列表中,利用字典 key 唯一的屬性處理數據
dicts.update({num[i] + num[j]: {i, j}})
# 打印出來的數據,是元素的格式,按照題目,將數據轉行成字典
lists = []
for nums in dicts[target]:
lists.append(nums)
return lists
print(test())
結果:
[0, 1]
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]] 如何一句代碼得到 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
a = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
lists = []
for i in a:
# 二次 for 循環,將數據存入到 lists 中
for j in i:
lists.append(j)
print(lists)
結果:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Process finished with exit code 0
二維數組取值(矩陣),有 a = [[“A”, 1], [“B”, 2]] ,如何取出 2
import numpy
a = [[“A”, 1], [“B”, 2]]
x = numpy.array(a)
print(x[1, 1])
結果:
2
Process finished with exit code 0
列表轉字符串,L = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6],如何得出 ‘12356’?
L = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6]
lists = [str(i) for i in L]
print(‘’.join(lists))
結果:
12356
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [“a”, “b”, “c”]
b = [1, 2, 3]
如何得到 {‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 3}
a = [“a”, “b”, “c”]
b = [1, 2, 3]
c = {k: v for k, v in zip(a, b)}
print
結果:
{‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 3}
如下列表
people = [
{“name”:”yoyo”, “age”: 20},
{“name”:”admin”, “age”: 28},
{“name”:”zhangsan”, “age”: 25},
]
按年齡age從小到大排序
people = [
{“name”: “yoyo”, “age”: 20},
{“name”: “admin”, “age”: 28},
{“name”: “zhangsan”, “age”: 25},
]
print(sorted(people, key=lambda x: x[‘age’], reverse=True))
結果:
[{‘name’: ‘admin’, ‘age’: 28}, {‘name’: ‘zhangsan’, ‘age’: 25}, {‘name’: ‘yoyo’, ‘age’: 20}]
Process finished with exit code 0
現有 nums=[2, 5, 7] ,如何在該數據最後插入一個數字 9 ,如何在2後面插入數字0
nums=[2, 5, 7]
nums.append(9)
nums.insert(1, 0)
print(nums)
結果:
[2, 0, 5, 7, 9]
Process finished with exit code 0
有個列表a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
如何打亂列表a的順序,每次得到一個無序列表
import random
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
random.shuffle(a)
print(a)
結果:
[2, 7, 9, 4, 8, 1, 3, 5, 6]
Process finished with exit code 0
輸出1-100除3余1 的數,結果為tuple
tuples = ()
for i in range(1, 101):
# 判斷除以 3 余 1 的數
if i % 3 == 1:
# 將數據加入元祖中
tuples += (i, )
print(tuples)
將(‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’) 和 (1,2, 3, 4, 5)兩個tuple轉成
(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)為key, (‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’) 為value的字典
def test():
a = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
b = (“a”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “e”)
# 使用 zip 函數將元素組合成多個元祖
c = list(zip(a, b))
dicts = {}
# 將數據轉換成字典類型
for i in c:
dicts[i[0]] = i[1]
return dicts
print(test())
結果:
{1: ‘a’, 2: ‘b’, 3: ‘c’, 4: ‘d’, 5: ‘e’}
Process finished with exit code 0
將字典裡的值是數值型的轉換為字符串,如a = {‘aa’: 11, ‘bb’: 222}
得到{‘aa’: ‘11’, ‘bb’: ‘222’}
def test():
a = {‘a’: 11, ‘bb’: 222}
for i in a.items():
a.update({i[0]: str(i[1])})
return a
結果:
{‘a’: ‘11’, ‘bb’: ‘222’}
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [1,2,3] 和 b = [(1),(2),(3) ] 以及 c = [(1,),(2,),(3,) ] 的區別?
a = [1,2,3]正常的列表
b = [(1),(2),(3)] 雖然列表的每個元素加上了括號,但是當括號內只有一個元素並且沒有逗號時,其數據類型是元素本身的數據類型
b = [(1,),(2,),(3,)]列表中的元素類型都是元組類型
map函數,有個列表a = [1, 2, 3, 4] 計算列表中每個數除以2 取出余數 得到 [1,0,1,0]
ef test():
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
lists = []
for i in a:
lists.append(i % 2)
return lists
print(test())
結果:
[1, 0, 1, 0]
Process finished with exit code 0
map函數將列表 [1,2,3,4,5] 使用python方法轉變成 [1,4,9,16,25]
def test():
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
new_list = []
for i in a:
new_list.append(i*i)
return new_list
print(test())
結果:
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Process finished with exit code 0
map函數對列表a=[1,3,5],b=[2,4,6]相乘得到[2,12,30]
a = [1, 3, 5]
b = [2, 4, 6]
print(list(map(lambda x, y: x*y, a, b)))
結果:
[2, 12, 30]
Process finished with exit code 0
reduce函數計算1-100的和
from functools import reduce
def test():
lists = []
# for 循環往列表中加入1-100的數據
for i in range(1, 101):
lists.append(i)
# 實現數據相加
return reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, lists)
print(test())
結果:
5050
Process finished with exit code 0
兩個字典合並a={“A”:1,”B”:2},b={“C”:3,”D”:4}
a = {“A”: 1, “B”: 2}
b = {“C”: 3, “D”: 4}
b.update(a)
print(b)
結果:
{‘C’: 3, ‘D’: 4, ‘A’: 1, ‘B’: 2}
Process finished with exit code 0
m1={‘a’:1,’b’:2,’c’:1} # 將同樣的value的key集合在list裡,輸出{1:[‘a’,’c’],2:[‘b’]}
