緊接上一篇文章《輕松了解Spring中的控制反轉和依賴注入》講解了SpringIOC和DI的基本概念,這篇文章我們模擬一下SpringIOC的工作機制,使我們更加深刻的理解其中的工作。再上代碼之前我們先來看看幾個類的設計目的。
BeanFactor接口:在Spring源碼中的定義是:持有對一定數量的Bean的定義,同時每個Bean都被唯一標識的對象(類),需要實現這個接口。根據對Bean的定義,該工廠將會返回一個包含Bean定義的對象的獨立實例(原型設計模式),或者單例共享(一個不錯的單例設計模式,)范圍是整個工廠的范圍(也可以理解成是整個容器下),返回哪種類型的實例依賴於Bean工廠的配置:API是相同的。因為Spring2.0中擴大了依賴范圍,可以根據具體應用上下問(如在Web環境中的請求和會話),BeanFactory是應用程序組件的中央注冊中心和集中配置。簡單的來說該接口定義了獲取Bean的方法,由子類去實現。
BeanFactory接口:是實現BeanFactory接口的抽象基類。實現獲取Bean定義的方法。
XmlContext類:繼承了AbstractBeanFactory抽象類,進行Bean的注冊和注冊XML的讀取器。
BeanInfo類:進行存儲Bean的信息。
接下來上代碼,需要注釋的地方我都添加上去了,類的目錄如下。
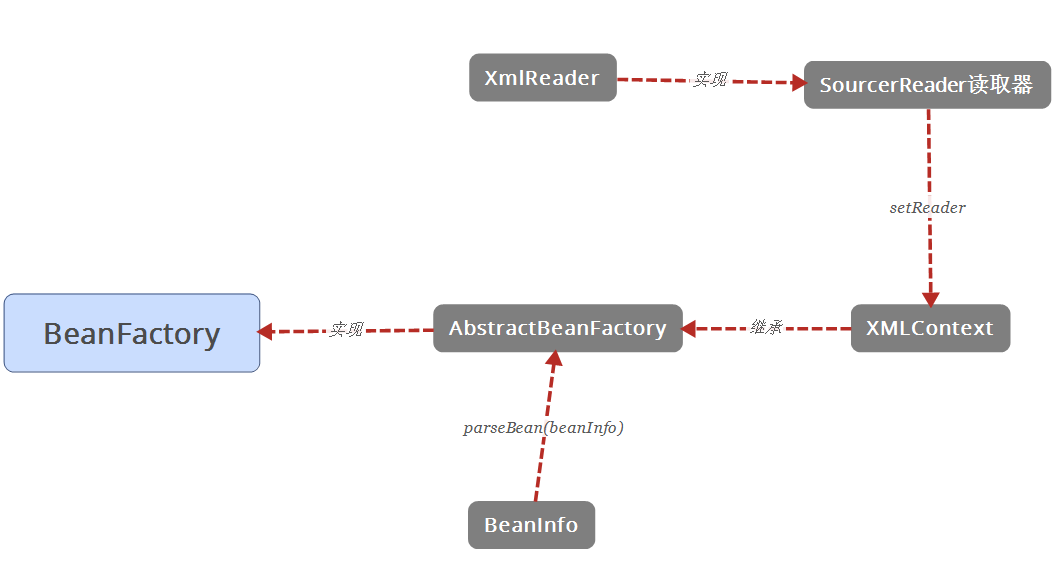
類之間的結構圖如下
以下是代碼
package ioc.factory;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* 根據對象的ID標識獲取對象實例
* @param name
* @return
*/
Object getBean(String name);
}
package ioc.factory;
import ioc.info.BeanInfo;
import ioc.reader.SourceReader;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
*
* 最頂層的IOC實現
* 該類負責從注冊器中取出注冊對象
* 實現從對象描述信息轉換為對象實例的過程
* 實現根據名稱獲取對象的方法
*
*/
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory implements BeanFactory {
private String filePath;
private Map<String,BeanInfo> container;
protected SourceReader reader;
public AbstractBeanFactory(String filePath){
this.filePath=filePath;
setReader(reader);
}
/**
* 由子類決定如果使用什麼樣的注冊讀取器
* 這裡使用了模板方法,父類定義抽象方法,但交給子類自由去設計方法內容
* @param reader
*/
protected abstract void setReader(SourceReader reader);
//注冊bean
public void registerBeans(){
this.container=this.reader.loadBeans(filePath);
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) {
BeanInfo beanInfo=this.container.get(name);
if(beanInfo==null){
return null;
}else {
return this.parseBean(beanInfo);
}
}
/**
* 解析生成並生成對象實例
* 主要通過反射完成
* 根據類名,加載指定類,並取得該類的Class對象
* 使用Class對象實例化該類,獲取一個對象。
* 逐個設置對象字段的值,這裡采用setter Method方式
*
* @param beanInfo 指定對象的描述信息
* @return
*/
protected Object parseBean(BeanInfo beanInfo){
Class clazz;
try {
//加載Bean的實例
clazz=Class.forName(beanInfo.getType());
Object bean=clazz.newInstance();
//獲取該對象下的所有方法,包括私有
Method[] methods=clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (String property:beanInfo.getProperties().keySet()){
String setter="set"+ firstCharToUp(property);
for(Method method:methods){
String methodName=method.getName();
if(methodName.equals(setter)){
Object value=beanInfo.getProperties().get(property);
//使用反射調用set方法
method.invoke(bean,value);
}
}
}
return bean;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private String firstCharToUp(String property) {
System.out.println(property);
char [] c=property.toCharArray();
String first=String.valueOf(c[0]).toUpperCase();
c[0]=first.charAt(0);
System.out.println(String.valueOf(c));
return String.valueOf(c);
}
}
package ioc.context;
import ioc.factory.AbstractBeanFactory;
import ioc.reader.SourceReader;
import ioc.reader.XMLSourceReader;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
* 上下文的構造方法
* 該方法中指明注冊讀取器(這裡采用的XML,讀者可以根據興趣去實現另外的方式如注解)
* 並在構造該方法時一次性加載注冊的對象
*/
public class XMLContext extends AbstractBeanFactory{
public XMLContext(String filePath){
super(filePath);
this.setReader(new XMLSourceReader());
super.registerBeans();
}
@Override
protected void setReader(SourceReader reader) {
super.reader=reader;
}
}
package ioc.reader;
import ioc.info.BeanInfo;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
* 注冊讀取器接口
* 負責讀取用戶注冊的對象
* 繼承該接口的類可以實現多種讀取方式,如從配置文件中讀取,根據標注讀取,從網絡中讀取等等