def test():
m1={“a”: 1, “b”: 2, “c”: 1}
new_dict = {}
# 循環 m1 字典中的數據
for key, value in m1.items():
# 判斷如果 m1 字典中的值不在新定義的 new_dist 字典中
if value not in new_dict:
# 則往新字典中添加鍵值對
new_dict[value] = [key]
else:
# 如果添加的鍵已經存在了,則直接添加值
new_dict[value].append(key)
return new_dict
print(test())
結果:
{1: [‘a’, ‘c’], 2: [‘b’]}
Process finished with exit code 0
d={“name”:”zs”,”age”:18,”city”:”深圳”,”tel”:”1362626627”}
字典根據鍵從小到大排序
def test():
d = {“name”: “zs”, “age”: 18, “city”: “深圳”, “tel”: “1362626627”}
# 將字典中的數據進行排序
dict2 = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda d: d[0], reverse=False)
# 排序之後的數據類型會變成列表類型,這裡將數據重新轉換成字典
new_dict = {}
for i in dict2:
new_dict[i[0]] = i[1]
return new_dict
print(test())
結果:
{‘age’: 18, ‘city’: ‘深圳’, ‘name’: ‘zs’, ‘tel’: ‘1362626627’}
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [2, 3, 8, 4, 9, 5, 6]
b = [2, 5, 6, 10, 17, 11]
1.找出a和b中都包含了的元素
2.a或b中包含的所有元素
3.a中包含而集合b中不包含的元素
a = [2, 3, 8, 4, 9, 5, 6]
b = [2, 5, 6, 10, 17, 11]
print(list(set(a).union(set(b))))
print(list(set(a).intersection(set(b))))
print(list(set(a) ^ set(b)))
結果:
[3, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 17]
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 17]
[2, 5, 6]
Process finished with exit code 0
函數計算10!
def f(num):
if num == 1 or num == 0:
return 1
else:
# 利用遞歸方式實現
return num * f(num - 1)
print(f((10)))
結果:
3628800
Process finished with exit code 0
有1、2、3、4數字能組成多少互不相同無重復數的三位數
分別打印這些三位數的組合
l = [“1”, “2”, “3”, “4”]
n = len(l)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
for k in range(n):
if i != k and k != j and i != j:
print(l[i] + l[j] + l[k])
在以下文本中找出 每行中長度超過3的單詞:
Call me Ishmael. Some years ago - never mind how long precisely - having
little or no money in my purse, and nothing particular to interest me
on shore, I thought I would sail about a little and see the watery part
of the world. It is a way I have of driving off the spleen, and regulating
the circulation. - Moby Dick
python的預期結果(盡量不超過3行搞定):
[[‘Call’, ‘Ishmael.’, ‘Some’, ‘years’, ‘never’, ‘mind’, ‘long’, ‘precisely’, ‘having’],
[‘little’, ‘money’, ‘purse,’, ‘nothing’, ‘particular’, ‘interest’],
[‘shore,’, ‘thought’, ‘would’, ‘sail’, ‘about’, ‘little’, ‘watery’, ‘part’],
[‘world.’, ‘have’, ‘driving’, ‘spleen,’, ‘regulating’],
[‘circulation.’, ‘Moby’, ‘Dick’]]]
a='''Call me Ishmael. Some years ago - never mind how long precisely - having
little or no money in my purse, and nothing particular to interest me
on shore, I thought I would sail about a little and see the watery part
of the world. It is a way I have of driving off the spleen, and regulating
the circulation. - Moby Dick'''
list1=[[j for j in i.split(' ') if len(j)>3 ]for i in a.split('
')]
print(list1)
結果:
[['Call', 'Ishmael.', 'Some', 'years', 'never', 'mind', 'long', 'precisely', 'having'], ['little', 'money', 'purse,', 'nothing', 'particular', 'interest'], ['shore,', 'thought', 'would', 'sail', 'about', 'little', 'watery', 'part'], ['world.', 'have', 'driving', 'spleen,', 'regulating'], ['circulation.', 'Moby', 'Dick']]
Process finished with exit code 0
a = [11, 2, 33, 1, 5, 88, 3]
冒泡排序:
依次比較兩個相鄰的元素,如果順序(如從小到大、首字母從A到Z)
錯誤就把他們交換過來
def bubbleSort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# 遍歷所有數組元素
for i in range(n):
# Last i elements are already in place
for j in range(0, n - i - 1):
if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]:
arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j]
arr = [11, 2, 33, 1, 5, 88, 3]
bubbleSort(arr)
print(arr)
結果:
[1, 2, 3, 5, 11, 33, 88]
Process finished with exit code 0
有一個數據list of dict如下
a = [
{“yoyo1”: “123456”},
{“yoyo2”: “123456”},
{“yoyo3”: “123456”},
]
寫入到本地一個txt文件,內容格式如下:
yoyo1,123456
yoyo2,123456
yoyo3,123456
def test():
a = [
{“yoyo1”: “123456”},
{“yoyo2”: “123456”},
{“yoyo3”: “123456”},
]
# 打開一個名為 test.txt 的文件,如果文件不存在,則自動創建
with open('test.txt', 'w') as f:
for i in a:
# 循環數組中的字典
for key, value in i.items():
# 將數據存入 txt 文件中
f.write("{0},{1}
“.format(key, value))
print(”{0},{1}
".format(key, value))
test()
 [original hard core] check the common encryption algorithms in Python crawlers. It is recommended to collect them!!
[original hard core] check the common encryption algorithms in Python crawlers. It is recommended to collect them!!
I believe that when you captur