*/
public interface SourceReader {
Map<String,BeanInfo> loadBeans(String filePath);
}
package ioc.context;
import ioc.factory.AbstractBeanFactory;
import ioc.reader.SourceReader;
import ioc.reader.XMLSourceReader;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
* 上下文的構造方法
* 該方法中指明注冊讀取器(這裡采用的XML,讀者可以根據興趣去實現另外的方式如注解)
* 並在構造該方法時一次性加載注冊的對象
*/
public class XMLContext extends AbstractBeanFactory{
public XMLContext(String filePath){
super(filePath);
this.setReader(new XMLSourceReader());
super.registerBeans();
}
@Override
protected void setReader(SourceReader reader) {
super.reader=reader;
}
}
package ioc.info;
import java.lang.Object;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
*/
public class BeanInfo {
private String id;
private String type;
private Map<String,Object> properties=new HashMap<String,Object>();
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map<String, Object> getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Map<String, Object> properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public void addProperty(String name, Object object)
{
this.properties.put(name, object);
}
}
package ioc.reader;
import ioc.info.BeanInfo;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by zzf on 2016/10/26.
* 使用 dom4j進行Xml的讀取操作
*/
public class XMLSourceReader implements SourceReader {
@Override
public Map<String, BeanInfo> loadBeans(String filePath) {
//讀取指定的配置文件
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
//從class目錄下獲取指定的xml文件
InputStream ins = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(filePath);
Document doc = null;
try {
doc = reader.read(ins);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//獲得根節點
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
Map<String,BeanInfo>beanInfoMap=new HashMap<String, BeanInfo>();
//遍歷bean
for (Iterator i = root.elementIterator("bean"); i.hasNext();){
Element element = (Element) i.next();
//獲取bean的屬性id和class
Attribute id = element.attribute("id");
Attribute cls = element.attribute("class");
try {
//利用Java反射機制,通過class的名稱獲取Class對象
Class bean=Class.forName(cls.getText());
//獲取對應class的信息
java.beans.BeanInfo info= Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean);
//獲取其屬性描述
PropertyDescriptor [] propertyDescriptors=info.getPropertyDescriptors();
Method method;
Object object=bean.newInstance();
BeanInfo beanInfo=new BeanInfo();
for(Iterator iterator=element.elementIterator("property");iterator.hasNext();){
Element foo2= (Element) iterator.next();
//獲取該property的name屬性
Attribute name = foo2.attribute("name");
String value = null;
//獲取該property的子元素value的值
for(Iterator ite1 = foo2.elementIterator("value"); ite1.hasNext();) {
Element node = (Element) ite1.next();
value = node.getText();
break;
}
System.out.println("name:"+name.getText()+"value"+value);
for (int j=0;j<propertyDescriptors.length;j++){
if(propertyDescriptors[j].getName().equalsIgnoreCase(name.getText())){
method=propertyDescriptors[j].getWriteMethod();
//利用Java的反射極致調用對象的某個set方法,並將值設置進去
method.invoke(object,value);
//將獲取的對象屬性信息存入我們自定義的BeanInfo當中
beanInfo.addProperty(name.getText(),value);
}
}
beanInfo.setId(id.getText());
beanInfo.setType(cls.getText());
beanInfoMap.put(id.getText(),beanInfo);
}
return beanInfoMap;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IntrospectionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
}